Technological advancements and innovations are disrupting the healthcare industry. Smart health monitoring systems, apps, wearables and handheld devices are already in use. The prevailing Covid-19 pandemic has created an urgency to adopt digital. Healthcare technologies will cover many more conditions than before. Dr. John Halamka, President, Mayo Clinic Platform expects more than 60% of healthcare services to go virtual.
This revolution in healthcare is not discretionary. This is the need of time. Currently, segregating meaningful data collected through various sources like medical records, wearables, apps, etc. is a challenge. But very soon, HealthTech will evolve across the globe. With Cloud, AI and advanced data analytics, patients and healthcare institutions will be able to access and utilize the right information in a fraction of seconds.
Let’s delve deeper into the new healthcare technologies that will disrupt patient care.
1. Telehealth
Telehealth corresponds to the accessibility of health services and information over the internet and telecommunication. Telehealth care allows remote or long-distance patient care through clinician contact, consultations, reminders, monitoring, and remote admissions. Simply put, telehealth care is the virtualization of most of the physical interactions between doctors and patients.
Today, HealthTech underpins telehealth, as it enables robotic surgeries through remote access, physical therapy via remote monitoring instruments, home monitoring and live feeds, and video telephony.
Recent advancements in AI and cloud-based technologies are enhancing remote healthcare experiences for patients. Solutions like chatbots, voice interfaces, and augmented reality are making digital experiences more intuitive for users.
2. Interoperability
To deliver informed and better care, healthcare organizations need to access patient health information over a distributed network. However, due to prevailing privacy regulations and lack of standardization in healthcare institutions, necessary information is still not available when required. That’s why interoperability has become a crucial aspect of HealthTech.
Interoperability is the ability to exchange, interpret, use, and annotate patients’ health information including medical reports, images (X-rays, CT Scans, Radiographs, etc.) and treatment information through secure communication channels.
Health data standardization is necessary to ensure interoperability. So far, many different standards development organizations (SDOs) create, update, and maintain health data standards. For example, the Interoperability Standards Advisory (ISA) is one of the institutions that define interoperability standards and implementation specifications for the industry to fulfill specific clinical health IT interoperability needs. DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is one of the methods of medical image sharing. Using the DICOM system, health management professionals, physicians, and radiologists access medical images in a secure distributed environment.
[Related: Medical Image Management: DICOM Images Sharing Process]
However, to create an ecosystem of connected healthcare services, information needs to be available on the cloud and in a uniform format. There are three levels of interoperability:
- Foundational: Here, one system can share information with the other. The receiving system cannot interpret the information but can acknowledge the receipt.
- Structural: Here, the receiving system can interpret and use the information but cannot modify it.
- Semantic: Here, both the sender and receiver can interpret, use, and annotate the information. Semantic interoperability is the most desirable system in today’s time.
Interoperability across healthcare service providers can also reduce the time and cost of lab tests. For instance, many health checkups are valid for about a year. In case of emergencies, instead of advising patients tests, medical professionals can access previous test information and start procedures — reducing the overall treatment time.
3. Biomedical Computing
Biomedical computing is the application of computer science in medicine. It involves medical data management, medical imaging systems, developing advanced user interfaces for medical professionals, remote monitoring systems, medical diagnosis, scientific visualizations, and other computer-aided medical solutions.
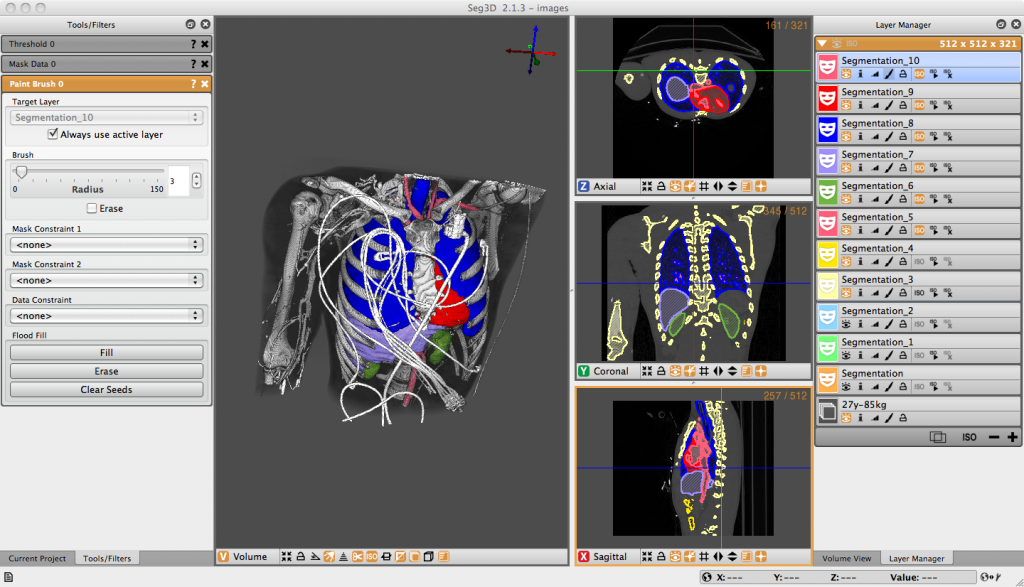
The advanced application of biomedical computing involves using machine learning models for cancer detection and grading, predictive biomarkers and accelerating drug discovery processes. For example, Seg3D, a volume segmentation & processing tool allows segmentation, contouring to plan complex surgeries.
4. Health Forecasting
The right information is important for delivering care, products, and services to people in need. Today, many devices generate health data — home assistants, fitness bands, health and sleep trackers, diabetes monitors, and other ailment specific apps. However, predicting a condition and preparing for it requires reliable data and appropriate analytical tools.
Extreme events test the efficiency of a healthcare system. Not all traditional techniques (e.g. analytics models that rely on historical data) can be applied to forecasting future conditions. The HealthTech systems call for probabilistic health forecasting methods to prepare institutions with information, finance, resources, drugs, equipment, and staff to serve any unforeseen event with the least possible lag.
The Future of Healthcare Technologies
Technologies like Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, AI, Machine Learning will play a crucial role in transforming patient experience as well as augmenting skills and education of future doctors. For example, Cleveland Clinic at Case Western Reserve University is already using AR to train human anatomy and surgery through 3D human models.
HealthTech in India will soon control patient care over traditional OPD services. Although critical medical surgeries will still require the dexterity of medical professionals, patient support and routine consultations will be accomplished through telehealth services. This will also make health services available in remote areas where setting up and managing a full-fledged hospital facility is not feasible.
To know about how healthcare industry is bringing hospitals to a customer’s doorstep, watch our webinar on Digital Health Beyond COVID-19.
Mantra Labs has been helping diagnostic and healthcare organizations like Manipal Hospitals, Suraksha Diagnostics in developing holistic patient management systems. We’ve also helped healthcare technology firms like PathomIQ in developing machine learning models for AI-based cancer detection segmentation and classification.
For your specific requirement, please feel free to write to us at hello@mantralabsglobal.com.
Common FAQs
HealthTech or Healthcare Technology is the application of knowledge and skills to solve a health problem and improve quality of life. It involves devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures and systems. WHO.
Telehealth is making healthcare services and information available to the public through the internet and telecommunications. It involves online or video consultations, remote monitoring, reminders to take medicine, remote mental health therapy, patient support, SOS alerts and more.
Interoperability corresponds to healthcare systems working together irrespective of geographical location. For example, medical images sharing via DICOM; guided permission to share patient data across clinics, labs, hospitals, and pharmacies.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




