The market for insurance in Belgium has been stable for over a decade. Unless Insurers adopt new strategies and embrace external partnerships, organic growth seems next to impossible.
While insurers in other parts of the world are leveraging technology for better customer acquisition, Belgian Insurers struggle with stringent customer data protection laws.
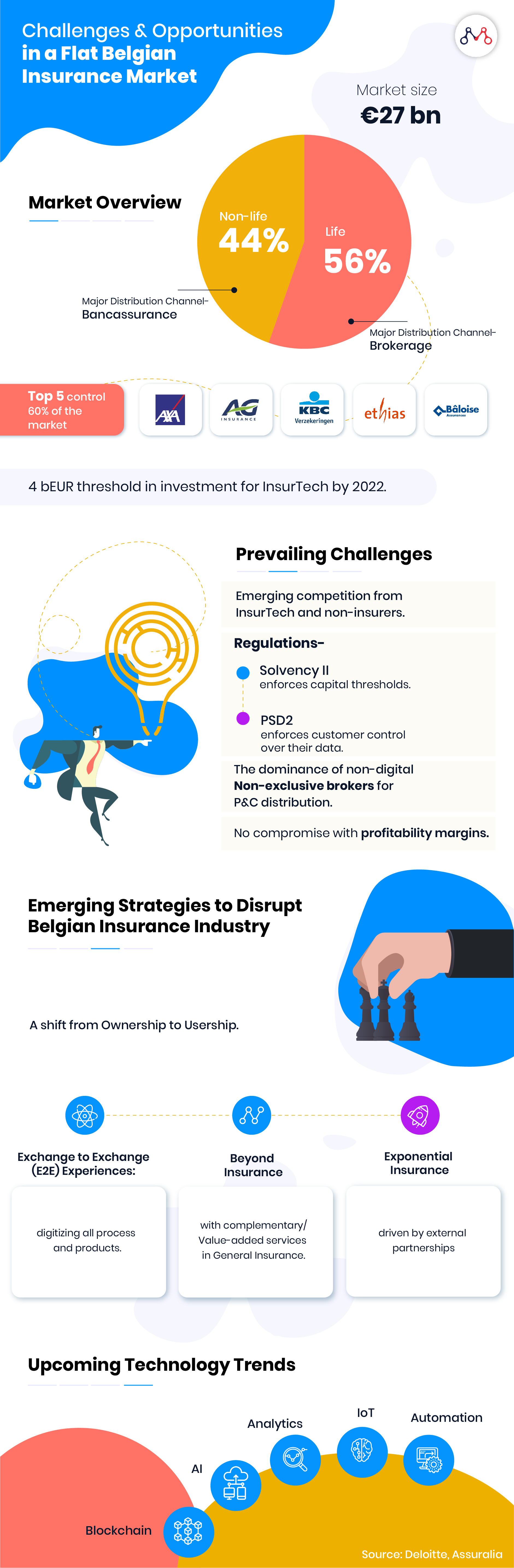
This is the time for major business alignments to keep up with the changing customer expectations. For instance, the brokerage system dominates nearly 60% of non-life insurance distribution in Belgium. Unfortunately, 31% of the brokers have a negative attitude towards digitization and InsurTech, mainly because of the lack of awareness about the subject.
With current business models, there’s negligible hope that Belgian Insurers will remain competitive. Let’s look at the key drivers of ‘change’.
The ‘Change’ Drivers for Insurance in Belgium
The threat to lose customers for being slow in a fast-moving age is imposing some serious pressure on Insurers in Belgium. The change in customer expectations and lifestyle will drive the transformation of the Belgium Insurance Industry. The other factors that will impact the insurance include- economy, technology, life expectancy, climate change, and competition.
Digital and Mobile Adoption
The Deloitte Global Mobile Consumer Survey 2018 reveals— 84% of Belgians own at least one mobile device. This indicates a growing preference for digital, self-service platforms, and ease of access irrespective of location. Insurers are, thus, compelled to look beyond agent-driven pitches.
For example, Trov— an American technology company provides ‘on-demand’ insurance for individuals’ properties for short durations. Customers only need to register their properties, activate insurance for a desired duration, and pay a daily premium.
Now that over 60% of non-life insurance products are distributed by brokers, this is also the time to train and equip brokers with handy apps.
Economical Changes
The world is rapidly moving towards a sharing economy, which involves short-term P2P (Peer-to-peer) transactions for shared use of products and services. The societal shift towards the open data economy fueled the open banking trend. Recently, insurers are following the trend as open insurance.
“..The economy has been moving beyond narrowly defined industries built around large, vertically integrated, and mainly “self-contained” corporations. New means of creating value have been developing everywhere in the form of ever-denser and richer networks of connection, collaboration, and interdependence…” (Business ecosystems come of age. Kelly, E., 1 April 2015, p. 4.)
Belgium is set to witness the following major economic shifts-
- Mobility – Belgians demonstrate an inclination toward multimodal mobility solutions. For example, Antwerp-based Olympus Mobility- an app for cars & bike pooling and parking services is set to expand its services in more Belgian cities.
- IoT – Lifestyle and product preferences are changing with connected devices. With new customer expectations, insurance needs and opportunities are also growing. For example, Phil at Home by AG Insurance is a compound product with services in the field of prevention, protection, and assistance for elderlies.
Adoption of Technologies across Industries
Digital has put customers in the center. While other industries stay ahead with technological adoption, Insurers need to invest in innovative products that cover emerging risks. For example, Spotify’s personalized recommendations and Apple’s assistant – Siri are setting a benchmark for customizing the products at an individual level. “Yet what has become the new normal for those companies, remains a challenge for insurers,” says Dirk Vanderschrick, CEO, Belfius.
The Insurance industry in Belgium is yet to adopt biometrics, recommender systems, sentiment detection, and natural language generation. Currently, 60% of Belgian Insurers use text analysis; 40% use chatbots and object detection; 20% exercise automated decision making and pattern detection; according to Monitor Deloitte’s One Minute Survey, Artificial Intelligence (May 2018).
Apart from AI-enabled tools, the Belgium Insurance sector will soon adopt blockchain, Automation, Analytics, XaaS, and IoT.
Related articles – 5 AI trends reshaping the Insurance sector , How does XaaS help your business, Blockchain in Insurance
Competition
Today, business models have a shorter life cycle because of digital disruption. The competition for incumbents is fierce- with 4 bEUR potential investment in InsurTech in Belgium.
Many have thought of phygital experience as progressive- where paper and paperless processes coexist. However, in the long term, their existence is questionable. For example, Lemonade is racing the core insurance with paperless and personalized insurance packages delivered to the customer in just 90 seconds!
In line with the fact that customers want a solution to their problems – the one who provides the most appropriate solution in the easiest way possible, wins.
Regulatory Changes
Compulsory health and car insurance policies had a great impact on sales volume. Apart from being an entry barrier for small players, the existing regulations no more align with climate changes, longevity, and technological disruptions.
The Belgian Government is set to launch Payment Service Directive 2 (PSD2) by 2024 and IFRS 17 (International Financial Reporting Standard) by 2021. Nearly 70% of Insurers believe PSD2 will have a positive impact in the insurance value chain.
‘Beyond’ Insurance is the Future
According to Insurance Experts from Deloitte, non-core insurance products and services drive 10-30% of the revenue. Therefore, complementary services or value-added services can bring a greater competitive advantage to the insurers.
For example, the US-based Oscar Health Insurance encourages a healthy lifestyle by financially rewarding its customers. It tracks footsteps, eating habits, workouts, etc. on its app through wearables. It further supports customers with doctoral advice and scheduling appointments. These value-added services, along with traditional health insurance is a win for customer loyalty.
We’re an InsurTech100 company championing back and front-office automation solutions along with interactive applications for the new-age digital insurer. Drop us a line at hello@mantralabsglobal.com to know more.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox






