The Google I/O 2016 is done for the year. We knew Google I/O 2016 would be hot, but this hot? The conference has been on fire since the keynote kicked off on Wednesday morning, and shows no signs of cooling down.
The Google I/O 2016 was mix of unexpected and expected announcements. There were a ton of cool announcements nestled inside of it that will hit market in soon future. The 8 major highlights of the Google’s I/O 2016 were:
Google Assistant, Google Home, Allo app, Duo apps, Android N, Google Daydream, Android Wear 2.0, Android Instant Apps, Firebase, Studio 2.2
From Android N, to the just-debuted Google Home, we’ve tried to put together the biggest moments from today’s keynotes:
Android N, Google Daydream, Android Wear 2.0, Google Home and the new Allo and Duo apps were the stars of the opening keynote, which were followed by other announcements which got atmosphere even hotter.
[section_tc][column_tc span=’12’][youtube_tc id=’https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S8exfLwoHKA’][/youtube_tc][/column_tc][/section_tc]
- Google Assistant:
The first major reveal of I/O 2016 was Google Assistant, a new personal AI for users. It lets users ask queries as much as they would do in the search engine, but in a Siri-like set-up. Google Assistant is the natural extension of search, supporting “conversational understanding” to make search more natural and to better support voice searches.
You can ask for Pablo Picasso’s first name, sports scores and to play a song you’ve had stuck in your head for all day.
- Google Home:
Just where Google Assistant ended, it was taken by Google Home, of course.
Pichai gave a shout out to Amazon Echo in announcing the new device, which is a white-and-gray Wi-Fi speaker that helps you handle everyday tasks. It plays music and lets you control smart home devices, including Nest products.
The Google Home speaker will be released later this year, and it will service as a portal into the Google Assistant experience. It will also let you control connected devices within the home, and you’ll be able to cast content with the speaker as well. Say “play Fast and Furious on my TV” and the movie will appear on your screen.
The entire experience is hands-free, powered entirely by voice. In fact, it doesn’t even have any buttons. Simple voice commands will control every aspect of the Home, as is the case with the Amazon Echo. Home even integrates with third-party services, allowing you to do things like call an Uber car or book a restaurant reservation using OpenTable.
You can, of course, ask Google Home anything you want to know, like you do in Google search.
Search is built in, drawing on 17 years of innovation to “answers questions that are difficult for other assistants to handle.”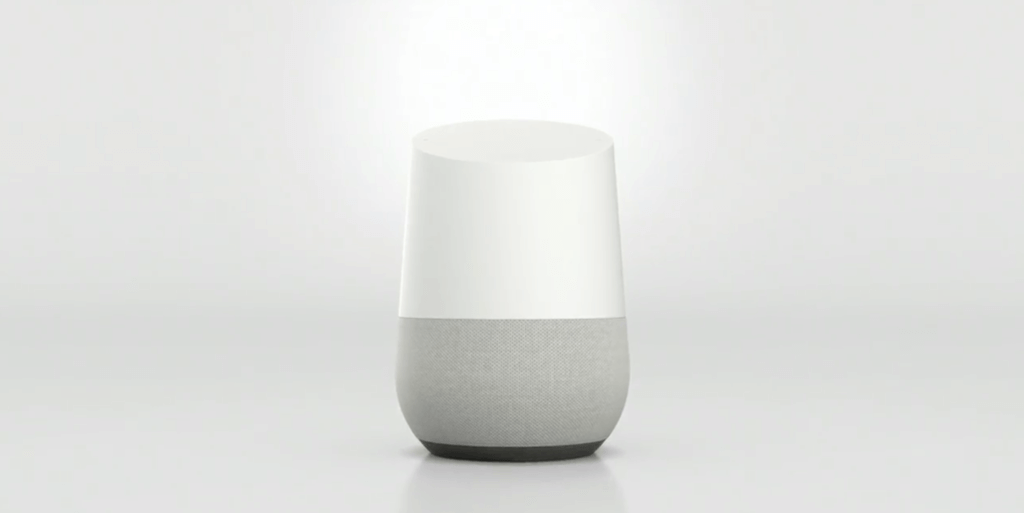
- Google Allo:
Meet Google’s new messaging app, Allo.
Google has fallen way behind top rivals like Facebook in the messaging space. Allo is the company’s new offering that includes a number of features Google hopes will help set its new app apart.
For example, the app has a whisper/shout feature that changes the size of the text you send using a slider to help communicate volume. Want to “yell” something? This feature lets you enlarge the text instead of using caps. Feel like “whispering” instead? Shrink text down with the same slider.
Another cool feature is smart replies, which create canned responses that evolve over time based on your conversations. Smart replies are even generated in response to photos thanks to Google’s photo analysis capabilities.
Also included, of course, is bot support. From right within the app, users can interact with a wide range of bots. For example, an OpenTable bot will allow users to choose a restaurant and book a reservation without ever leaving an Allo chat. And of course, there’s also a Google Assistant search bot. Want to search for a cute cat GIF from within a chat? No problem.
Lastly, Allo includes an incognito mode. All Allo chats are encrypted but incognito mode offers end-to-end encryption and an option to send messages that self-destruct. Additionally, once you close a chat, the entire conversation is deleted forever.
The app launches this summer on Android and iOS.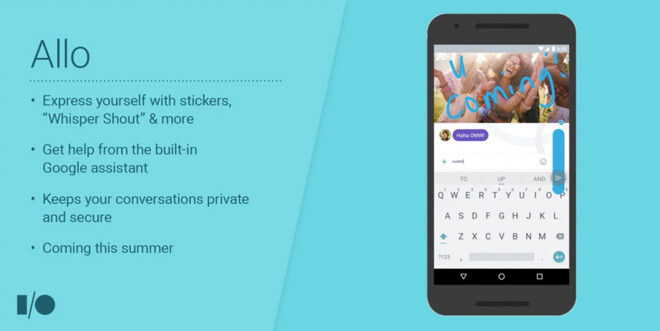
- Duo App:
Then came the announcement of Duo, a simple one-to-one video calling app for everyone.
Duo is the video companion to Allo, and includes a feature called Knock-Knock that lets you see a stream of whomever is calling you before you answer. That way, Google says, you can see who’s calling you and what they’re doing before you start a conversation.
Duo also switches seamlessly between cellular and Wi-Fi connections, and it manages video and audio in real-time to adjust quality on the fly when available bandwidth increases or decreases.
Duo will be available later this summer for iOS and Android.
- Android N:
Google’s next major mobile software release is Android N, and it’s going to be a huge update when it’s released later this year.
Still not decided on the name, calling it Android N, the new Android OS has improved graphics, reduced battery consumption and storage and security enhancements.
It is more secure than before with media framework hardening, file based encryption and seamless updates. Users can now quick switch to the previous app by double tapping the recent button in Android N. Multi-window mode comes to Android N, too. Split screen along with picture in picture modes are available.
Vulcan is the software that powers these improvements on the graphics side, while a series of software optimizations boost performance elsewhere.
Most impressively perhaps, Android N will download and install system updates automatically.
Moving on to the app switcher screen, Android will automatically remove apps from the UI when it determines the app is no longer needed. This way, the app switcher UI is decluttered and it’s easier to find the app you’re looking for. There’s also a new quick switch function accessed by double-tapping the recent button on a phone or tablet.
N’s window management framework has also been redesigned to support both split-screen apps (side by side) and picture in picture (a small windows in the corner of the screen). The former will work across phones and tablets while the latter is for Android TV only.
Where notifications are concerned, Android N has a new direct reply feature that lets users reply to messages right from the notification. Unicode 9 emoji will also be supported in Android N, complete with support for all skin tones.
Android N will be released to the public later this summer, but a beta has already been pushed out. Check out more details on our Blog “Android N- Developers Review”.
- Google DayDream:
Google then announced Daydream, a new VR platform built on Android N that will arrive this autumn. Similar to the home view you find inside of Oculus Rift, Daydream is an all-in-one experience that brings games, apps, movies and even the Google Play Store in its entirety into a VR headset.
There was no Android VR headset to show off, though Google has come up with a reference design for other manufacturers to build off. It also displayed a small, Wii-like controller that provides motion control.
Several Daydream-ready devices will be launching this year from the likes of Samsung, HTC and other popular manufacturers.
Virtual reality is a huge component of Android N, and the new VR platform is what Google call Google Daydream.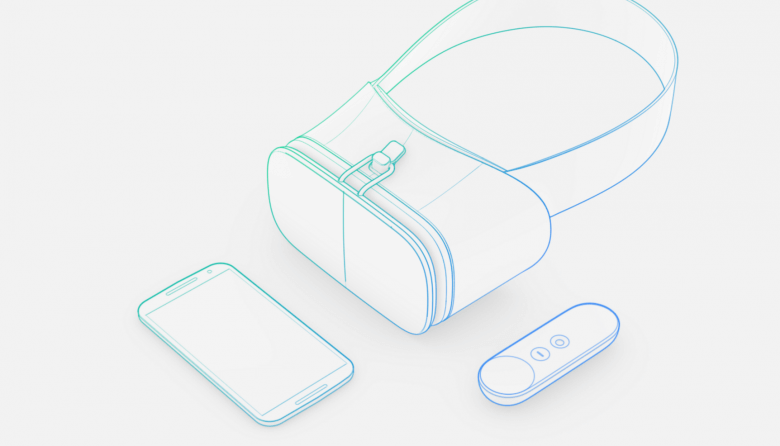
- Android Wear 2.0:
The next major announcement was Android Wear 2.0. Developers can download a preview of it starting today, and it will come to all users in the fall.
Some improvements include the ability to show any app data on any watch face, improved handwriting recognition, and a big update for Google Fitness. Even better news for fitness fans is Google will now allow apps to talk to one another – so if you bring in calories in your nutrition app, you can offset that with your running app.
In other words, apps no longer need a connected smartphone in order to function. With a phone completely powered off or even left behind, apps can function and even communicate without a phone, as long as the wearable device is connected to the internet via cellular or Wi-Fi.
- Instant Android Apps:
The I/O 2016 was steaming atmosphere with every announcement.
Google announced Instant Android Apps, which lets you instantly access an app without needing to download it.
Android Instant Apps takes Google’s concept of Accelerated Mobile Pages, which loads webpages near-instantly, to Android apps. Users will no longer need to download an app in order to use its features.
With Android Instant Apps, users will be able to run any app with one tap, no installation needed.
It is Google’s answer to the pain of installing phone apps you know you’ll use just once or twice, like for shopping. With this approach, the app runs on Google’s servers instead of your phone. It also has compatibility all the way back to Jellybean OS.
It’s only in preview as Google says it will take a lot of time to get right, but it holds exciting possibilities.
The Google had something in store for developers as well:
- Firebase
Google launched an expansion of Firebase at IO 2016.Going beyond a mobile backend, the platform helps developers quickly build high-quality apps, grow their user base, and earn more money across iOS, Android and the mobile web.
- Studio 2.2
Google launched Android Studio 2.2 preview, the latest version of its integrated development environment (IDE). It has a new layout designer and a firebase plugin adding services like Analytics, Authentication, Notifications, and AdMob.Studio 2.2 will be better for developers who are aiming emerging.The first day of the Google I/O 2016 was full of future tech realities, from Android N, to the just-debuted Google Home. They had some or the other thing stored for everyone from user to developers.
The 2nd day expectations are also high. For updates of 2nd day stay with Mantra Labs.
If any queries approach us on hello@mantralabsglobal.com
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox






