Augmented Reality (AR) adds virtual interactive experiences in real-world objects. It uses computer-generated perceptual information to enhance users’ sensory experience in a Dimensional Digital World. The majority of AR users are 16-34 years age and 73% of them have expressed deep-satisfaction with their mobile AR experiences. Here’s a gigantic list of augmented reality use cases!
Transportation
With features like 3D navigation, driving directions, and visuals of terrains augmented reality is taking the transportation industry to a new dimension. Technically, AR is capable of projecting information on any surface.
#WayRay
WayRay’s Navion tool projects navigation instructions on the windshield. It uses a holographic optical element to create real AR experience without the need for special eye-wear or headgear.

#AeroGlass
Aero Glass’ AR headsets display VFR (Visual Flight Rules) navigation for airports, cities, villages, airspace, and terrains. It is a great aid for pilots to decide landing approaches, especially when clouds and fog reduce visibility. And, of course, visual cues explain the scenario better than audio instructions.
Mobile Commerce
The current generation is way ahead of the E-commerce era and dwelling in the world of mobile commerce. Here consumers can purchase products through their hand-held devices. Brands are using AR to improve customer interaction on their mobile app.
#Manor
Manor, a Swiss department store chain introduced 48 pages augmented catalogue. With a simple scan, users can instantly shop or extract product information, ‘how to use’ guide, etc. from the catalogue.
Augmented Reality Use Cases in Manufacturing, Engineering & Warehousing
AR-enabled wearables in manufacturing can help measure changes, identify unsafe working conditions, and visualize design components and structures. With field-service knowledge engineers and technicians can monitor the field and provide remote expert support in real-time. Organizations are also using AR to improve productivity in out-of-office or away-from-desk jobs.
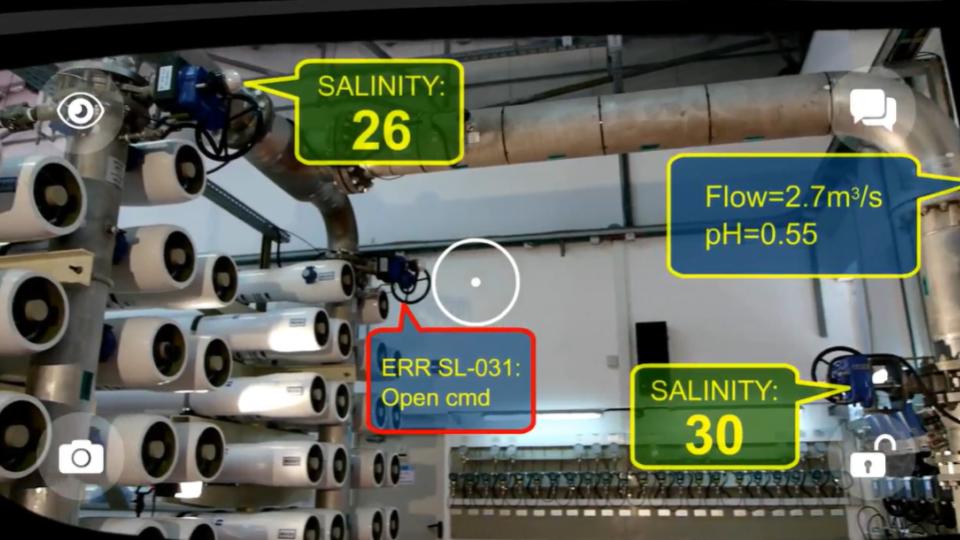
#National Water Company, Israel
Israel’s National Water Company uses AR smart glasses and mobile app platform to superimpose markings, messages, and diagrams directly onto the engineer’s field of view.
#Boeing
Boeing’s Engineering division is using Skylight AR Glasses, a wearable alternative to finding instructions on laptops or papers.
“We now want to introduce AR into the services part of our business so we may service our own, and third-party products, for our end-customers.”
Ted Colbert, CIO, The Boeing Company
#Atheer
Atheer offers real-time service resolution through step-by-step task guidance.
#Ubimax
Ubimax has developed AR glasses (wearables) to provide pickers route guidance in warehouses.
AR Use Cases in Healthcare
AR can provide visual prosthetics and is helping the healthcare sector in many ways. Researchers and doctors are aspiring to perform complex surgeries with AR.
#NuEyes
NuEyes uses special AR glasses to help people with visual impairment. Using AR glasses, people can accomplish day-to-day computer work, traveling within airports, Ubers, and other cities.
#AccuVein
AccuVein is using AR’s tracking feature to spot veins while inserting IVs. It is making clinical processes (viz. cosmetics, vascular, and blood-draw) more accurate.
#Sahlgrenska University Hospital Research on Phantom Limbs Pain
The Chalmers University of Technology in collaboration with Sahlgrenska University Hospital have successfully tested augmented reality to reduce phantom limb pain felt by amputees.
<Image – screen shot: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=120&v=0wp-SigTeLs>
Augmented Reality Use Cases in Education
Academic institutions are using AR for interactive in-depth training.
#Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland Clinic at Case Western Reserve University trains human anatomy and surgery through 3D human models.
#Jaguar X Bosch
Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) trains employees to assemble and repair with more than ‘X-Ray’ vision of the car. This saves the time and effort of reinstalling the entire dashboard of the Range Rover Sport vehicle.
#AR Flashcards
Edshelf’s AR Flashcard is making learning interactive and engaging for toddlers. Pointing smartphone at printed flashcard pops-up a 3D object on the screen.
In-store Experience
In the quest for customer-engagement, companies are deploying AR to bring immersive experiences.
#Starbucks
Starbucks Roastery at Shanghai gives visual cues like a hummingbird flying across the walls, baristas handcrafting beverages in contemporary and vintage brewing devices, Princi bakers baking bread, and much more.
“It’s like Alice in Wonderland meets Willy Wonka.”
Emily Chang, Sr. VP & CMO, Starbucks, China.
Home Decor
Brands are harnessing 3D rendering features of AR to provide a test-view for customers. AR can merge and position digital items into the real-landscapes. Thus, instead of impulsive buying, customers can test and “be sure” of their purchase decision.
#IKEA
IKEA allows users to view furniture from different angles on its app – Ikea Place. Post reviewing, customers can proceed to buy the product from the same app.
#Estiluz
Estiluz uses AR to project virtual lighting into the real-world. The app requires users to print and place ‘markers’ at places where they want to test the lighting. Estiluz app detects the marker and demonstrates how particular lighting will look at that place.
#Home Depot – Project Color
With Home Depot’s Project-Color App users can see how a wall color will look. The app portrays a real picture considering shadows, lightings and objects in the room.
AR Use Cases in Retail
BRP reports, by 2020, nearly 50% of customers would be more likely to shop at a retailer that utilizes augmented reality. Retailers are deploying AR for 3D virtual trials on clothing, compile in-store information, and to build brand authority through unique experiences.
#LensKart
Lenskart allows users to experience a 3D Try-on of its glasses using AR.
#Lacoste
Lacoste utilizes the tracking feature of AR to let their users try on different shoes virtually.
#Sephora
Users can try different makeup on their photo in the Virtual Artist App from Sephora. The app bridges the gap between product trial and purchase.
#Zara
By positioning the smartphone at Zara’s graphic signage, mannequins seemingly come to life in people’s screen displays. Customers can purchase their look in a single touch on the Zara AR app.
Gaming
The gaming industry is an early adopter of AR technology. Gaming only brought people’s attention towards AR on a commercial scale.
#Pokémon GO- Mobile Game
The game incorporates 3D visuals of virtual creatures (Pokémon). Using the player’s mobile device GPS, the game locates, captures, battles and trains Pokémon in a real-world location.
Augmented Reality Use Cases in Marketing
Marketers are rolling out AR-based campaigns to amplify the brands’ perception among consumers. AR is not only helping brands harness customer engagement, but also promote the product to a wider customer base.
#Airwalk
In a campaign to promote the relaunch of limited-edition Jim shoes, Airwalk used geolocation (an AR feature) to create invisible pop-up shops.
#Stubhub
For Super Bowl LII, StubHub rolled out an AR feature on its mobile app allowing ticket buyers to see a virtual 3D model of the U.S. Bank Stadium.
#Pepsi
In 2014, Pepsi introduced an augmented reality bus stop campaign to give commuters an unbelievable moment in their day.
Market and market research states, growing at a CAGR of 40%, Augmented
Reality applications will explode in the near future and reach $61.39 bn in revenue by 2023.
We specialize in developing industry-specific interactive products and solutions. Drop us a hello at hello@mantralabsglobal.com for queries related to augmented reality.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox




