The years 2018-19 are the banner years for the US$ 5.17 trillion global insurance sector. However double-booking, counterfeiting, and premium diversions through unlicensed brokers still throb insurance companies. And one of the prime reasons for such unethical activities is the lack of tight coupling between stakeholders. A simple solution to these challenges is distributed ledgers- a contemporary technology that ensures transparency. Distributed ledger technology in insurance can create a collaborative environment for handling information, minimizing instances of fraudulent activities.
How Can Distributed Ledgers Accelerate Insurance Workflows?
Where most insurtech startups and small insurers are looking for “insurance-in-a-box” technology, big players demand bespoke technology to develop distinct capabilities for customer convenience and manage their enterprise workflows. Fortunately, distributed ledger technology solves a major chunk of this problem.
For startups and small to medium size insurtech firms, cloud-based, customizable workflow management products can simplify the processes and create a collaborative work environment. Large enterprises can, of course, afford time and investment for tailor-made technologies suitable for their overall business requirements.
#Smart Contracts
Smart contracts can automatically determine whether to transfer an asset to the nominee or back to the source, or a combination of both. It does not necessarily create a contract or legal act, but can sure validate a condition. For example, Ethereum provides a prominent smart contract framework.
Smart contracts allow credible transactions with or without involving third parties (oracles).
For example, Etherisc uses smart contracts concepts for building insurance products. The fundamentals used for Etherisc’s insuring flight delays product is applicable for insurance products like crop insurance, flood, earthquake, etc.
#Claims Management
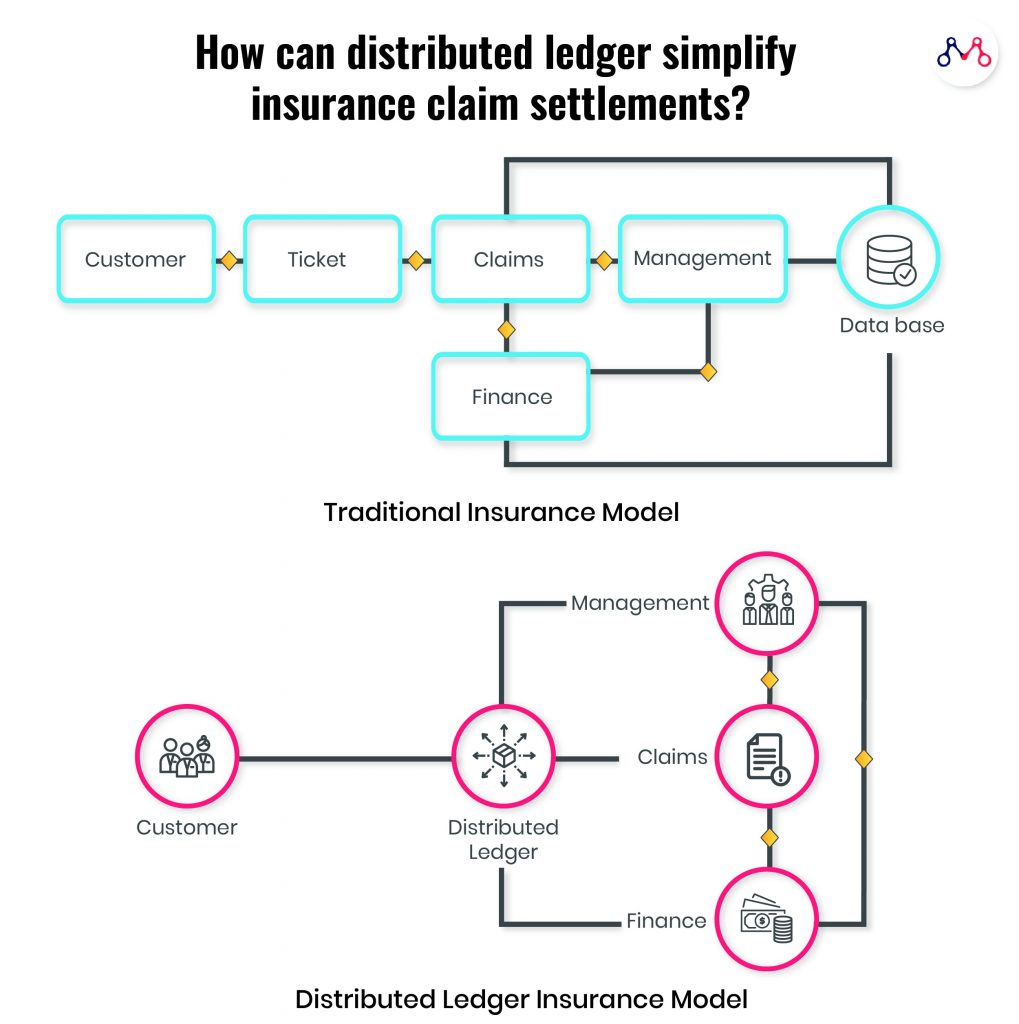
Cifas reports a 27% rise in false insurance claims across the UK in the past year. Moreover, insurers identify 1 in every 30 claims as fraudulent. Organizations can track records better with distributed ledgers minimizing the illicit instances.
Blockchain technology allows for automated real-time data collection and analysis. BCG expects Property and Casualty (P&C) insurance has the potential of processing claims up to 3x faster and 5x cheaper than traditional processes.
It can also enhance customer experience by removing indirections due to various touchpoints between him and the claim settlement manager. Distributed ledgers can overall benefit processing time, automating payments, eliminating trust issues, and fraud reduction.
#Reinsurance
Reinsurance (passing a whole or part of insurance liabilities to another company) will simplify the sharing of data like bordereau and claims databases. For the insurance companies not preferring to share their client’s data, access rights can be customized in distributed ledgers.
According to PWC research, the reinsurance industry can save up to $10B by increasing operational efficiencies through distributed ledgers.
#Underwriting
“A shared, distributed ledger lends itself to this need for exchanging transparent, trustworthy data in a standard format in real-time.”
Stefan Schrijnen: Director, Insurance, EY
Having accurate real-world data can help underwriters reduce paperwork and measure the assets and risks effectively.
Insurwave, a blockchain-enabled insurance platform uses a distributed database with secure access for insuring shipments across the world. Maersk, the world’s leading shipping and logistics company have partnered with Insurwave for insurance renewal of its fleet of 800 container ships.
In the words of Lars Henneberg, Head of Risk Management at A.P. Moller – Maersk. “A simple dashboard gives us a live overview of how our assets are insured, and our brokers and insurers have access to the same overview. If the location, cargo, or other data about our ships changes, everyone is notified — no delays, no paperwork, no mistakes.”
#Product Design using Distributed Ledger Technology in Insurance
Instead of all-encompassing insurance policies, consumers look for short, custom-built policies that satisfy their immediate needs. Therefore, to stay competitive, insurance companies (and even e-commerce startups) need to consistently build new and relevant insurance products. Expanding features or building new products on the same fundamentals can be effectively realized with strong and transparent ledgers.
AXA’s smart contract product Fizzy is a next-generation Parametric Insurer, which uses transparency as its USP. It provides travel insurance on flight delays and cancellations. The claims displayed on the website are stored in a blockchain and no one can change the terms after purchase. User can buy the insurance online. When the flight is delayed or canceled, the public databases of plane status information automatically triggers the insurance holder’s compensation. The event confirmation executes and closes the claim process instantly.
Precautions to Take With Distributed Ledgers in Insurance
- Enterprises should be cautious about sharing access rights on distributed ledgers.
- Blockchain transactions are irreversible, therefore every click from an authorized user should be mindful.
- Instead of mimicking a trend, insurance companies can deploy the distributed ledger technology to best suit their business requirements.
Conclusion
MarketsandMarkets expects blockchain technology’s share in the insurance market to reach $1.4 billion by 2023.
The insurance industry has already deployed distributed ledger components for insuring flight delays, lost baggage claims, and is expanding to shipping, health, and consumer durables domains.
The future can also witness blockchain, AI, drones, and robotics disrupting the insurance industry together.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




