Many products were at some point rumored to have a possible connection with WWDC 2016, including the next-generation Apple Watch, MacBook Pro, and Thunderbolt Display. Those that have been following rumors consistently, however, will know that the most of the products were actually in the second half of wwdc 2016. The day 4 didn’t have much for store, so they were beating around the announcements of first day. Mac, Home Kit and Apple Watches continued to be the main attraction of the day 4.
The highlights of day 4 were:
Macs
Prospective buyers were hopeful that Apple would surprise with a new MacBook Pro at WWDC 2016, despite the keynote being billed as a no-hardware affair, but the comapny delivered upon expectations and focused on software announcements only. So, when will the 2016 MacBook Pro be released?
Launched in the second half of 2016. KGI Securities analyst Ming-Chi Kuo said Apple will launch three new MacBook models by year’s end: a thin and light 13-inch MacBook in the June-September quarter, and two thinner and lighter 13-inch and 15-inch MacBook Pro models in the September-December quarter.
Kuo said the 2016 MacBook Pro will feature a thinner and lighter form factor, Touch ID, and a new OLED touch bar positioned above the keyboard. Leaked photos of what appears to be the notebook’s unibody revealed space for the OLED touch panel and four USB-C ports. The new MacBook Pro is also expected to adopt metal injection mold-made hinges, which are reportedly already shipping.
The new MacBook Pro lineup is also expected to feature faster Intel Skylake processors, USB-C ports with Thunderbolt 3, and possibly AMD’s new 400-series Polaris graphics chips for the top-of-the-line model by the year fall. 
Apple Watch
watchOS 3, which will be available for all Apple Watches in the fall, launches apps and lets you navigate between them more quickly, offers streamlined iOS-like control of settings and quicker watch-face changes, and makes sending and receiving messages easier. In other words, watchOS 3 makes the Apple Watch deliver more on its original promise of at-a-glance utility.
The most obvious improvement is that your frequently used apps—both Apple’s own and third-party—can update themselves in the background, launch with hardly any delay, and show updated information right away. Launch delay is probably the most common complaint about the Apple Watch, and the improvements (at least as shown in Apple’s demonstration) are significant. Switching between watch faces is now a left-to-right swipe instead of a force-touch and scroll, so you can quickly switch between, say, a health-focused Activity ring face and more traditional dials. Apple has added gestural text entry, so you can more easily send or respond to messages from the Watch face. A new Dock of recently used apps replaces the dial-a-friend spinner in the current watchOS, and a swipe-from-the-bottom Control Center (along the lines of the one in iOS) looks to be much more useful—and more usable—than finding the Settings app. Fitness tracking has become more inclusive with the addition of profiles that, among other things, recognize wheelchair users (one of many straightforward usability improvements that caught our eye).
Also announced was a new SOS feature that lets you call 911 (or corresponding international emergency services) with a press of the Watch’s side button, so long as you’re connected to LTE or Wi-Fi via a mobile device. The SOS function sends your location and shares basic medical information you’ve chosen to store on your phone. It isn’t a flashy innovation, but it is a smart use of the technology at hand.
HomeKit
HomeKit, Apple’s system for integrating smart-home devices without the use of a hub, receives an important upgrade in iOS 10 in the form of an official app called Home. Prior to the Home app, users of HomeKit-compatible devices could integrate their products’ features in third-party apps, with different levels of success and support. Now, with an Apple-designed app, you should experience better and more-uniform support of device features. The Home app allows you to access all your HomeKit devices, including smart door locks, doorbell cameras, smart plugs, light switches, and more (Apple claims nearly 100 different products), from one place, rather than opening all the individual apps for those devices.In addition to device control, you’ll be able to create and access scenes, such as “Good Morning” or “Good Night,” from within the app. You can trigger the scenes either by tapping the scene button in the app or by using your voice via Siri. For example, a “Good Morning” scene can turn on your lights, adjust your thermostat, and start your coffee. A “Good Night” scene could turn off all your home’s lights and lock the front door. Apple has made it easier to get to your smart-home devices by adding Home to the phone’s Control Center. The Home app also puts your device notifications, including video from security cameras, in the Notifications Center from the lock screen.
Though HomeKit is technically hubless, if you have an Apple TV, you can use it as a gateway for remote access to your HomeKit devices when you’re away from home.
The Home app will be available on both the iPhone and iPad, and it will also be supported by the Apple Watch (which reps described as being able to function as a whole-home remote).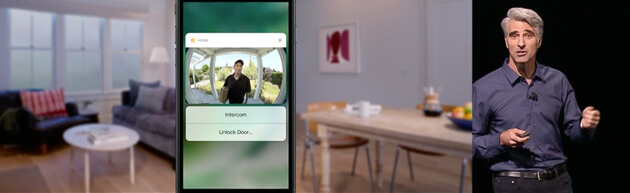
Day 4 was going slow in the beginning but these announcements made it exciting. The 5th day expectations are high as it is closing day of WWDC 2016. For updates of 5th day stay with Mantra Labs.
If any queries approach us on hello@mantralabsglobal.com
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox





