Chatbots have come a long way – from a hyped technology under the AI umbrella to a direct-to-consumer product, that has incessantly penetrated the tech-enabled services we use today. While the adoption of chatbots is still in its infancy, the proliferation and mushroomed effect it has had so far is remarkable. Most of us, are perhaps not even aware of how seamless this transition has been – since many now interact with several bots almost everyday!
“Nearly 1 in 4 customers have interacted with a brand via chatbots in the past 12 months, according to a Salesforce study published in late 2018.”
Chatbots have permeated the Indian Landscape
In India, like most countries, both businesses and consumers rely on telephone and email as the most preferred channels to conduct business, yet they are also the slowest for quick resolution. The average time-to-resolution using email interactions was reported at 39 minutes while in India it was reported at 2 hours 17 minutes. In addition, global data shows only 49% of problems are solved on the first interaction.
Most people in India (59%) however, still prefer to talk to an actual person for customer service needs. While this is true, customer service experts believe this trend will reverse in the near term. A majority (61%) of “the Digital Indian” or tech-savvy users see the benefits for chatbots in customer service.
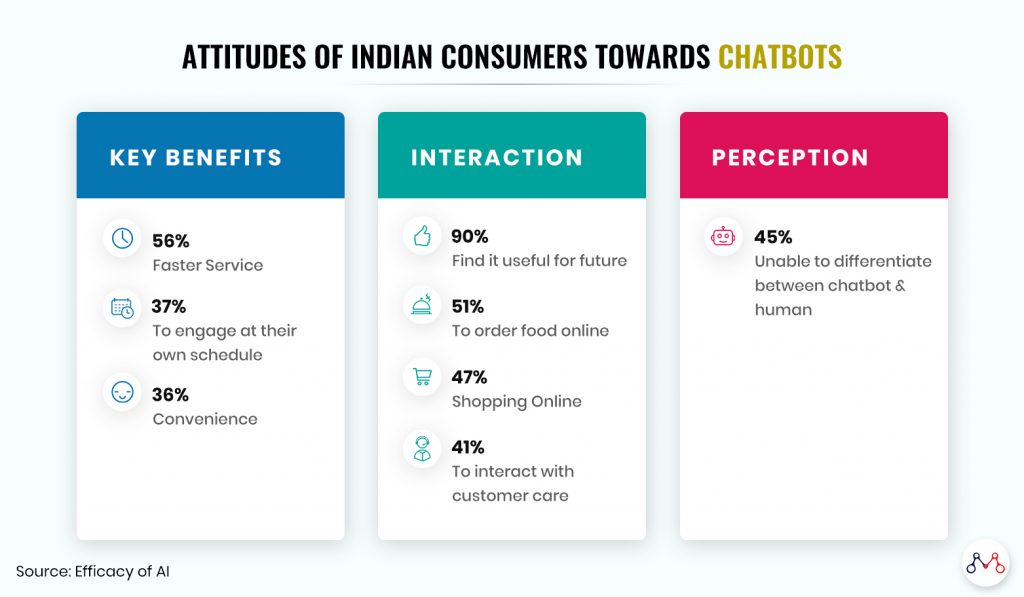
AI is already providing benefits to e-commerce businesses in India by improving decision making & recommendation systems using machine learning algorithms, while simplifying the product search journey for the customer. When done well, 43% feel chatbots can be almost as good as interacting with a human, revealed a study titled “Efficacy of AI” conducted by digital marketing solutions firm iCubesWire.
Bots among us
Conversant bots have augmented our ability to quickly access information, services, and support – even taking over some of our day-to-day tasks. The passage deeply signifies an unmistakable shift in our digital communication patterns. Here are some well-known instances of chatbots in use, around us.
GoHero
This AI-enabled personal travel agent assists customers in booking flights, hotels, taxis, buses etc. It integrates with messaging apps to use sophisticated algorithms to understand traveller’s preferences and is available across nine platforms such as Facebook Messenger, Telegram & Skype.
Aisha
A voice assistant (similar to Siri, Google Assistant) by Micromax performs daily tasks like initiating a google search, fetching movie reviews, making calls, reading news articles, view stalk market details and more. The Handset Speech Assistant with AI integrated into its backend is gently becoming an accepted, must-have tool for the average consumer.
Lawbot
A customer facing AI application that automates specific legal tasks that would otherwise require extensive legal research. It analyses and reviews legal documents, like contracts or agreements, and identify problems in them in seconds – saving customers valuable time and money.
FitCircle
This health and fitness chatbot offers its users personalised weight-loss workouts, yoga guides and nutrition guides. The AI empowered fitness companion, called ‘Zi’, helps the Digital Indian achieve fitness goals through custom-fit workouts and diets.
Oheyo
Formerly Prepathon, Oheyo helps students (the digital Indian of the future) prepare for exams, by connecting them to experts anywhere. It messages students the subject of the day, answers queries and additionally sends across motivational messages. They also provide a video Q&A platform through which students can find a lot of their queries answered and archived for later use.
Skedool
Skedool’s ‘Alex’ is a B2B smart assistant, that excels at automating repetitive everyday tasks for business executives, sales and recruiting professionals. It handles B2B scheduling activities and calendar management. The AI assistant uses natural language processing and machine learning supervised by humans to enable customers to communicate with the service via email just as they might with a human assistant.
Hitee
A one-of-a-kind chatbot with voice, video, and multilingual features. It’s custom NLP-powered workflow builder solves a number of purposes like operations, HR, IT, logistics, and more.
While these are just a few highlighted examples, there are many more in use across the country, each with a unique use case and problem it is trying to solve. For example, Aapke Sarkar – a chatbot (developed by Haptik) launched by the Maharashtra Govt. for people to access information regarding public services in the state, in Hindi or Marathi; or the bot introduced by IRCTC called ‘AskDisha’ (Digital Interaction to Seek Help Anytime) that helps railway passengers access customer services support in multiple regional languages and even voice-enabled chat.
Bots and The Digital Indian
The Indian chatbot industry, although still in its nascent form, is a $3.1B market, according to analysts. The market, in the coming years will evolve to a point where interactive and intuitive AI will become the bare standard for customer service across a variety of sectors.
AI in Insurance will value at $36B by 2026. Chatbots will occupy 40% of overall deployment, predominantly within customer service roles.
DOWNLOAD REPORT
Related Reads:
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox





