The outbreak of pandemic COVID-19 put the healthcare sector into a tizzy. From dealing with a rising number of patients and lack of medical supplies and infrastructure to falling in-patient and out-patient footfalls and elective surgeries; it was indeed a difficult period. The latter affected the business of private healthcare due to their inability to sustain cash flow and fixed costs. However, the healthcare system did come around and in response to the COVID-19, new care packages were introduced which included services such as Medical Kits, App to Check Vitals, Home Delivery of Medicines, Remote Doctor Consultations, Remote Nurse Consultations, Helpline for Query Resolution, etc. to give a meaningful digital health experience.
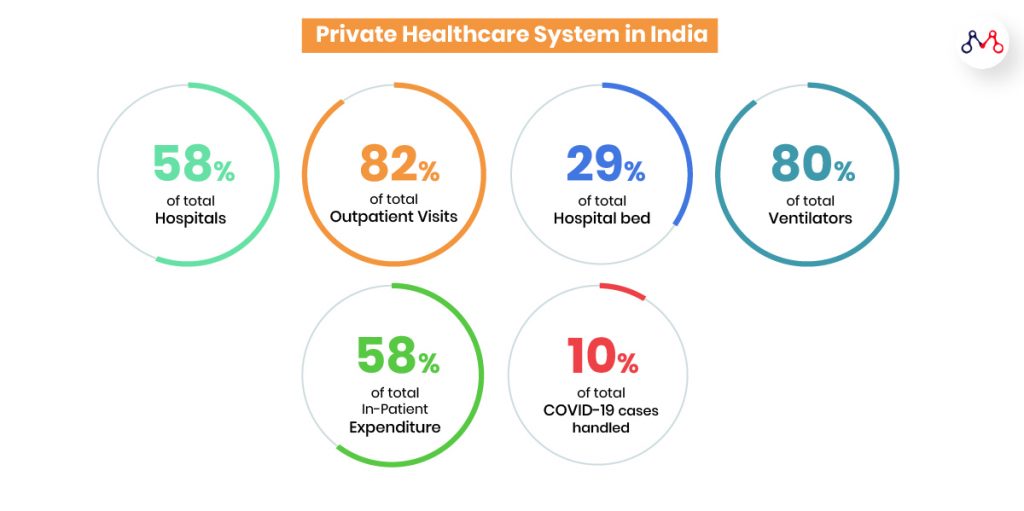
Post-COVID: Future of Indian Digital Healthcare
The pandemic has been around for quite some time now and we’re halfway through the New Normal. In India, the consumer-led healthcare ecosystem is changing to consumer-led digital health. At-home/doorstep delivery is reducing the number of physical touchpoints. The rapid growth of telemedicine and preventive healthcare apps are some of the driving forces for the Indian Healthtech market which is expected to grow up to $21bn by 2025 (which is only 3.3% of the total addressable healthcare market of $638 Bn by 2025). One of the untapped opportunities that the healthcare ecosystem could look into is providing out-patient insurance for day-to-day doctor visits or health needs.
Key takeaways from the webinar
Here are some takeaways from a very insightful and interactive webinar on Digital Health-
Evolving digital health behavior
During Pandemic: 35% of Consumers are impacted at their jobs, 25% are still saving & stockpiling essentials, 38% are in a ‘hibernating & spending’ state, while the remaining 2% are least affected and will continue their old spending behaviors. Here’s a brief overview of changing patient behavior and benefits of patient-generated data-
Patterns of Consumption and Health-seeking Behaviour
People have certainly become more health-conscious since the outbreak of the pandemic. A major shift in consumer behavior is that now they are data-oriented. Tracking health conditions and using medical records to make decisions via mobile apps is trending. Consumers want ownership of their health data. Amongst at-home consumers (in the last three months)
- at least 1 in 3 have used a fitness app
- at least 1 in 4 have used a telehealth service
- at least 1 in 5 have consulted with a virtual doctor
Doctors’ digital behavior is evolving too
In India, doctors’ are now finding clinical information and engaging with medical reps digitally. Each general physician on their platform now consults around 100 patients. Doctors too are leaning towards digital health platforms to increase engagement with new prescription influencers and auxiliary stakeholders such as pharmacists (formularies) and insurers. Telehealth apps and e-pharmacies will see a boom in the upcoming months as both patients and doctors are getting accustomed to virtual health trends.
Rise of mHealth Apps
mHealth market in India is expected to touch $2.4B by 2024. mHealth apps are more popular in preventive healthcare space. There are 400,000 mobile health apps in India, for self-monitoring a variety of health data — heart rate, bp, sleep pattern, blood glucose level, etc. Some of the top use-cases of mhealth apps are in the fitness and nutrition areas. Now there’s increased adoption of apps in mental health, e-prescriptions, and diagnostics as more consumers demand door-step services.
Real World Use Cases for Pre and Post-Op Care
Even though the economy has slowly started to open up, the COVID scare has not yet gone. People are still being cautious about stepping out of their homes. We have seen the maximum usage of mobile apps and door-step services during this period. Demand for home care services driven over mobile applications is on the rise. This has opened up so many opportunities in the digital health space to making healthcare accessible from anywhere for both patients and doctors.
Let’s take a look some of the use cases in Digital Health-
Using AI for Doctor Consultations
Many doctors face challenges in managing high patient volume. Digital self-care tools such as an AI doctor can assist here by coming up with a basic diagnosis and treatment plan. These results are then validated by an actual doctor.
E.g. around 20% of consultations on 1mg is done by an AI doctor.
Know how Mantra Labs helped PAHOMIQ build and train AI models to enhance their Image processing techniques to allow earlier detection of abnormalities and treatment monitoring.
Digital Mental Health Therapy Chatbots
Mental Health and Emotional Wellness were not considered serious health conditions. But in the light of recent events, with depression and suicide rates going up, detecting mental health conditions early-on has become very important. An AI conversational chat tool can help users by monitoring their moods coupled with self-care exercises for dealing with mental health issues. Furthermore, AI can help give people preliminary diagnoses that open ups treatment options, freeing up resources for mental health providers. AI can even triage patients based on the data it collects from patients which will enable doctors to come up with treatment plans.
Ex: Wysa — App supports and encourages users to achieve defined mental health goals.
ORCHA, the World’s leading health app evaluation, and advisor organization awarded Wysa an overall rating of 93%, including 100% on clinical safety. Wysa has also rated the best app for COVID-19 stress and anxiety.
Digital Lab
Managing digital pathology workflows is a challenge for both patients and doctors as it requires a lot of coordination and is time-consuming. A mobile app with features of a digital lab such as case-based tracking, schedule appointments, extract diagnostic data from pathology reports, receive alerts, prescription, billing & inventory management will help both patients and doctors save time and effort.
Know more about how Mantra Labs built Manipal’s Digital 360° Patient Management app which included features such as scheduling appointments and uploading medical records. Thus, improving the quality of care and patient satisfaction.
Mobile Phlebotomist App
Tier 2 and Tier 3 markets have limited access to healthcare services. One way to make medicine and testing more accessible to people in these markets is by mHealth apps. The appointment booking feature can help a phlebotomist to manage online patients bookings. The phlebotomists will collect blood samples following a specific protocol and use bar-coded stickers with patient identification information that they stick to collection vials. This enables the field team to manage home sample collection requests, view daily collection schedules and drop-off points, with geo-location services.
Mantra Labs Five-Factor Model for Digital Health Mobile App Transformation
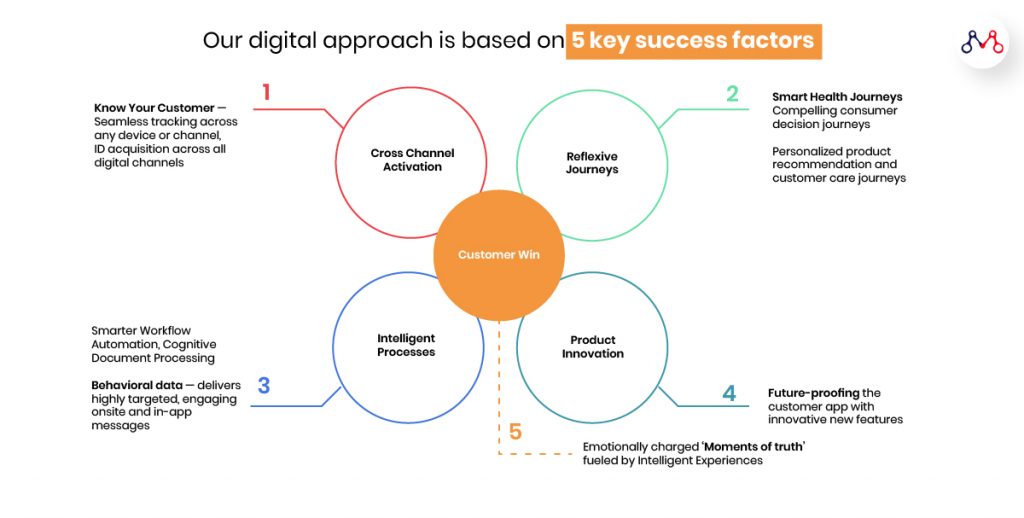
Building Truly Engaging Apps
There are many healthcare apps in play today running from fitness and nutrition trackers to hospital apps. But, how many truly keep the user engaged?
Personalization
A one-size-fits-all approach will not engage with the majority of the population due to diverse personas. With features like providing timely & relevant advice will make users feel privileged keeping them engaged.
Digital Nudges
One of the reasons why Health and Wellness apps are more popular is because they help users to self-monitor their progress. Apps with gentle reminders or notifications act as triggers to get desired results.
Empathy by design
A deep study into the user behavior through surveys/secondary research can help get qualitative data which is crucial to incorporate into the app. If the app matches the user needs, then they are more likely to stay on it.
Frictionless Touchpoints
Lengthy workflows, frequent pop-ups, and advertisements can create a distraction for a user while on the app. An app should not interfere with a user’s daily routine or disrupt their behavior.
Gamification
The gamified approach grabs a user’s attention and keeps him interested in the app. A plain layout will wear out a user soon. Gameplay focuses on the user’s attention better.
E.g. Using reward badges for completing virtual exercises, with an added caveat like, “This badge will expire in 6 days. Keep exercising to earn more badges.”
In a nutshell
As we move towards more digitization of the healthcare sector, it is important to determine specific KPIs for mobile apps and digital platforms. Good KPIs will inform the need to change before a material loss occurs. Digital transformation is a multi-year effort, and the return on investment is not always immediate. Data is going to be the key. Turning data into actionable information through advanced analytics will help in a long-term improvement strategy. Ultimately, setting the right business outcomes and working backward to solve the problem areas through technology will help achieve those goals.
Know more about our work in Digital Health and how we have helped clients such as Suraksha Diagnostics, Abbvie, Religare Health Insurance, and SBI Health Insurance build mobile and web applications improving their operational efficiency and customer experience.
Check out the webinar on our YouTube channel.
Further Readings:
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox






