ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a process of extracting data from different data sources; manipulating them according to business calculations; loading the modified data into a different data warehouse. Because of the in-depth analytics data it provides, ETL function lies at the core of Business Intelligence systems. With ETL, enterprises can obtain historical, current, and predictive views of real business data. Let’s look at some ETL features that are necessary for business intelligence.
The Importance of ETL in Business Intelligence
Businesses rely on the ETL process for a consolidated data view that can drive better business decisions. The following ETL features justify the point.
High-level Data Mapping
Leveraging data and transforming them into actionable insights is a challenge with dispersed and voluminous data. Data mapping simplifies database functionalities like integration, migration, warehousing, and transformation.
ETL allows mapping data for specific applications. Data mapping helps in establishing a correlation between different data models.
Data Quality & Big Data Analytics
Huge volumes of data aren’t of much use in their raw form. Applying algorithms on raw data often leads to ambiguous results. It needs structuring, analyzing, and interpreting well to gain powerful insights. ETL also ensures the quality of data in the warehouse through standardization and removing duplicates.
ETL tools combine data integration and processing, making it easier to deal with voluminous data. In its data integration module, ETL assembles data from disparate sources. Post integration, it applies business rules to provide the analytics view of the data.
[Also read: Popular ETL Tools for 2020]
Automatic & Faster Batch Data Processing
The modern-day ETL tools run on scripts, which are faster than traditional programming. Scripts are a lightweight set of instructions that execute specific tasks in the background. ETL also ‘batch’ processes data like moving huge volumes of data between two systems in a set schedule.
Sometimes the volume of incoming data increases to millions of events per second. To handle such situations, stream processing (monitoring and batch processing data) can help in timely decision making. For example, Banks batch process the data generally during night hours to resolves the entire day’s transactions.
Master Data Management
Using ETL and data integration, enterprises can obtain the “best data view” across multiple sources.
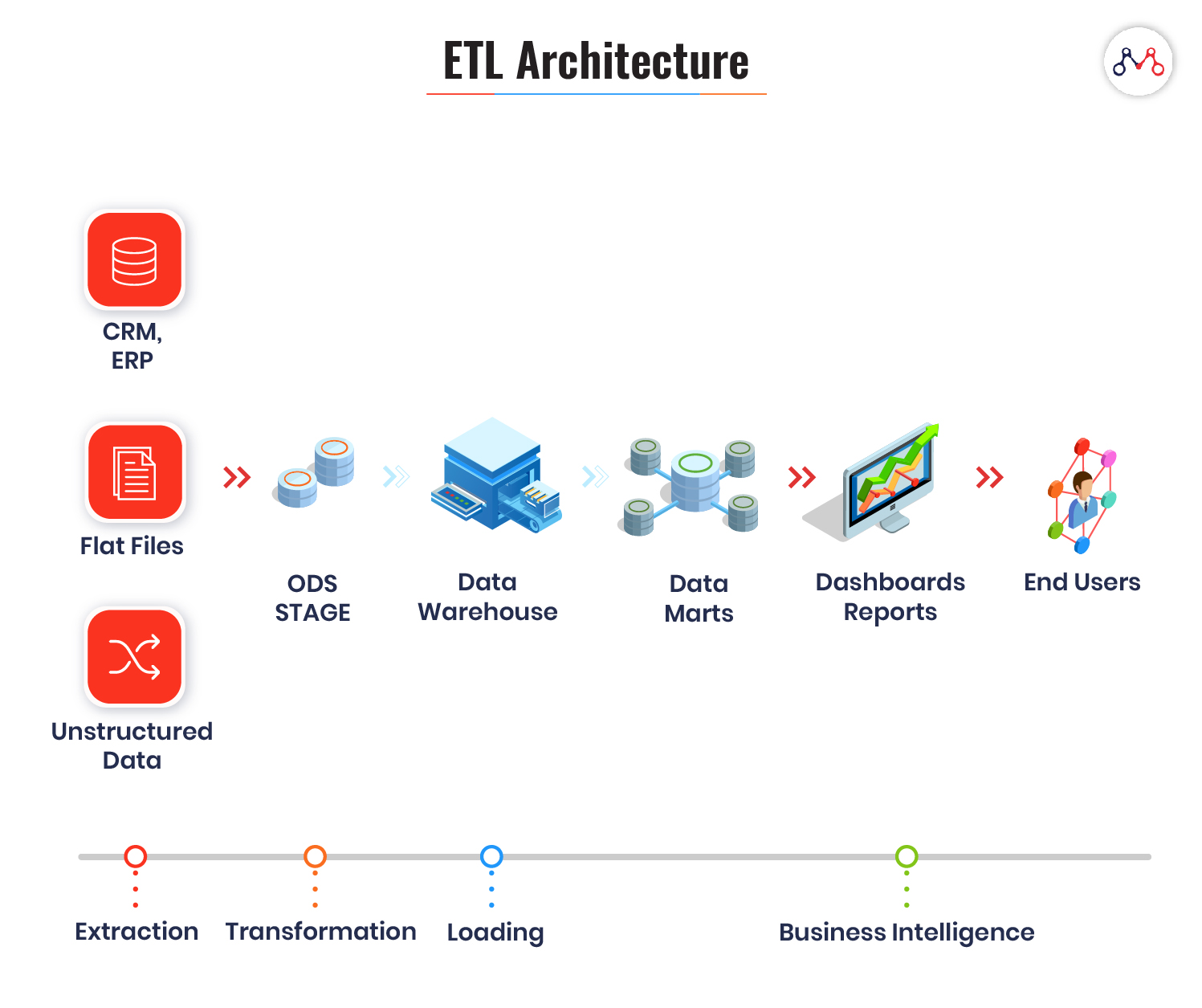
How ETL Works?
ETL systems are designed to accomplish three complex database functions: extract, transform and load.
#1 Extraction
Here, a module extracts data from different data sources independent of file formats. For instance, banking and insurance technology platforms operate on different databases, hardware, operating system, and communication protocols. Also, their system derives data from a variety of touchpoints like ATMs, text files, pdfs, spreadsheets, scanned forms, etc. The extraction phase maps the data from different sources into a unified format before processing.
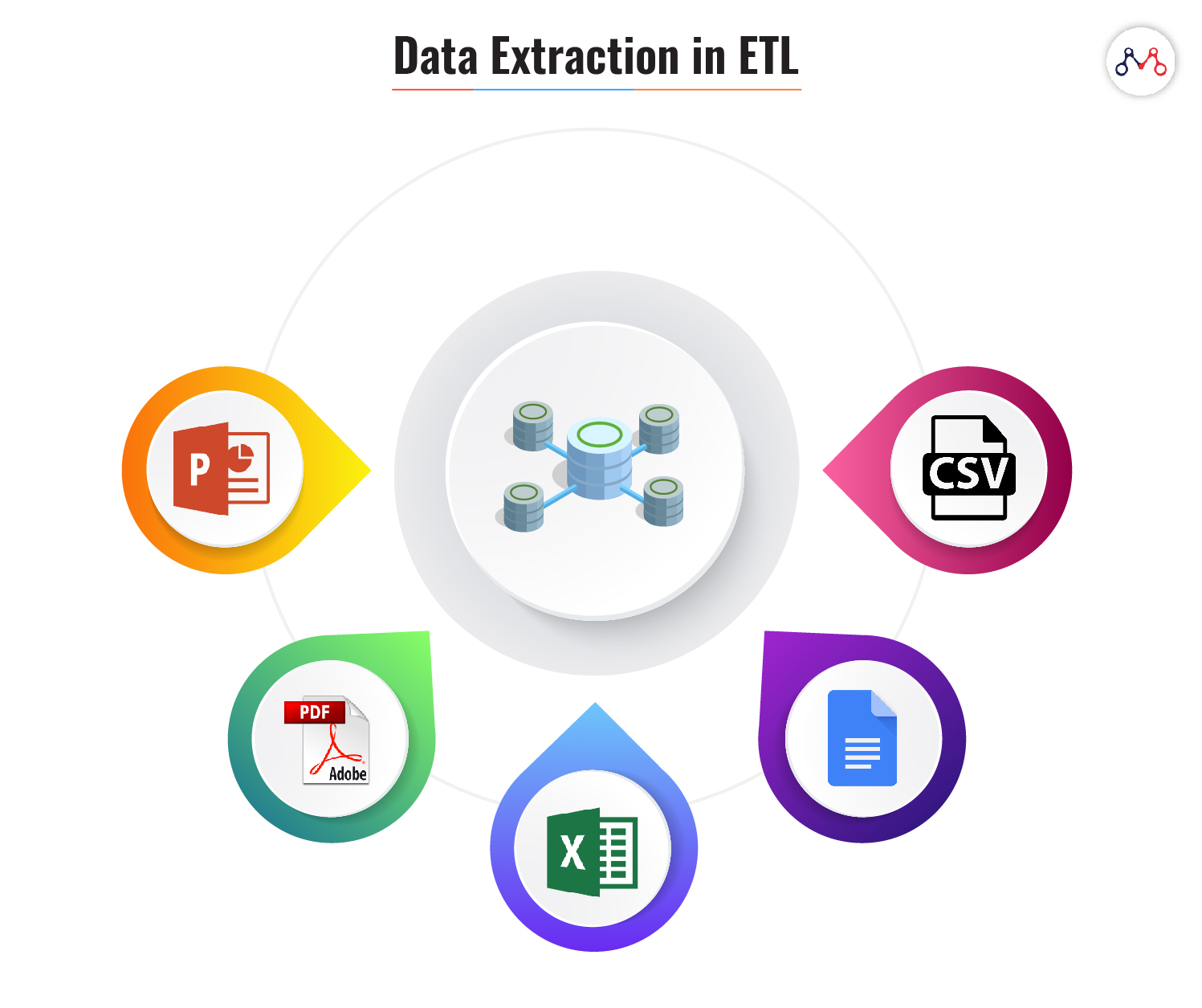
ETL systems ensure the following while extracting data.
- Removing redundant (duplicate) or fragmented data
- Removing spam or unwanted data
- Reconciling records with source data
- Checking data types and key attributes.
#2 Transformation
This stage involves applying algorithms and modifying data according to business-specific rules. The common operations performed in ETL’s transformation stage is computation, concatenation, filters, and string operations like currency, time, data format, etc. It also validates the following-
- Data cleaning like adding ‘0’ to null values
- Threshold validation like age cannot be more than two digits
- Data standardization according to the rules and lookup table.

#3 Loading
Loading is a process of migrating structured data into the warehouse. Usually, large volumes of data need to be loaded in a short time. ETL applications play a crucial role in optimizing the load process with efficient recovery mechanisms for the instances of loading failures.
A typical ETL process involves three types of loading functions-
- Initial load: it populates the records in the data warehouse.
- Incremental load: it applies changes (updates) periodically as per the requirements.
- Full refresh: It reloads the warehouse with fresh records by erasing the old contents.
The ETL systems validate the following data loading parameters-
- The Business Intelligence report on view layer matches with the loaded facts
- Data consistency between the data warehouse and the history table.
- Models are based on transformed data and not the raw data from the original databases.
The modern-day ETL applications utilize NoSQL database systems for warehousing. NoSQL systems are suitable for big-data and real-time web-applications. NoSQL executes queries faster than traditional databases and is more memory efficient.
ETL Business Applications
Transactional databases are not enough to resolve complex business queries. Also, dealing with unorganized data formats is more time-taking. ETL can help in obtaining-
- Memory efficiency
- Real-time query processing
- Mapping data historical, current, and predictive data to derive actionable insights
- Smart data storage and retrieval.
Almost all industries can deploy the benefits of ETL systems. However, businesses like banking, insurance, customer relations, finance, and healthcare are the early adopters of this technology.
If your business needs intelligent data processing, we’re here to listen to your requirements. Drop us a word at hello@mantralabsglobal.com to know about our previous works on developing ETL applications.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




