A website’s page load time plays an important role in customer acquisition. Google states that if your website takes more than 3 seconds to load, over half of the visitors will leave it. Eventually, it leads to conversion and profits. Although there are online tools available to check your website loading time and performance (Lighthouse, for instance), it’s important to understand what affects your website’s page load time. You can then optimize your web page accordingly.
8 Factors that affect the page load time
#1 Web hosting
Today, no one would like to wait for a website to spin and load at its speed. Websites that load quickly perform more in user engagement, conversion rates, and user experience. Hence, it is very important to have a high-availability web hosting plans.
#2 Size of files
The page speed always depends on the size of the assets loaded on the browser. It is, therefore, good to have an optimum number of assets with the least possible file size. This will require lesser bandwidth.
#3 Number of HTTP requests
Greater the number of HTTP requests from a browser to server/server to server, the higher will be the bandwidth consumption. Therefore, keep the number of HTTP requests to the minimum possible.
#4 Absence of CDN
Using CDN will boost the performance of the web site. The absence of it will affect the load time. CDN is a content delivery/distribution network. It is a network of proxy servers and their data centres distributed across the globe to increase the performance and availability of services to the end-users.
#5 Mediocre coding
Bad coding will always affect the page performance and SEO ranking of the website. It is good to follow best practices starting from the initial stage of development.
#6 The number of redirections
The number of redirections impacts the DNS lookup time.
#7 Lack of Keep-Alive
If you’re using HTTP/1.0 protocol and have not configured Keep-Alive, then there’s a higher possibility that the browser to server connection will break. It will not load the page properly.
#8 Hotlinking
Sourcing page content from other sites might affect the load time and performance of your website.
You might also like to read about 11 proven techniques to optimize website performance.
Strategies and checklist for website optimization
You can implement either bottom-up or top-down strategy for website optimization (discussed later). However, website optimization is an iterative process and you can repeat the following loop after completing a cycle.
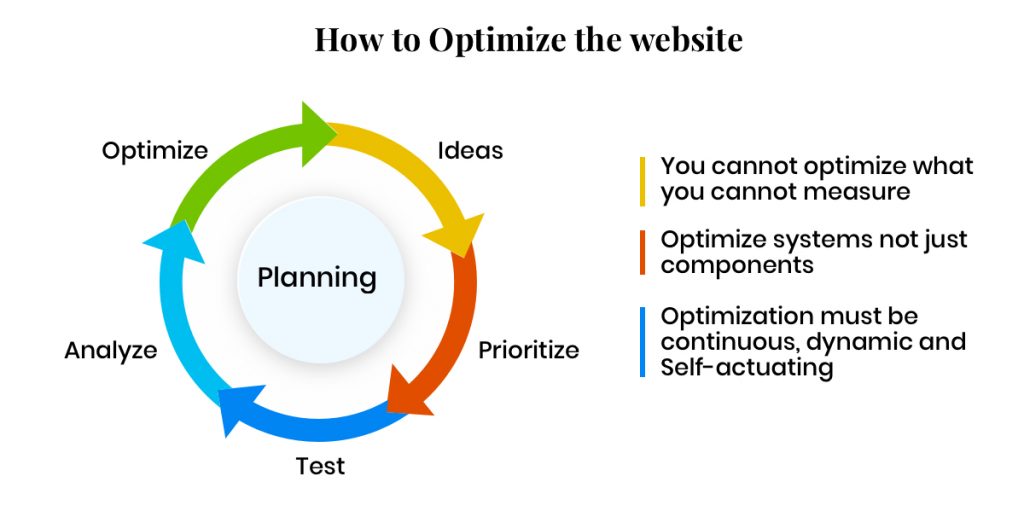
- Ideas: Prepare a checklist of all the possible strategies for the target website to optimize.
- Prioritize: Prioritize the prepared checklist strategies and act on them.
- Test: Test the applied strategies for enhanced performance.
- Analyze: Analyze the impact and performance of the website and check if any further strategies are required.
- Optimize: For further enhancement, perform the cycle again until you achieve the best.
#1 Bottom-up strategy
This strategy starts from planning to production (Proactive). It defines a set of rules and actions before/while starting the actual development.
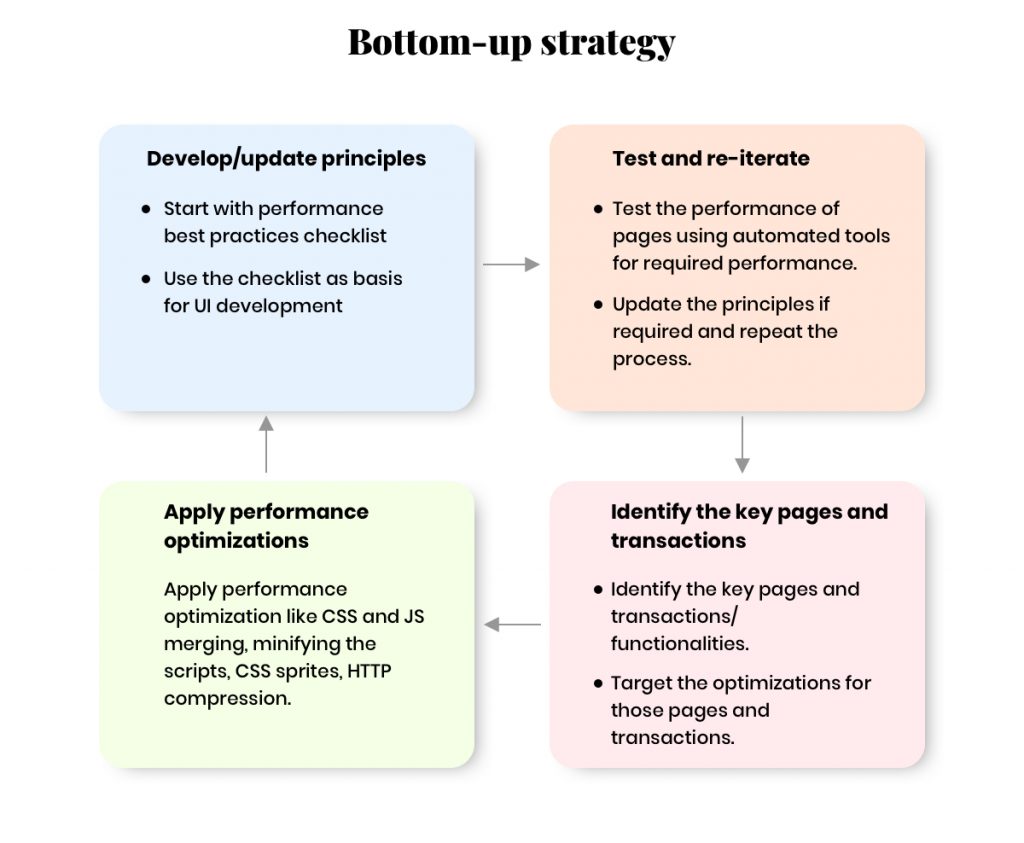
The above infographic represents the lifecycle of Bottom-Up strategy in web page optimization.
#2 Top-down strategy
It is a reactive method, which analyses the existing process to find the issue/lag, then reworks on behavioural grounds to accomplish the target. It is a reverse engineering process to identify the performance-issue gap and methods to fix them.
You can identify the resources which are affecting in maximum page load by considering the following-
- Resource size
- Asset positioning
- Render blockers
- Uncompressed contents
- Bad requests
Once you’ve identified the sources, lay down the process of optimizing the content and keep iterating to achieve the desired results.
Basic checklist for both bottom-up and top-down strategies
- Layout performance principles
- Page load time
- Responsiveness
- Minimizing the number of requests
- Use Cache headers
- Minify CSS and JS contents
- Use CSS sprites
- Encourage Lazy loading on contents wherever possible
- Avoid iframes and redirects
- Executive performance principles
- During application design
- During application development
Consider the following aspects during the design and development phase.
#1 Application design optimizations
- Simple & lightweight: Include only key functionalities on load to keep it lightweight.
- Client side components: Adopt client side validation to catch errors.
- On demand data loading: Use on-demand data instead of pre-loaded data. (E.g. use paginations, pop-up contents on click instead of on load)
- Asynchronous calls: Adopt implementation of AJAX calls from the presentation tier and the business tier.
#2 Application development optimizations
- Include JS files at the bottom of the page (to avoid render blocking of page).
- Combine multiple CSS files and optimize unwanted rules as per page requirements.
- Avoid using external scripts at the beginning of the page.
- Combine smaller images/icons to sprite & have optimi.
- Use CSS rules/files in the head section of the document.
- Reduce the number of requests to server.
- Implement server/browser caching on possible sections.
- Implement Mobile-specific sections to avoid overloading on small screen devices.
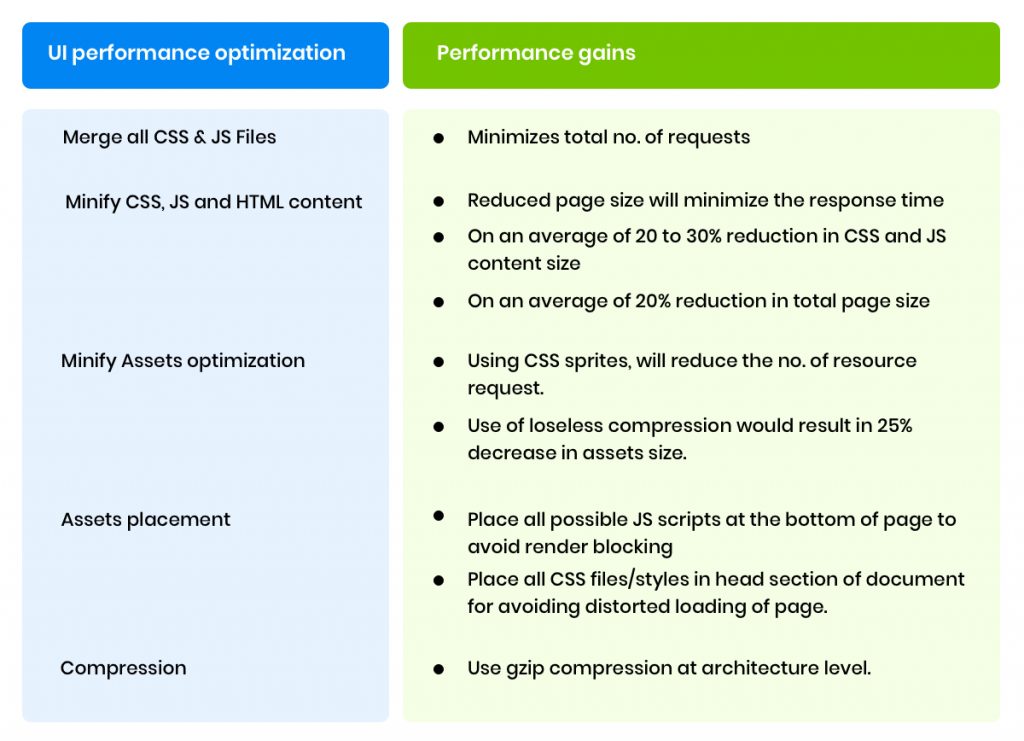
Below are few improvisation observations which are affected by optimizing the Webpage and it’s assets.
We’re technology tinkerers, experimentalists, and experts in customer experience consulting. Get in touch with us at hello@mantralabsglobal.com to know more about our ventures in website design and experience consulting.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




