It is essential to optimize a website for speed and user experience in the fast-paced, competitive digital world of today.
Websites that take too long to load may turn away potential customers, resulting in lower conversion rates and less revenue. The use of web optimization techniques is essential in tackling these issues, enhancing website functionality, cutting down on load times, and ensuring an excellent user experience. In the last two blogs, we discussed why web optimization is a must for businesses and also some essential checklists that can help firms understand how easy is the website/app to use for their customers. Well, in this blog post, we’ll focus on essential web optimization techniques that can help organizations improve website performance, draw in and keep users engaged.
- Optimizing Images and Multimedia: Pages with loads of images and multimedia content typically take longer to load. That is why techniques like image compression, lazy loading, image resolution, image tag optimization, and picture tags in images might aid in enhancing the efficiency of a website.
Image Compression
File sizes can be significantly reduced by optimizing images and adopting modern image formats like SVG and compressing them without losing quality. For instance, if we have two identical photos, one is 900 kb in size and the other is 340 kb. The second image will then put less strain on the server and conserve bandwidth.
Lazy Loading
Lazy loading techniques can be used to load images and multimedia content only when they are about to enter the user’s viewport, saving bandwidth and accelerating the initial page load.
For instance, if a user must scroll down a web page to see an image, you can show a placeholder and lazy load the complete image only when the user reaches its location.
Image Resolution
The file size increases with increasing resolution. Using high-resolution photos online slows down page load time. Similarly to this, if a visitor uses a mobile device to access the website, bandwidth will probably be more constrained, and large graphics will probably take longer to load. In the case of high-resolution images, the thumbnail is used to load the complete image only when the user requests it.
Image Tag Optimization
This approach involves uploading the same image with different properties as required for different devices. For example, smaller size images for mobile devices.
Including all types of images required for mobile, web, etc in a single code will add lines in code and increase loading time. It’s better to always include both small and large-size images, different formats, etc, and ask the system to select the appropriate one based on the device type – mobile, web, or tablet.
This reduces loading time and the images displayed will be suitable to the device, hence enhancing user experience.
- Minifying and Compressing Assets: Minification is the process of removing unnecessary elements such as whitespace, comments, and formatting from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, reducing their file size. Compression, on the other hand, involves using techniques to reduce the size of the files during transmission. Because reduced file sizes result in faster downloads and better page rendering, minifying, and compressing files can drastically reduce load times.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): CDNs help lower latency and minimize the distance between the user and the server, resulting in faster content delivery, by distributing the website’s assets over numerous servers. Additionally, CDNs also manage traffic peaks, enhancing website accessibility and performance.
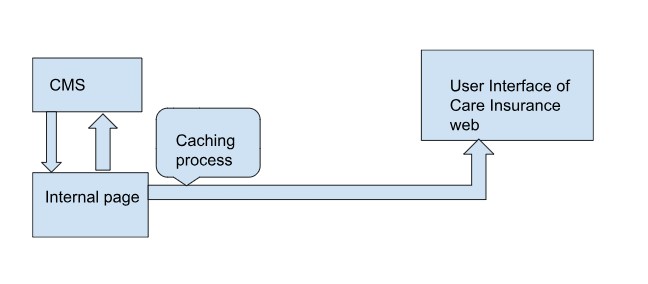
Steps followed in CDN(Content Delivery Unit)
-Data to be displayed in the user interface of the website is entered in CMS (similar to WordPress) and gets copied to the internal page (like a prototype of the original website user interface) so that we can have a view of how it’ll be displayed to the end user.
-When someone tries to make changes on the Internal page directly, it’ll be accepted only if the same input has been fed on CMS and acknowledged
-Through a syncing process, also called ‘Caching’, it’ll be displayed on the real-time user interface from the internal page, thus providing us a chance to take a look at how it’s delivered to the user and check the viewing experience.
- Responsive and Mobile-Friendly Design: In an era where mobile devices dominate web browsing, responsive design is a must-have for optimal user experience. Websites that are responsive automatically change their layout and usability to fit different screen sizes and resolutions on different devices, leading to higher engagement and customer satisfaction.
- Script Optimization : Also called ‘code cleanup’, this involves checking the code periodically / with functionality changes and updating it then and there. This will help us eliminate redundant code and improve the LCP (Loading Capacity of Page)
- Implementing Microservice: Microservice refers to a piece of code that will influence the behavior of individual elements when input is received. Related dependency code will be added with the element (react js, angular, etc).
This is used as an alternative to the conventional approach where the code of an entire page will load if we skip following the above-mentioned section-wise approach.
Conclusion:
Techniques for web optimization are essential for boosting website performance, improving user experience, and gaining an advantage in the digital marketplace. By implementing the above-mentioned techniques, organizations can ensure that the website loads quickly engages users effectively, and drives business growth.
Check out our latest case study:
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox