Web development starts with index.html. The major components of web development are HTML, CSS, and Javascript(JS). HTML is used to interact with users, CSS is used for styling HTML elements and Javascript is to run the process in the background.
With JS, we can create/read/update/delete HTML elements. React is an open-source JS framework library that can be used to implement component-based development where the entire website is split into small components(JSX) like building blocks for re-usability, processes based upon life-cycle events, easy maintenance, etc. React will convert components into plain JS to render components in the browser.
Source: https://developer.ibm.com/tutorials/wa-react-intro/
Client Side Rendering:
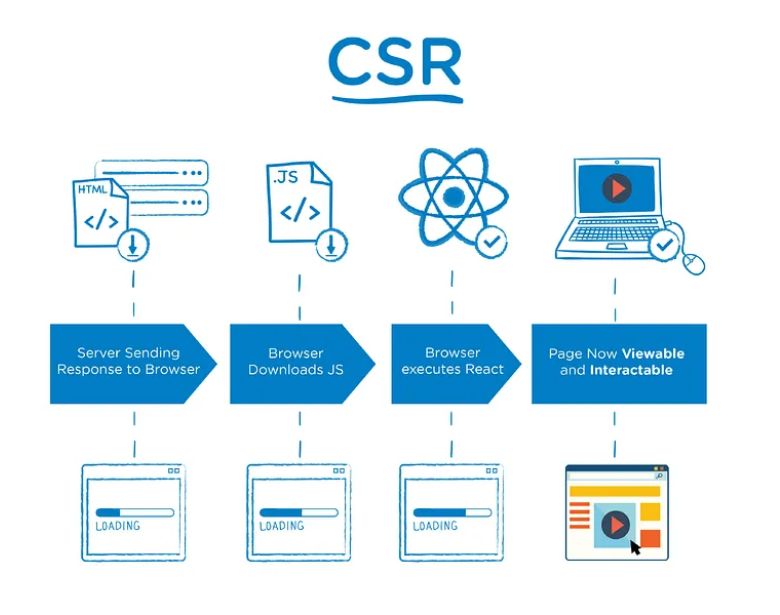
Client Side Rendering(CSR) is a mechanism in which the JSX render mechanism is completely run at the browser level. Virtual dom is the mechanism created by React which will be handled in the system memory before it renders in the actual dom. So the mechanism will process the following steps,
- React source will be built from actual source code for better performance. The Built source code will be placed on the server.
- When a client requests the server, then the entire source will be downloaded from the server and cached in the browser.
- On every user interaction other than the backend server request, every page render will happen on the browser as client-side rendering.
- Libraries used for routing and state management are being handled at the client level.
Server Side Rendering
Server Side Rendering(SSR) will serve the website with ready-to-be-rendered HTML on the browser. So when there is a request to the server, the component will be rendered on the server side and it will give the data to the browser to render on the web page. It will reduce half of browser performance as it is being handled on the server. So the lifecycle of ssr will be like this,
- The server will be ready to serve pre-rendered HTML content from React component.
- The client sends a request to the server.
- On every request, the server will render components and give the HTML-rendered page as a response along with JSON data and required JS files.
- On the browser side, non-interactive content which is plain HTML will be shown to the client as the initial phase, and after that hydration will happen with the existing rendered page to make it interactive by the client.
CSR vs SSR
- SSR servers pre-render HTML that will support fast loading on the client browser. And also it will reduce usage of system memory as most of it is handled on the server.
- Let’s consider a scenario where a page has to display and before that, we need to collect details from the backend server. In that case, SSR has a high hand compared to CSR. SSR will make a call through VPC in its private subnet and collect the required details from the backend server. So the data communication time will be reduced, and the page will be rendered on the server and shared with the client.
- When it comes to a simple website with minimal data processing, CSR will have higher performance as all the libraries, CSS and HTML are already cached in the system. It will quickly render on the virtual dom and present to the client.
Search Engine Optimization
Most organizations come to SSR mechanism only because of high support for SEO. Search engines like Google will crawl through the website to collect the details. So when the user searches on the website, it will appear in the list. SEO works the same for both CSR and SSR. But it will help to improve the other web performance vital metrics such as page load time etc and also increase the web rankings.
Security
When it comes to CSR, all the secured details will be sent from the backend and it will be used to perform follow-up operations. Those operations can be controlled with SSR to give a rendered page by keeping secret data in the server.
How to find CSR or SSR:
Checking whether the website is CSR or SSR can be done by viewing the website source. If it is SSR, then the source will have the rendered pages. If it is CSR then the page will have a simple body just like below,

If the page is rendered with SSR, then we can see the complete rendered HTML page in the source. To view the source, we can either right-click on the website and choose view source option or add the view source key before the website like,
Why Next.JS?
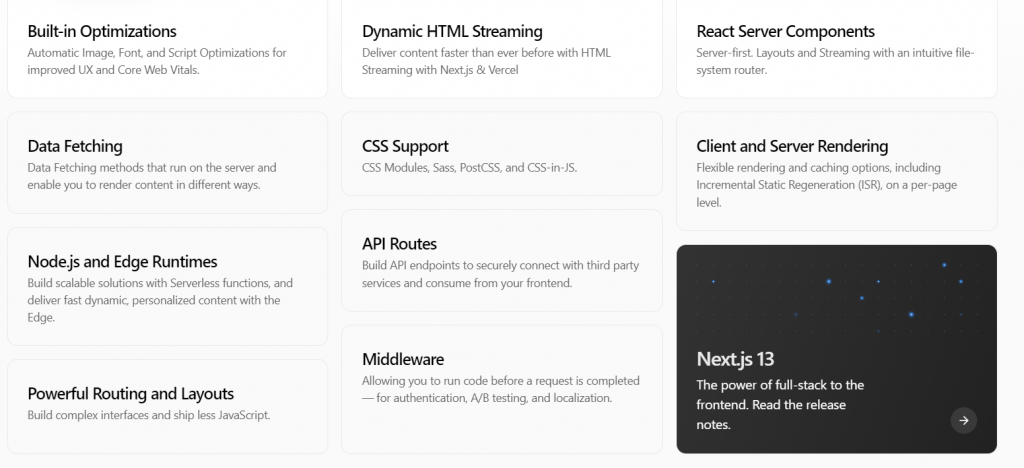
Next.JS is a structured framework that builds for SSR and keeps React as its core. It gives support to routing, image optimization, font optimization, etc., as default. Next.JS is an open-source framework that acts as a middle layer to connect the client and server.
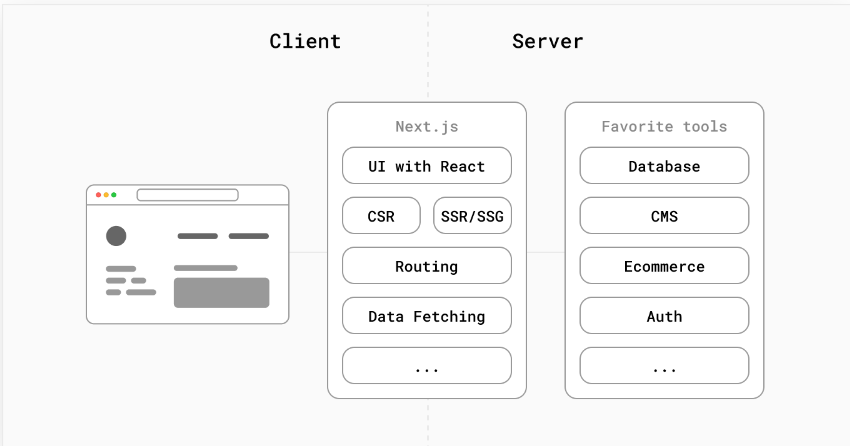
With Next.JS, the team can build a fully performant web application and configure web applications as per the business requirements. The features supported by the Next.JS team
Kickstart on Next.JS
With the latest Node environment, kickstarting any framework/library has become very easy. The steps go like this,
- Install NodeJS.
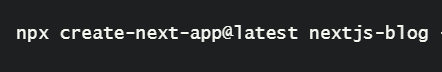
- Open the command prompt and navigate to the respective folder location where we want to create a setup for the Next.JS project and one command is all it takes to kickstart on Next.JS. In the following command, it will create next.js-blog folder.
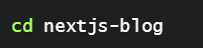
- Navigate to next.js-blog using the command,
- Start the development using the following command and it will open the URL localhost:3000 in the browser.
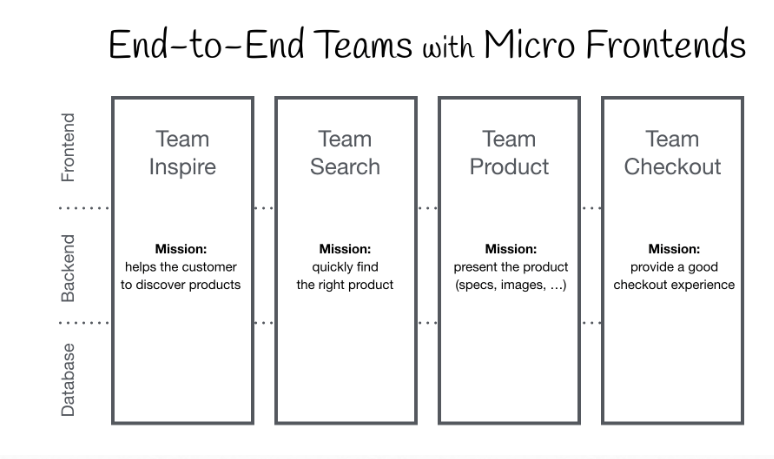
Micro-frontend
Micro-frontend is the mechanism that will help us to develop an entire application into multiple pieces. So the team can be divided and work on their module without disturbing other modules.
Some of the key benefits of micro-frontend,
- Technology Agnostic
- Not completely depend on any framework/library/technology. Based on the system requirements, we can wisely choose to align with the system
- Isolate module
- Team can develop their particular module instead of having a dependency on the entire website. So the development, testing, and deployment can be taken at their convenience.
- One major issue that we’ll face is to avoid duplication. So the components have to be moved to a common module and have to be used everywhere etc. CSS duplication can be avoided with complete tailwind CSS integration. So a decision has to be made on every part of the development for the integration of shared pieces on every module.
- Testing
- Testing will be easy as we isolate modules. So the regression testing process will occupy less time for the testers. Building automation testing will be very easy as we’re developing only for a particular module.
Conclusion
Like many developers advised, it all goes with business requirements. Carefully consider all the business requirements before making major decisions on the technical architecture such as choosing SSR or CSR micro-frontend or monolithic or micro-frontend etc. One extra thing is to keep everything aggregated. Even if the business requirements change, we can reduce the amount of time for the migration.
About the Author: Naren is working as a Senior Technical Lead at Mantra Labs. He is interested in creating good architecture and enjoys learning at every step.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox