The deadly outbreak of the pandemic, coronavirus has claimed more than 110,000 lives and infected over 18,30,000 people worldwide. While the government chalks out COVID-19 risk mitigation plans, including social distancing, healthcare advisories, remote working and quarantine the infected; many organizations are taking technology initiatives to provide visualization and real-time situational awareness along with ways to run the lives of daily wagers.
To curb the spread of infection the entire nation has been subjected to rigorous lockdown. Unaccounted migration of daily wagers has made ghost settlements a recurring feature. Business tycoons say it is a daunting task to keep thousands of engineers safe while ensuring business continuity. This situation may affect the global economy because of supply chain, production, oil prices, currency and interest rate fluctuations. According to estimates, the economic cost of the pandemic would be over $4 trillion.
As the world gears up to combat this crisis of unforeseen magnitude, researchers, businesses, and innovators around the world are putting technology to work to mitigate the effects of the global health crisis. From using big data to understand the virus’ genetic tree, to keeping hospitals afloat with telemedicine; countries are trying every tip and trick in the book to contain the disease and provide a pattern amidst pandemonium.
Here is a list of technology-driven initiatives taken worldwide to combat the corona pandemic.
Aarogya Setu App
The Aarogya Setu application is the Government of India initiative to bring essential health services available to people. The most commonly used technology by the government is tracking people’s whereabouts through the location information on their cell phones; which in this crucial time has proven to be a means to restrain the spread of coronavirus. Using this technology this application alerts you when COVID-19 infected people are around. It also gives a detailed view of where the patient was before quarantine and who were in close proximity with them.
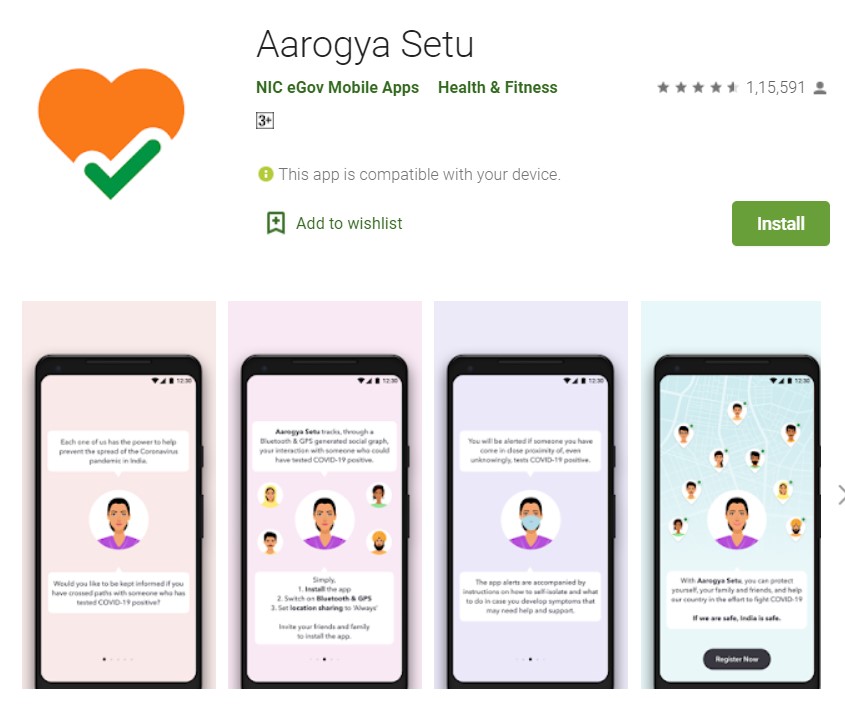
The app aims at amplifying the services of the Department of Health, in proactively reaching out to and informing the users of the app regarding risks, best practices and relevant health advisories related to the confinement of COVID-19 virus.
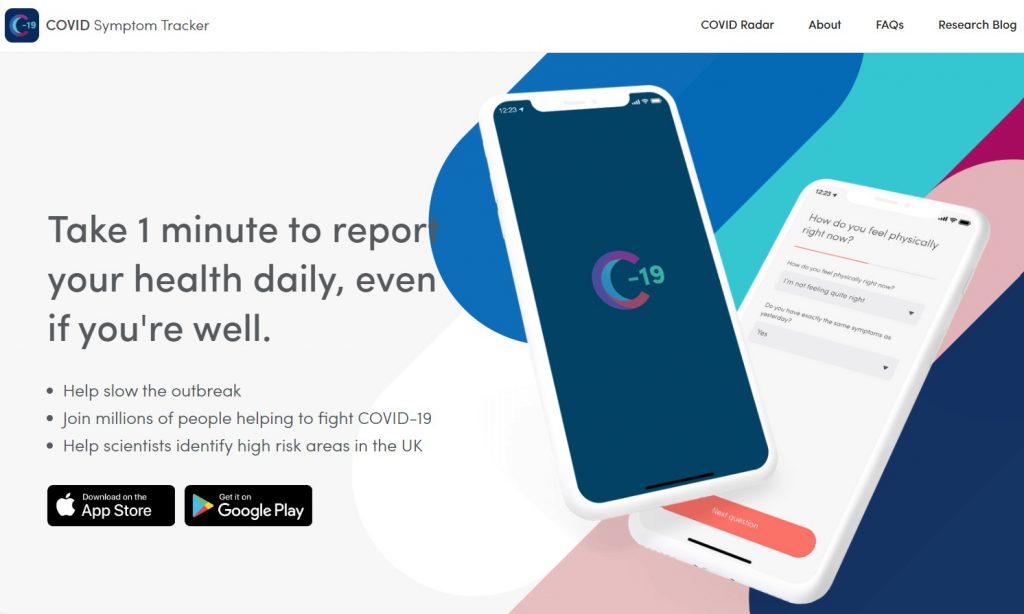
COVID Symptom Tracker & Corona 100m
C-19 COVID Symptom Tracker, an application developed by a UK startup, helps people self report their symptoms of coronavirus. It also helps to identify high-risk areas. It uses data science and machine learning models to study the data provided by the masses and identify those at risk sooner.
The corona 100m, application by South Korea maps the whereabout of a corona positive patient and alerts the user when the infected person is within the reach of 100m.
China is using AI-powered thermal cameras on drones to enable contactless and rapid temperature detection in a crowd. This helps to identify those who have a fever. They have also deployed facial recognition systems to screen out people not wearing masks in public.
WHO Health Alert
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a dedicated messaging service, the WHO Health Alert chatbot to provide information about coronavirus, answers to frequently asked questions about the disease, the current infection rates and preventive measures to be taken against it.
The service is available in 7 different languages such as English, French, Hindi, Arabic, Italian, Spanish and Portuguese. People can activate conversation related to COVID-19 facts by simply typing a ‘hi’ to +41 79 893 18 92 on WhatsApp.
Video Calling Apps to keep Business as Usual.
With this pandemic taking a toll on the day to day business, companies are trying hard to keep employees safe with options like remote working and using tech tools to collaborate. As the world continues to fight the pandemic, flatten the curve and try to maintain normalcy by working from home. To deal with this containment and yet keeping it business as usual, video calling applications have become the most essential tools.
Read to know more about how Enterprises investing in Workplace Mobility Can Survive Pandemics.
The popular video calling applications like Skype, WhatsApp, Google Hangouts, Duo, Webex and Zoom, received approximately 600,000 downloads in one day. There has been a 70% increase in activity in Facebook Messenger’s video call functionality since the beginning of the outbreak.
Relief Fund for Daily Wagers
Due to this lockdown, as the economic activities of the country grind to a halt; millions of underdeveloped regions face penury and deprivation. With the lockdown suspending all kinds of work, daily wage workers are the ones to suffer the most. However to provide some relief to this horrifying situation, tech companies like Swiggy, Zomato and Ola have reached out to help.
Ola’s Drive the Driver’s Fund is to offer relief to the driver community. It provides financial assistance for essential supplies and emergency support.
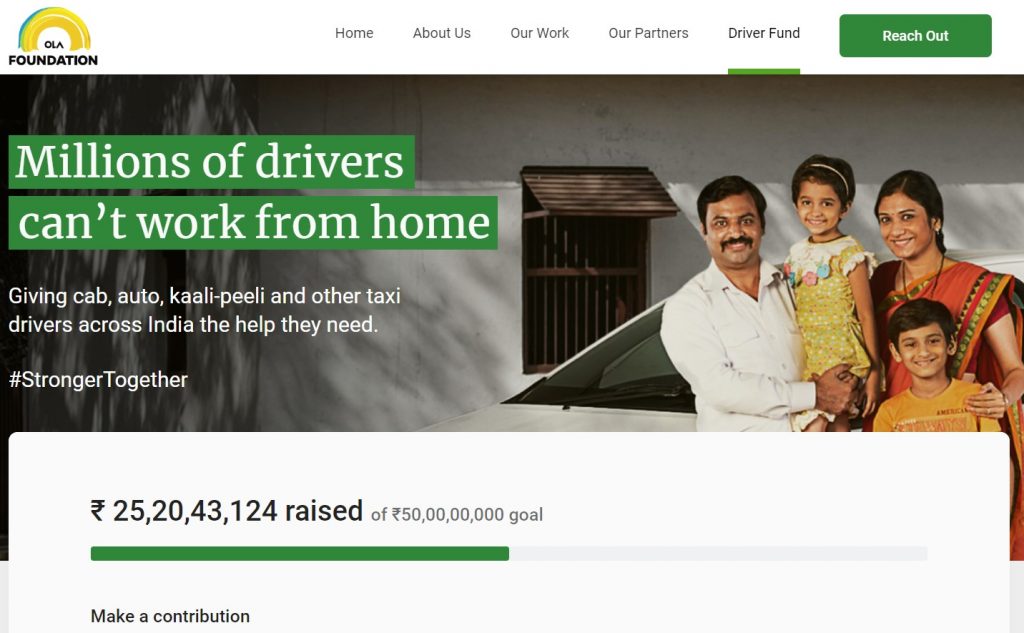
Whereas Swiggy and Zomato are taking donations on their app and feeding India without involving a middle man. The financial help directly reaches the labours.
MyGov Corona Helpdesk
To mitigate the spread of fake news and offer immediate information related to coronavirus, the government of India has launched an official helpdesk, called MyGov Corona Helpdesk. One can initiate the conversation by simply texting a ‘hi’ to 9013151515 on Whatsapp.
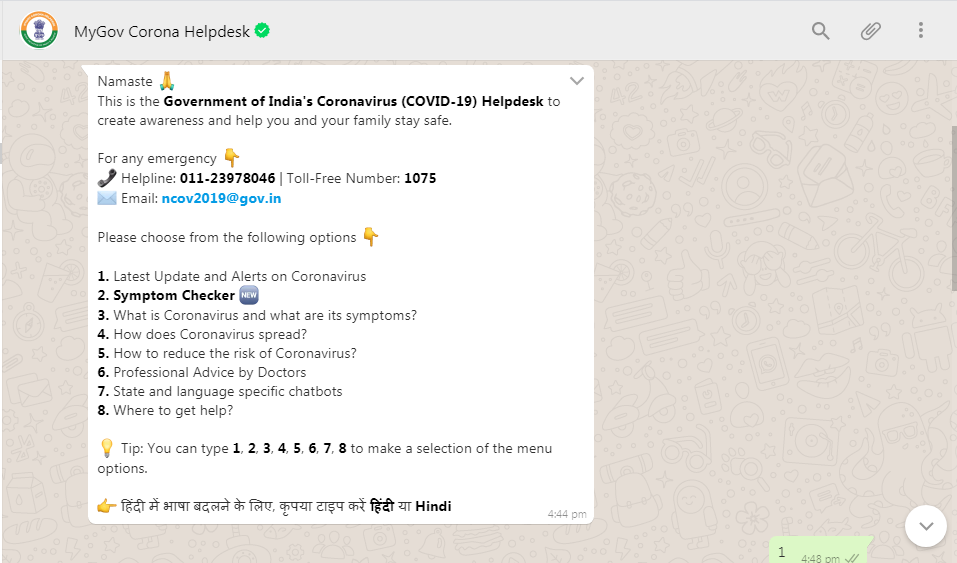
The government has also taken to other social media platforms such as Youtube, Facebook messenger, Linked In, Twitter, Instagram, Facebook Page and Telegram App to spread awareness and prevent the spreading of coronavirus.
Corporate technology-driven initiatives
Coronavirus Helpline India
ACKO, an Indian general insurance firm has created a portal – Coronavirus Helpline India to connect the government and common mass. It has listed all state wise essential helpline numbers, FAQs and important news related to coronavirus outbreak in India.
Lockdown Helping Hands
MantraLabs has taken the initiative to create a platform for people all over India to share their problems. The platform Lockdown Helping Hands is an effort to give voice to those who need help at this crucial hour of need. Others can directly share their, or other person’s problem on the portal. Using the share option, one can post the issue on various social sites to amplify the voices to reach the ears of the respective authority. The platform also provides state-wise helpful links, essential contact numbers and list of shops that are providing home delivery.
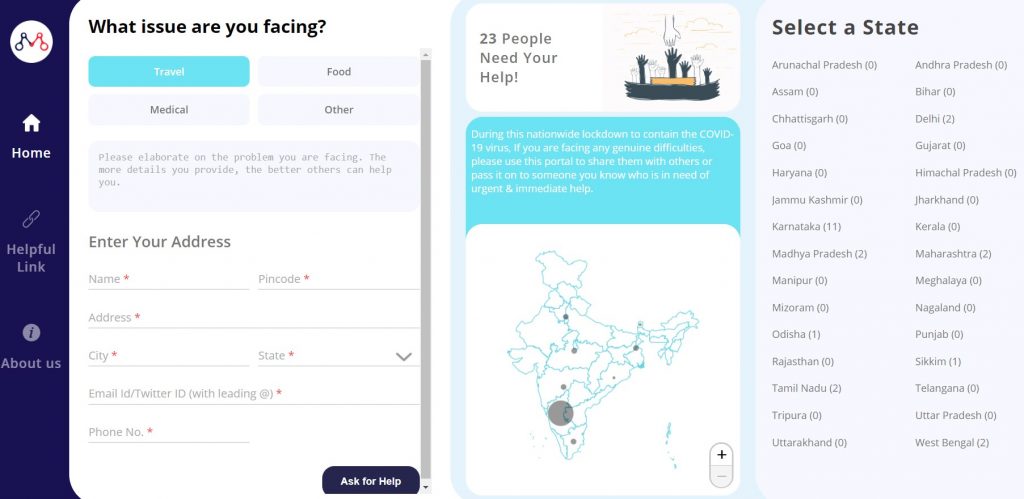
Due to the lockdown, there are several people far away from their loved ones, and struggling for help and information. There are many groups of people volunteering and ready to assist senior citizens, new mothers, physically challenged and people with medical conditions get access to basic daily essentials & medicines. Let us also do our bit and help lend a hand of help at this hour of need.
#StayHome #StaySafe
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox






