Even when the customer has successfully added items to cart, it all means zilch until the purchase is complete. The average cart abandonment rate for all sectors worldwide was 75.6% last year. Simply put three out of every four digital customers leave websites without completing the purchase.
At the customer acquisition phase, you’ve to compete with zero-profit offers, despite the fact that your product is the best in its niche.
Although 80% of businesses claim they offer a great customer experience, only about 8% of customers express satisfaction with their experience.
So, what went wrong? Why are customers leaving your site without purchasing? And more importantly, what can you do about it?
Mastering the art of understanding user persona, discovering bottlenecks in the delivery process, and designing a user-friendly interface will help you build the product that supersedes customers’ expectations.
Mapping the Customer Journey
It involves understanding your customers’ behavior and feelings throughout their interaction with your products/services and visually mapping them to tell a complete story of their overall experience.
More precisely, the journey begins from the moment they first come to know about your product and the phases they pass through while making a final purchase decision.
“For brands, customer journey mapping is like walking a mile in their customers’ shoes and understanding their circumstances with empathy.”
Apart from managing complex user experience problems, you can tweak customer journeys to understand past, present or a future state surrounding a day in the life of your customer.
According to Gartner, Eighty-two percent of organizations have created a customer journey map, but only 47% are using those maps effectively. The mapping of the customer journey begins by creating a cross-functional team led by the CIO, CMO or even the CEO.
A journey map is different from process maps. They detail multiple channels and touchpoints before and during the buying process. Interestingly, the more value-added layers you can include, the better is your view of your customer.
Top Customer Journey Map Layers
Source: Uxpressia
Adding convenience to the customer experience value chain can create powerful moments of truth. For instance, while shopping on your portal, a customer might want to know more information about your product, it’s features, reviews, etc.
A proactive service that goes to the customer first using real-time messaging and custom product recommendations, is how innovative solutions can address such pain points, impacting the overall experience.
Choosing the Right Attributes
Before we look at how to select the most relevant inputs for outlining behavior, it’s important to grasp the fact that customer journey mapping is an iterative process. For instance, the questions answered by customer journey maps a decade ago is totally different from today.
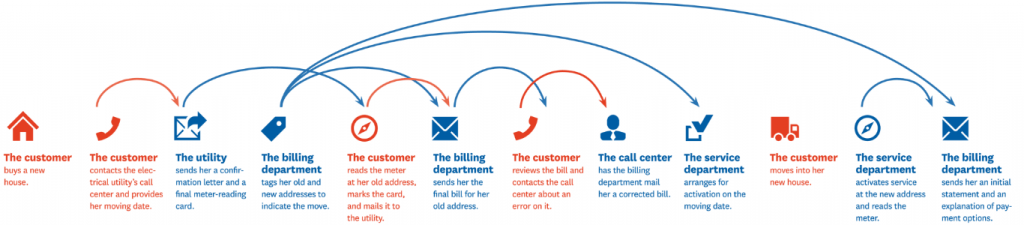
Source: Harvard Business Review | Linear customer journey map in 2010
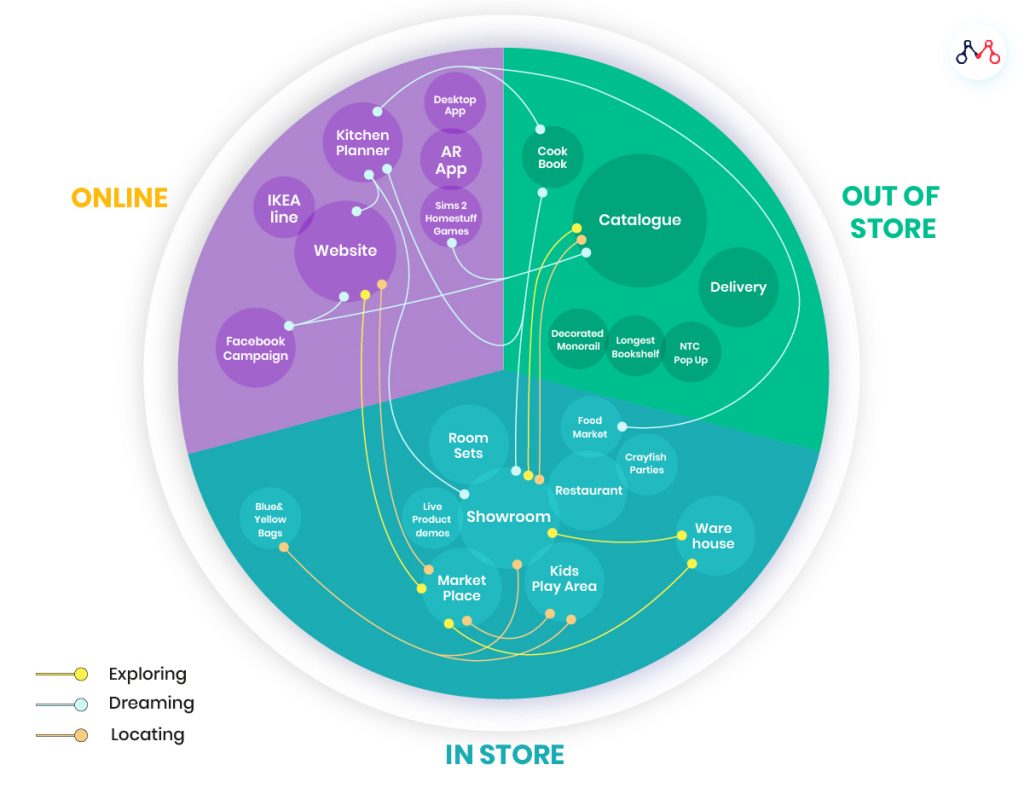
Source: Medium | The present-day non-linear customer journey map (eg: Ikea)
The goal is to build a comprehensive map that will conclusively identify gaps from multiple touchpoints — areas of customer experience that are disjointed or painful.
To achieve this, it is vital to map out each phase of the pre-buying and actual buying journey and map them alongside data-driven personas. Data is critical for customer journey stages — it is almost impossible to create customer journey maps without it.
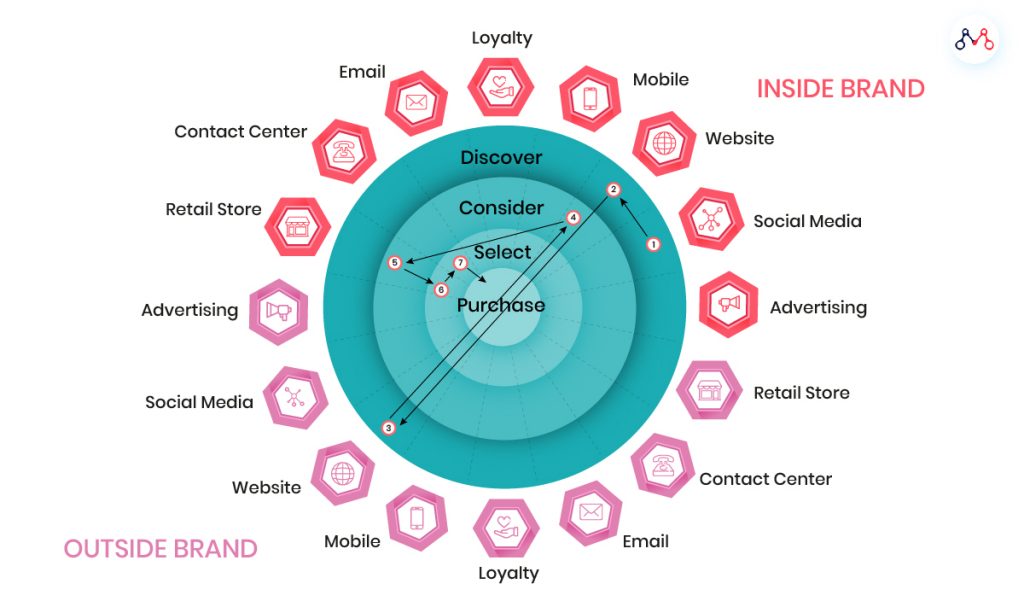
The Modern Customer Journey
Source: G3 Com
The modern customer journey map needs to cover the complete omnichannel experience. Customers are now communicating with companies through 10 channels on average. Their expectations are fast-moving and rapidly evolving. They expect communications about the latest products from their favorite brands to happen in real-time.
For instance, Magalu, one of Brazil’s largest retail companies, recognized that its app was growing in popularity. They decided to enable deep linking, so that loyal customers who tapped on a Magalu ad were taken directly to the mobile app they already have installed, resulting in more than 40 percent growth in overall mobile purchases.
Customer journey maps are drawn from the customer’s point of view and are based on people’s mental models (how things should behave, the flow of interactions and possible touchpoints). They combine user personas, user scenarios & user flows to understand and predict how the customer will behave next.
5 Key Attributes of an efficient Customer Journey Map
- Most relevant brand goals: The goals should be reflective of the inner aspirations of the organization that outwardly manifest into creating the best experiences consistently for the customer.
- Key customer touch-points: Identify touch-points across all channels, and define the action and available paths for each. This layer is critical to understanding how the service structure forces customers into unnecessary interactions and take measures to avoid them.
- Empathy Map: This map depicts exactly what the customer thinks, says, does and feels about your product/ service or the complete attitude towards the brand itself. One can also find utility in creating one-user vs multiple-user empathy maps.
- Affinity Diagram: This is a great planning tool, and it enables you to organize the data and insights gathered up to this point into bundles.
- Sketch the Journey: Now is the time to visualize the structured data into powerful story-driven narratives pointing out gaps in the process. This step will inform what solution or fix will remedy your customer’s pain-point for the long term.
Why You Need Customer Journey Mapping?
You’re doing great if you understand your customers and are able to exceed their expectations. Retaining a loyal customer base might make you think about the essence of understanding the customer journey.
But, how are you planning to face the competitive landscape? Because customers constantly lookout for change. What if your competitors satisfy your customer’s needs with a better emotional connection? Mapping the customer journey will allow you to transform the experience delivery process creating ‘wow’ moments that strengthen loyalty.
“The term ‘customer experience’ won’t exist in the organization of the future. It will be deeply entrenched in a company’s product, process, and culture that it will be synonymous with the brand and represent the only way to do business.”
Ann Lewnes, EVP and CMO, Adobe
We specialize in helping organizations build attractive and easy-to-understand user journey maps for faster omnichannel integration. Reach out to us on hello@mantralabsglobal.com, to learn more.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




