The evolution of the language or tool depends on the problem statement and advancement of hardware.With the emergence of cloud computing few languages like Java, PHP, .NET, Python, JS and their respective tool sets are in trend. In this article we shall concentrate on three technologies i.e Java, Node JS and Python and see a comparative study of them.
The internal workings
Here I want to present the working principle of the three. One thing is clear, Java is the only compiled language but Node JS and Python are interpreted languages.
For beginners that may not be a big deal, but this may change the whole discourse. When we compile the code, it is ready to consume by the hardware but when it’s interpreted the code is converted to byte code on the runtime, it may turn out to 10X performance improvement depending upon the situation.
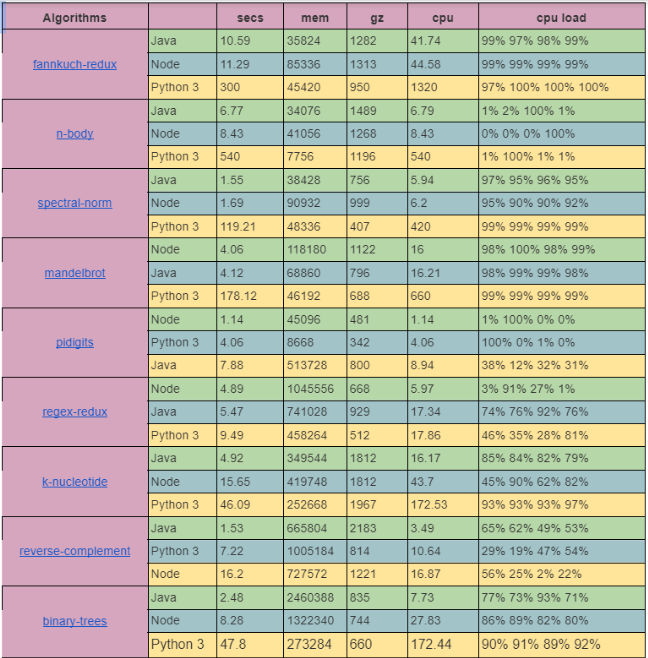
Following is the table which will depict execution time, CPU, memory utilization and the code size for some standard algorithms. Credit goes to benchmarksgame-team. For details of the unit, you can refer here.
The following table depicts the comparison between on the basis of speed, performance, scalability and more:
| Parameters | NodeJs | Python | Java |
| Speed | Faster | Fast | Fastest |
| Performance | Low | High | High |
| Scalability | Highest | Medium | High |
| Simplicity | Medium | Very Simple | Simple |
| Community | Strong | Strong | Strong |
| Library | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Cost | Free | Free | Paid |
| Cross-functionality | High | High | High |
Speed
As Java is compiled as bytecode and statically linked code the performance is always faster, in most of the cases ten times faster than the other two. There are a few odd cases where Java falls short of speed. In those cases, it boils down to mismatched use cases, legacy code, and wrong coding practices.
NodeJs speed is better than Python thanks to the V8 engine. The V8 engine interprets the javascript code to machine language and optimizes the solution to reduce load time. NodeJs programs run on a single thread. However, you can easily find multi-threaded libraries. The libraries were used to create a thread pool and used multiple CPU cores simultaneously in the background.
Performance
Computer performance is the amount of useful work accomplished by the computer system. So the performance of a system depends on the right kind of technology picked for a particular workload. Java naturally supports multithreading hence if an application does heavy parallel processing, it will be really a great choice. If an application makes lots of networks, it calls Node JS which will be the winner as it naturally supports event-driven programming and hence asynchronous programming. Python is mostly evolving as a middle ground to achieve a decent performance and it always has the advantage of being a simple language to learn.
Scalability
Looking at the current evolution of cloud infrastructure, to achieve scalability using infrastructure tricks for stateless web applications is a norm. The real challenge is to scale a stateful application. The scalability depends on the purpose of the application and the technology we pick.
Node.js is quite scalable, owing to microservices, event-driven architecture, and non-blocking I/O. It allows the creation of microservices and modules. Whenever the solution expands, these microservices and modules resort to dynamic process runs and keep the performance and speed in check.
Java being garbage collected by the resource optimized JVM, it becomes a decent choice to scale.
Python is hard to scale as it’s dynamically typed it’s always slower. As the code goes the system also gets slower and the system gets too tangled.
Simplicity
It is measured as the amount of time one needs to spend learning the language and using it. So it boils down to the familiarity with syntax, expressions and concepts. Also with ease, a developer adapts an existing project and starts contributing.
Java is object-oriented programming and memory management is taken care of by the JVM hence its learning curve is small.
Python on the other hand is a high-level language and its syntax is more intuitive. Hence the learning curve is even smaller than Java and that is definitely the factor used in most non-software industries like data science and others.
The learning curve of the NodeJs is simple too, but the inner workings of the run time environment like async programming, hook, and patterns are difficult to grasp.
Community
All of them established themself in their own markets. Both Java and Python have been around for quite a long time and have healthy communities. NodeJs is a relatively new technology still looking at the adaptation and as its open-source, it has a sizable community.
Library
All three have a voluminous library to support various functions and they are well documented.
When working with NodeJs, you will find NPM (NodeJs Package Manager.) It is a free online repository that fuels and simplifies JavaScript development by storing NodeJs packages.
Cost
Python comes with lots of open source libraries and frameworks that help to reduce the cost of python. Whereas Java is now owned by Oracle and it’s licensed and to get the support we need to pay the license cost. The cost involved for NodeJs using the NPM packages is cost-free, there will be a cost involved for the paid library for payment gateway and third-party integration.
Cross-Functional
All of the above work seamlessly across different environments. As Java is meant for code once and it will run everywhere hence it’s suitable for network application, parallel processing, and web application development. Python can easily run as far as the runtime remains the same, it’s suitable for web applications and data science applications. NodeJs works for multiple OS and devices hence it’s good for web applications and cloud-based IoT solutions.
Conclusion
There is no winner or loser in these comparisons, many factors depend on the tools or language that we use, it depends on the problem we are resolving, the performance criteria, the compatibility to the existing framework and toolsets. Finally the learning curve of the team who will use this.
About the author:
Manoj is Solution Architect at Mantra Labs working on cloud native solutions. He loves to follow emerging trends in Software technology. Currently, he is working on Cloud Native tools and technologies.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox