Apple’s WWDC this year was full of incremental updates to OS’s for the Mac, iPhone, Watch, and TV, as well as moves to open up services like Siri and iMessage to developers. A lot of the changes were geared toward moving between Apple devices easier — Siri is now on desktop, and Apple Pay will now work on Safari, for example. There were also a bunch of redesigns: new notifications and lock screen interactions for iOS; a new command center for the (faster) Apple Watch; and changes to Apple News, Music, Maps, and other services.
[section_tc][column_tc span=’12’][youtube_tc id=’https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tOUlvdLOI2A’][/youtube_tc][/column_tc][/section_tc]
We’re updating all day, so come back for additional news later.
MacOS has a new name, more continuity across devices, and Siri
OS X is now macOS, and this iteration will be called Sierra. The public beta will launch in July with the final version coming in the fall. One of the big focuses of the new OS is continuity across devices. Craig Federighi demonstrated a feature called Universal Clipboard, which allows users to copy and paste across multiple Apple devices. You can also save your Mac desktop to the cloud and access it from a different computer using iCloud drive. There are other smaller updates as well, including a storage-saving measure that moves old files to the cloud and a way to unlock your Mac using your Apple Watch.
Sierra will also bring Siri to the desktop. Siri will be accessible in the dock as well as in the top-right corner near Spotlight. You’ll be able to use voice commands to find files, search the web, send messages, and other standard Siri functions.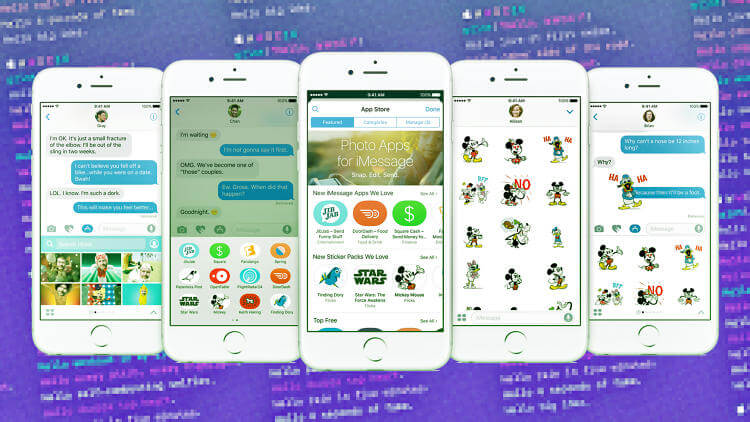
Apple pay is coming to the web
You’ll be able to use Apple Pay to make payments online through Safari. Authentication will work through TouchID, either through your phone or Apple Watch, eliminating the need to type credit card details. Apple Pay is available in the US, UK, Canada, Australia, and Singapore, and will be rolling out to Switzerland, France, and Hong Kong.
The apple watch gets faster and ADDS new features
watchOS 3 brings a host of updates, but perhaps most importantly, it loads apps seven times faster than the previous OS, thanks to background refreshing and keeping apps stored in memory. Navigation supposedly will be easier on the new OS, too. The side button can be used to access a “dock,” which allows wearers to scroll through their apps, and the Watch will act a little more like an iPhone with a new Control Center. A swipe up on the Watch allows wearers to quickly switch into airplane mode or Do Not Disturb, just like the iPhone.
Other new features include a keyboard called “Scribble” that wearers can use to respond to a message. Instead of typing or dictating a response, they can draw out each individual letter. It works in either English or Chinese. Apple Watches will also come with a new SOS feature, which activates when the side button is held down and calls 911 and sends location information to first responder and emergency contacts. It’ll also share users’ medical ID, which displays their allergies, age, and existing medical conditions. The feature works internationally and will call country-specific emergency numbers, so long as the watch is tethered to a phone or is connected to Wi-Fi.
Apple emphasized fitness with the introduction of new activity-specific watch faces, a meditation app called “Breathe,” and activity sharing to view friends’ fitness levels.
ios gets a slew of updates
Craig Federighi called the iOS changes “the biggest iOS release ever for our users,” including complete redesigns for Music and Maps, new notifications, and an expanded role for 3D Touch. A new feature called “raise and wake” will wake the lock screen when you lift your phone, revealing redesigned notifications that you can interact with using 3D touch.
Apple news gets a redesign and supports subscriptions
Apple News now features over 2,000 publications and over 60 million monthly readers. Apple is rolling out an all-new design that features clear sections, including Top News, Trending, and Sports. The app pulls together new sections based on your reading habits, and includes a Featured Stories section with editor picks. Apple News now also features subscriptions, which means you can subscribe and read full newspapers and magazines from the app. It will also send breaking news notifications and deliver them to your lock screen.
Apple music gets a discover playlist and a complete redesign
After only a year of existence, Apple Music is getting a complete redesign. New sections make it easier to navigate, including one section for downloaded music and another for recently added songs and albums. Apple also appears to be coming directly for Spotify with its new “discovery mix” that tailors a playlist to listeners’ tastes. There will also be daily curated playlists and new sections to help users find new music curated by Apple’s music editors. You can also read song lyrics now.
Maps is redesigned with navigation in mind
Maps is getting a whole new feel. Its redesign will show more of a map when a user opens the app. Users can also book rides through Maps, pay for them with Apple Pay, and make restaurant reservations. Navigation is getting easier too, with directions that include traffic. Maps is also coming to CarPlay, which will show traffic and offer alternative routes, as well as precise navigation right from a car’s display.
Messages Get snazzier
Apple is revamping iMessage to include bigger emoji as well as suggestions for turning certain keywords into emoji. People can share songs directly from Apple Music and write notes to one another in their own handwriting. There are animated effects — like strobe lights, balloons, and confetti — and invisible ink hides messages until they’re swiped over. Invisible ink! Developers are also getting access to Messages and can develop apps like stickers. iMessage is turning into some kind of Snapchat-WhatsApp-Facebook Messenger conglomerate.
Photos takes on google photos
Photos is being updated with new features to help you organize and manage your collection. You can organize your collection automatically by person using facial recognition. The app is also adding Memories, which bundles together photos according to events and locations. You can also create a montage set to music automatically from Memories, much as you’re able to do in Google Photos.
Voicemail transcription comes to ios 10
iOS 10 will now feature voicemail transcription, which will automatically transcribe voicemails and offer them up like texts. In addition, iOS is taking on spam calls: the iOS will support APIs that can alert you to possible spam calls and warn you before you pick up. With VoIP, you’ll be able to see caller ID right on the lock screen.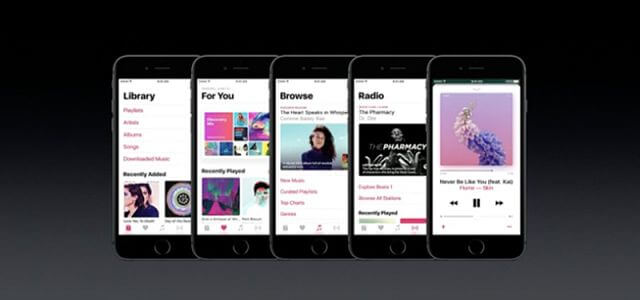
tvos is all grown-up
tvOS is less than a year old but now hosts 1,300 video channels and over 6,000 apps. That library is going to be expanding shortly: Dish’s Sling is coming to tvOS today; Fox Sports Go is coming later this summer; and Molotov, a French TV service, is coming next month. Apple is rolling out a new Apple TV remote app, which will have all the functionality of the… Apple TV remote. You’ll be able to use touch for navigation, Siri for voice command, and the phone’s built-in sensors for gaming control. Plus, you’ll have your trusty keyboard. Siri will now be able to search through the service’s 650,000 movies and shows, as well as live channels by name or category (“German high school comedy from 1962, please”). You’ll also now be able to use Siri to search in YouTube.
Apple’s also introducing a single sign-on system that lets your log into all of the network apps at once. You’ll have a page that shows you all the channels you have access to. Download a channel app onto your phone, and it’ll automatically appear on your tvOS. Seamless integration, folks.
And Apple quickly introduced two kits for developers: ReplayKit, which lets you live broadcast gameplay or save it for later, and HomeKit, which will let you control all the devices in your house, including tvOS. tvOS will roll out in a free upgrade this fall.
Siri is opening up to app developers
Siri, which now services over 2 billion requests per day, is now opening up to developers. That means you’ll be able to ask Siri to send a message through WeChat, ask it to call an Uber, search for photos on Pinterest and start and stop your workout apps all with voice command.
Predictive type takeover
QuickType will bring Siri intelligence to the keyboard, using deep learning to enable more intelligent predictive typing using expanded context. That means Message can now help you with text responses, and offer up your location when someone is wondering where you are. Now that it’s open to developers you’ll be able to look up movies or restaurants straight from the keyboard. The QuickType keyboard will also now support multilingual typing. Apple also made a point of noting that, unlike Google, its AI analysis will stay on your device and won’t transmit your texts to the cloud.
What’s next
WWDC was packed with updates, many of which seem minor on their own, but taken together could make it easier navigate Apple’s ecosystem. With the Watch, incremental changes in speed and the command center could go a long way toward making it a more appealing device, and the new HomeKit hub could make connected appliances more attractive. It remains to be seen how well all these services work outside the Apple ecosystem, and whether opening up things like Apple Pay and Siri will be enough to surmount the lead of companies like Amazon, which has been aggressive about forming partnerships and developing frictionless ways to purchase. And of course, we’ll still be waiting for the Apple car.
If any queries approach us on hello@mantralabsglobal.com
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox