What is Blockchain:
A distributed ledger – It tracks ownerships through historical assets and identities – and everyone has a copy.
Unique Tokens – long numbers are tracked through the ledger
Anonymized Processing / Mining – transactions are processed through miners.
Immutable, encrypted, pseudo anon – and they are immutable once they’ve happened, and are encrypted.
Consensus Mechanisms – as long as 51% of the network agree, it holds.
Is The Blockchain a New Web 3.0?
The blockchain gives internet users the ability to create value. It may revolutionize the future and a couple of places it is making a difference today.
12 potential business applications are listed down for blockchain.
Smart Contracts – Distributed ledgers enable the coding of simple contracts that will execute once the specific conditions are met.
The Sharing Economy – By enabling peer-to-peer payments, blockchain opens the door to direct interaction between parties – a truly sharing economy results.
CrowdFunding – Blockchain takes this interest to the next level, potentially creating crowd-sourced venture capital funds.
Governance – By making the results fully transparent and publicly accessible, distributed database technology could bring full transparency to elections or any other kind of poll taking. Ethereum-based smart contracts help to automate the process.
Supply chain auditing – Distributed ledgers provide an easy way to certify that the backstories of the things we buy are genuine. Transparency comes with blockchain-based timestamping of a date location.
File Storage – Decentralized file storage on the internet brings clear benefits. Distributing data throughout the network protects files from getting hacked or lost.
Protection of Intellectual Property – Smart contracts can protect copyright and automate the sale of creative works online, eliminate the risk of copying and redistribution.
Internet of Things (IoT) – Smart contracts make the automation of remote systems management possible. A combination of software, sensors, and the network facilitate an exchange of data between objects and mechanisms.
Identity Management – Distributed ledgers offer enhanced methods for proving who you are. Having secured identity will also be important for online interactions – for instance, in the sharing economy.
Data Management – In the future, users will have the ability to manage and sell the data their online activity generates. Because it can be easily distributed in small fractional amounts, Bitcoin – or something like that.
Land title registration – AsPublicly-accessible ledgers, blockchain can make all kinds of record-keeping more efficient. Property titles are a case in point. They tend to be susceptible to fraud, as well as costly and labor-intensive to administer.
Stock Trading – When executed peer-to-peer, trade confirmations become almost instantaneous. This means intermediaries – such as the auditors, and custodians – get removed from the process.
What Problems does Blockchain solve?
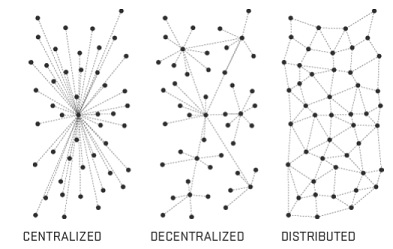
Removal of the Middlemen to make system decentralized. There is no, a single entity that controls the network, Instead, it’s analogically similar to BitTorrent. Own your own data in the new Data Economy.
The Central Point of Failure – Reliability on the Central Server containing all the data is less in case of Hacker’s attack on the server, Blockchain Technology makes us move towards a permanent web. A web where links never die. Stupid 404 !!!
Establishing Transparency, to make system Trustless. In other words, no need to put the trust on the peers, as the designed system is highly tamper-resistance.
Faster Data Transfer – A peer-to-peer network helps the transfer of data super fast as compared to the central server serving data.
In general, Blockchain is creating a world with more and more value. It can be applied to any need for a trustworthy system of record.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox