‘Insuring’ has always been a mundane and complicated subject for businesses. Distribution channels allow customers to access and purchase products efficiently. According to JM Financial, online insurance sales for new business are fast catching up and are likely to grow at a CAGR of 13 percent to become a $37 billion break by 2025.
Each distribution channel requires different resources to be effective and impact the pricing structure. The type of insurance business model determines its structure, strategy and placement in the market.
Take, for instance, India. The market size of the online insurance business in India is currently $15 billion, but the overall insurance penetration rate is just 3.7% (Statista, 2018).
The regions where insurance penetration is low poses an immense potential for the digital premium market. Insurers can leverage the following distribution channels to undermine the profound potential.
1. Self-directed or Direct Distribution Channel
Through Self-directed or direct distribution channels, insurers can reach out to the customers without shelling out commission for any middle man. With an increase in the population of tech-savvy customers, the ready availability or online channel of advice or transaction capabilities is the need of the hour.
Online channels, websites, social media platforms, e-commerce and kiosks are some examples of the direct distribution channels in insurance. The 2017 Global Distribution and Marketing Consumer Study reveals that nearly 51% of digitally active groups of consumers (39% of all Insurance consumers) have purchased insurance through an online channel. The direct insurance distribution channel encourages self-service and independent decision making.
NLP-powered chatbots are a great way to provide a self-service portal for buying/renewing insurance policies. Leading Insurers like Religare are leveraging the direct distribution channel by integrating chatbots in different platforms like their website, mobile app, and even on third-party apps like WhatsApp.
2. Assisted Distribution
Agents and brokers are typically the key players in the insurance distribution channel, with market shares of 42% and 25% respectively. The old school face-to-face distribution channel is very much alive and is integrated with tech assisted models to ensure more leads and conversions. They mainly play a part in advising and managing complex insurance products.
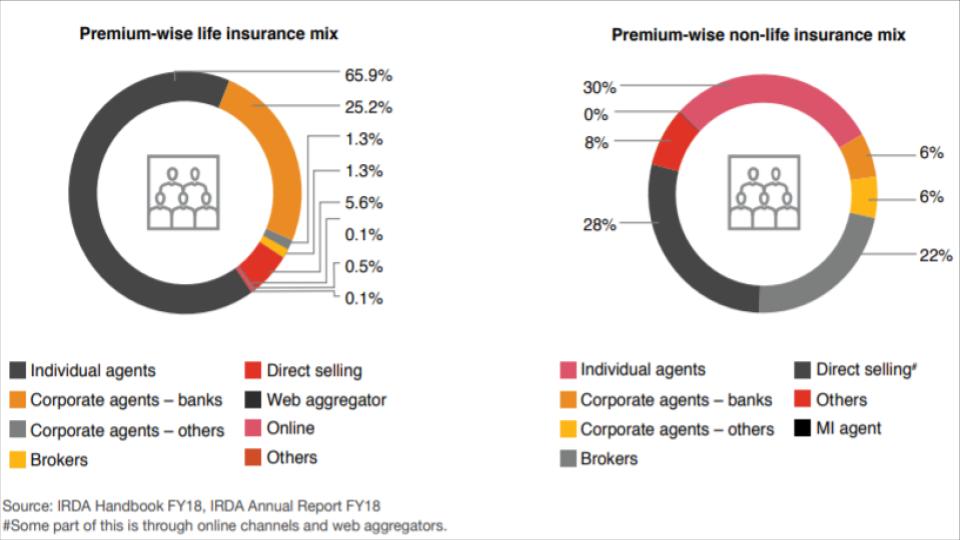
Agents, insurance brokers and reinsurance brokers remain the most recognized insurance purchase channel. The Gartner Group reports that 60% of the US GDP is sold through assisted or indirect channels. Cognitive technology is becoming a key enabler to strengthen the assisted distribution channel. PwC suggests leveraging analytics solutions (mainly predictive analytics and behavioral analytics) to increase sellers’ knowledge as well as skills.
[Related: How behavioral psychology is fixing modern insurance claims]
The technologies that are empowering learning for Insurers include augmented reality, machine learning, data analysis and NLP.
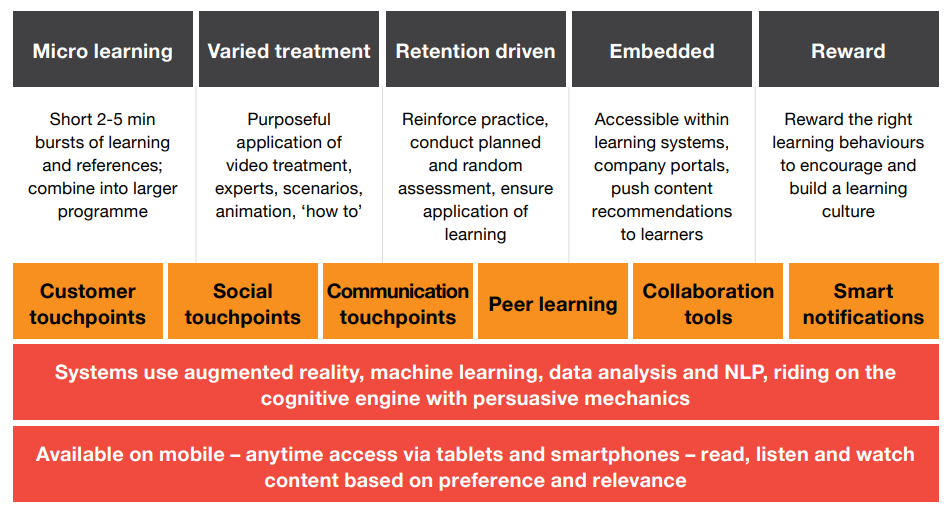
For example, Zelros, a European AI startup, is augmenting the knowledge of sales and customer representatives through best product recommendations, advisory, and pricing based on the customer profile in real-time.
3. Affinity-based Insurance Distribution Channels
The affinity channel focuses on distributing products to a tightly-connected group of consumers with similar interests. Traditionally, the affinity-based distribution channel involved peer-to-peer networks, brokers and aggregators. While the network model remains the same, the model has become digital and tech-driven for affinity channels. And technology is playing a vital role in expanding the consumer base. The key benefits of the affinity distribution channel are-
- Common platform for all stakeholders.
- One-stop access to policies and claims.
- Centralized database for insightful analysis.
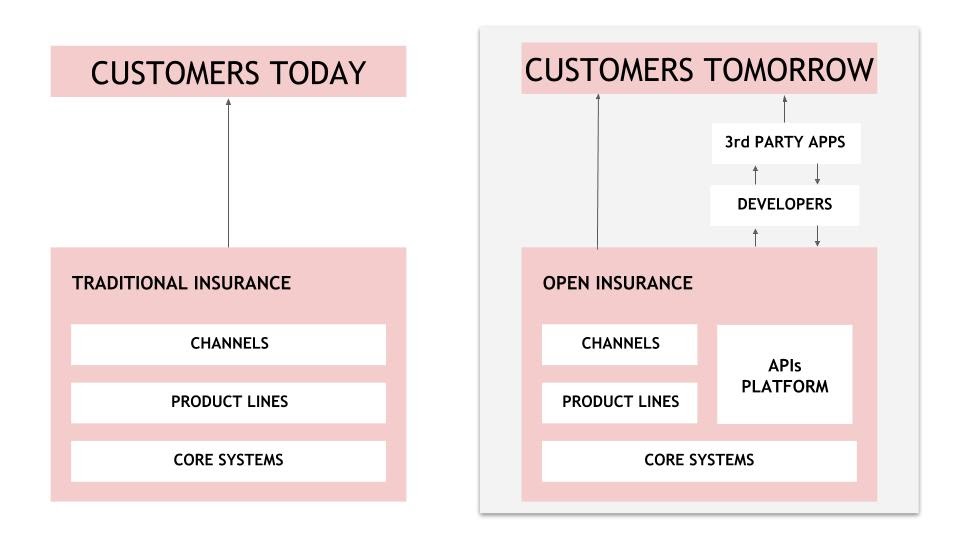
This distribution channel is also a part of B2B2C or API-based insurance business models. Here, Insurers can leverage 3rd party apps to distribute their policies. APIs or Application Programming Interfaces are lightweight programs to extend the functionality of existing apps. Travel, airbus, hotel, bank and retail are some examples of affinity-based distribution channels.
Finaccord estimates that airline companies hold a distribution share of up to 10% of the travel insurance market. The annual revenue from airline and travel insurance providers partnership may range from $1.2 billion to 1.5 billion in premiums.
[Related: 4 New Consumer-centric Business Models in Insurance, How InsurTech-Insurance Partnership Delivers New Product Innovations]
The majority of travel insurance policy sales across the globe are done through some kind of affinity partner instead of via a direct sales channel.
Jeff Rutledge, President & CEO, AIG Travel
Source: Insurance Business UK
The Bottom Line
In the countries where buying an Insurance is not mandatory, market penetration is extremely low for Insurers. Being meticulous in sales and marketing efforts and educating customers about the benefits of insurance is just not sufficient. Convenience is the key to new generation consumers. Therefore, insurers need to invest in technology and make insurance policies accessible to the new-age digital consumers through the channel of their choice.
Michael D. Hutt and Thomas W. Speh, in their book – Business Marketing Management: B2B, suggest a six-step process to select among the most efficient insurance distribution channels-
- Determine the target customers.
- Identify and prioritize customer channel requirements by segment.
- Access the business’s capabilities to meet those customer requirements.
- Use the channel offering as a yardstick against those offered by competitors.
- Create a channel solution for customers’ needs.
- Evaluate and select the most effective among the distribution channels.
We’ve developed insurance chatbots for organizations like Religare to automate policy distribution and renewal. For your business-specific requirement, please feel free to reach us at hello@mantralabsglobal.com.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




