Augmented reality began in a lab at Harvard back in the 1960s, and over the years, it has been used for defense, sports, entertainment, and gaming applications, among others. Most of us got our first taste of augmented reality while chasing Pikachu through city streets in Pokémon Go. But in factories, AR isn’t about catching ’em all—it’s about keeping production lines running smoothly, minimizing errors, and turning workers into efficiency powerhouses with a simple glance through a headset.
In manufacturing, AR has evolved beyond simple overlays to become a transformative force, seamlessly integrating with Artificial Intelligence (AI), IoT, and digital twin technologies. We all recognize the value AR brings to manufacturing, but what happens when AI enhances AR? How is AR transforming the industry, and how does it work? That’s exactly what we’ll explore in this blog.
The Next Evolution of AR in Manufacturing
Manufacturing is no longer just about automation, it’s about augmentation. AI is helping AR enable a new level of precision, real-time decision-making, and predictive capabilities that were once considered futuristic. Let’s take a closer look at how AR is elevating factory operations today.
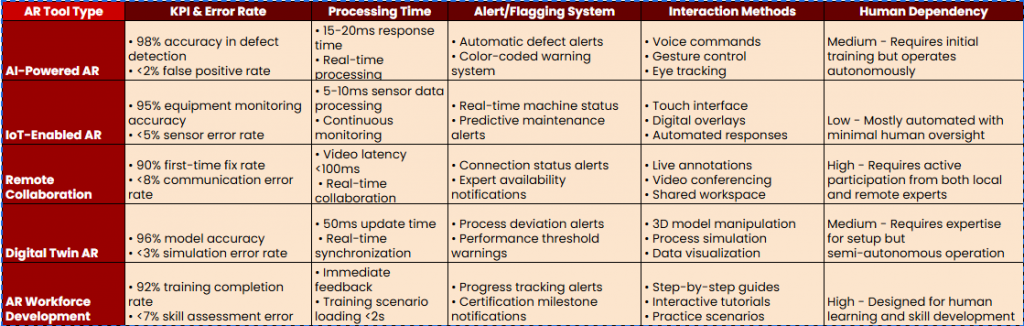
1. AI-powered AR for Adaptive Workflows
Picture this: you’re on a bustling factory floor, working on an intricate assembly task. Traditional AR systems would simply float static instructions in front of you like flipping through a digital manual that doesn’t know if you’re stuck or making a mistake. Helpful? Sure. Dynamic? Not so much.
Now just imagine you are working with AI-powered AR which doesn’t just display instructions, it learns, adapts, and reacts. These intelligent systems analyze your workflow in real-time, adjusting guidance based on how you’re performing, the machine conditions around you, and even environmental factors. Hesitate on a step? The system modifies the instructions instantly. Does a component deviate from standard specifications? AR overlays flag the issue before it snowballs into a costly error.
Companies like PTC and Vuforia are pioneering AI-driven AR solutions, analyzing operator performance to deliver real-time coaching. How Volkswagen has integrated AI-driven AR into its assembly lines, automatically detecting errors and suggesting corrections to workers on the spot, significantly reducing rework time.
2. AR and IoT: The Connected Factory
What if the mere thought of ‘I wish these machines could just communicate’ could be true? AR, when combined with IoT, transforms equipment into interactive entities, providing real-time sensor data directly overlaid onto machinery. Instead of waiting for a malfunction, workers can spot anomalies, take proactive measures, and keep production lines running smoothly.
Siemens has already embraced this technology, equipping workers with AR dashboards that display real-time diagnostics and alerts, significantly reducing unexpected machine failures. According to Deloitte, Factories integrating AR-powered IoT solutions drop machine failure rates, leading to reduced downtime and operational costs.
3. AR-Enabled Remote Collaboration and Assistance
In the past, troubleshooting a complex issue on the factory floor meant waiting for an expert to arrive, causing delays in production. But with AI-powered AR, remote collaboration has become seamless. Experts can now “see” exactly what you see, overlaying real-time annotations, guiding your hands, and helping resolve issues instantly! no waiting, no guesswork.
Airbus has developed AR-based remote assistance solutions where engineers worldwide provide instant support to factory workers, reducing troubleshooting time by 60%. Similarly, Caterpillar’s AR-powered remote support system has led to a 50% reduction in equipment downtime, directly improving operational efficiency.
Source: Belcan.com
4. AR-Driven Digital Twins for Real-Time Decision Making
The virtual replica of your factory floor is not just imagination, it’s a reality with digital twin technology. Imagine standing in your factory and seeing a real-time, interactive model of the entire operation floating in front of you. These AI-powered digital twins mirror every aspect of your machinery and workflow, allowing workers to test processes, predict failures, and optimize operations before making real-world changes.
Instead of relying on outdated reports or delayed diagnostics, workers can access instant, data-driven insights overlaid onto their environment. This helps them tweak operations on the go without shutting down production. Whether optimizing machine performance, identifying bottlenecks, or improving workflow efficiency, digital twins give workers the power to make smarter, faster decisions right on the spot.
GE integrates AR with digital twins, allowing engineers to simulate and optimize workflows before execution, minimizing errors and improving efficiency. Companies leveraging AR-driven digital twins report a 40% boost in operational efficiency, making real-time decision-making more data-driven than ever.
5. AR in Workforce Development: AI-Coached Training and Skill Retention
Forget static manuals and lengthy onboarding sessions, AR is revolutionizing training by offering augmented reality training immersive, AI-assisted learning experiences tailored to individual skill levels. Workers learn by doing, receiving real-time, interactive guidance that accelerates skill acquisition and improves long-term retention.
Lockheed Martin has implemented AR-driven training programs, which have reduced the time required for workers to master complex assembly tasks. AI-integrated AR training systems can even predict potential human errors before they occur, offering instant corrective feedback and creating a more proactive, skilled workforce.
The Impact of AR on Manufacturing
The adoption of AR in smart manufacturing has not just improved the quality of output but has transformed the entire industry. By enabling real-time decision-making, predictive maintenance, and adaptive learning, AR is creating more agile, efficient, and error-free production environments. Workers are experiencing faster task completion rates, fewer errors, and enhanced safety measures, while companies are seeing increased ROI, reduced downtime, and higher production yields.
According to a PwC report, companies implementing AR in industrial settings have achieved a 32% improvement in productivity and a 25% reduction in errors. These advancements are not just making production lines smarter but also reshaping the role of human workers, empowering them with real-time insights and hands-free operational guidance.
Conclusion:
With AI-powered Augmented Reality on factory floors, the manufacturing industry has evolved in every way possible. AI is not just assisting AR—it’s amplifying its impact. Machine efficiency has soared, processes have become more seamless, and workers are now equipped with real-time insights that make their jobs more engaging and rewarding. Error rates have dropped drastically, and safety concerns are becoming a thing of the past, thanks to AI-driven predictive alerts and color-coded warnings that flag potential issues before they escalate.
But the real game-changer? Precision and quality. AI’s ability to analyze and adapt in real time has led to higher product quality, reduced downtime, and smarter workflows. The result – factories that are not just automated, but intelligently optimized.
At Mantra Labs, we build AI-driven solutions that help businesses scale sustainably, reduce inefficiencies, and streamline operations. From minimizing downtime to optimizing supply chains, we make manufacturing smarter and more resilient.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox