IoT is emerging as a disruptive technology and is growing significantly, as consumers, businesses, and governments recognize the benefit of connecting inert devices to the internet.
With breakneck speed, the Internet of Things (IoT) has branched out of the B2B and industrial markets where its concept first took root and exploded into the consumer market in a major way. IoT extends beyond just “smart homes,” that can gather useful data and automate some of our everyday activities. It seems like almost every consumer device will be equipped with IoT connectivity. It joins sensors, devices, data and connectivity together to make the Internet a mesh of Things which can interact, exchange, act with intelligence and transfers data inside networks. Though it is still evolving but it’s promising and pragmatic applications are seen in all verticals, there are already a number of consumer products that use the IoT technology.
With companies joining this new epoch in technology, we also are building our “Smart Clock” (right now in prototype), which is inspired by Ingrein Clock (a kickstarted project).
For Quick Prototyping we started with readymade circuit boards Raspberry PI / Arduino / Particle.io, including various sensors to have a fair idea about the components and modules required to build the final product . We also started minifying the board and breaking down the circuit to absolute components that are required in building Smart Clock. Before proceeding further let us know
- What is Raspberry PI?
It’s a mini computer with GPIO pins. The device is quite powerful and is able to run complete Operating Systems like Linux. It simplifies a lot of hardware and software specs altogether.
We just need to connect any hardware module to the GPIO pins and then program Raspberry (in any language) though Python has a lot of libraries for raspberry.
The device will cost around 2-3K. One can get started using Raspberry PI soon.
- What is Arduino?
Arduino Board has a micro-controller and a set of digital and analog I/O pins to communicate with other hardware devices. Arduino is more hardware oriented since it does not come up with installed Operating System.Arduino also provides you its own programming development toolkit where you could submit your code and the software mounts the code to micro-controller. We do not have language choices here but one must know the basics of C++. We can turn this Arduino into any smart device we want to and we can use multiple sensors.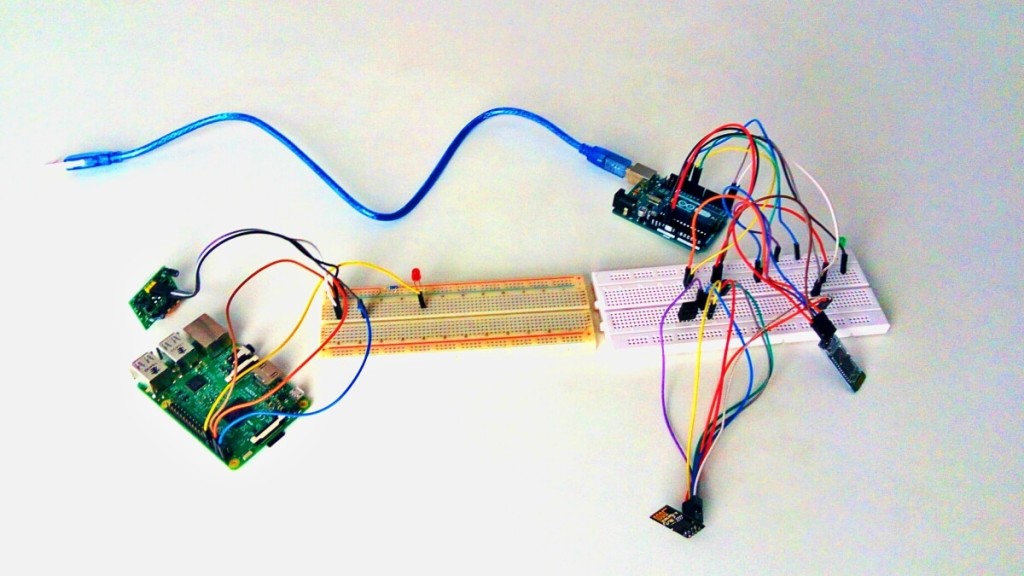
While building this Smart Clock, we did couple of experiments on Raspberry PI and Arduino. For example, we face problem to check whether the meeting room is empty or not, for that we added PIR motion sensors to Raspberry PI and programmed it in Python.
The next task was to exchange data between Raspberry PI and server so one could get the status of the room from his mobile. We implemented Mqtt/Mosca for this (node.js). Now if there was any motion, the PI would send a message to the server and the same could be retrieved on the mobile. This was a simple exercise just to get started.
The next current task we are doing is trying to put minimal required components and sensors together to build a Smart Clock (expected to be changed). 
Mantra’s Smart Clock:
A smart clock could read your notification alerts and check other daily tasks.
Currently we have picked one feature that is the clock could tell whether someone from the family is about to arrive. For example at evening, if you are coming from office, as soon as you are near your home- around 200-400 metres away, the clock would notify about your incoming and hence someone at your home could start preparing beforehand whatever you want – food/snacks etc. The clock will be connected to internet and will come with an app that keeps pushing user state to the servers.
Smart Clock quick points:
– Connectivity: the clock will come with an app which will be used
to connect with clock using Bluetooth. The clock will be configured
using this app such as connecting it with internet and other basic
setttings.
– Currently we are only focusing on very few activities such as
notifying family members about activities such as notifying member is about to arrive ,
weather and app notifications
Prototype Technical Specification:
Connectivity: Bluetooth/Wifi
Sensors: PIR motion detector
Board: RaspberryPI/Arduino
The project is currently under progress. We are customizing the circuit board with lesser components, what are needed only.
For a complete updates on “Smart Clock” and other latest technology, approach Mantra Labs at hello@mantralabsglobal.com.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




