We’re about to witness the evolution of autonomous vehicles from Level 0 to Level 2. While Level 0 is completely human-driven; Level 1 vehicles can control braking and parallel parking themselves. Level 2 vehicles can operate automatically, but with a human ready to control exceptional situations.
The success of self-driving cars depends solely on the safety it brings to transportation. With increased safety, will we even need insurance for autonomous vehicles?
Perhaps, the traditional insurance policies might face a setback. But, autonomous vehicles will certainly open new avenues for innovative insurance products.
The Stevens Institute of Technology predicts that there would be over 23 million fully autonomous vehicles by 2035 in the US alone.
To stay competitive with the changing dynamics of auto insurance, insurers need to address new risks. But before, let’s take a look at potential risks in the autonomous vehicle insurance sector.
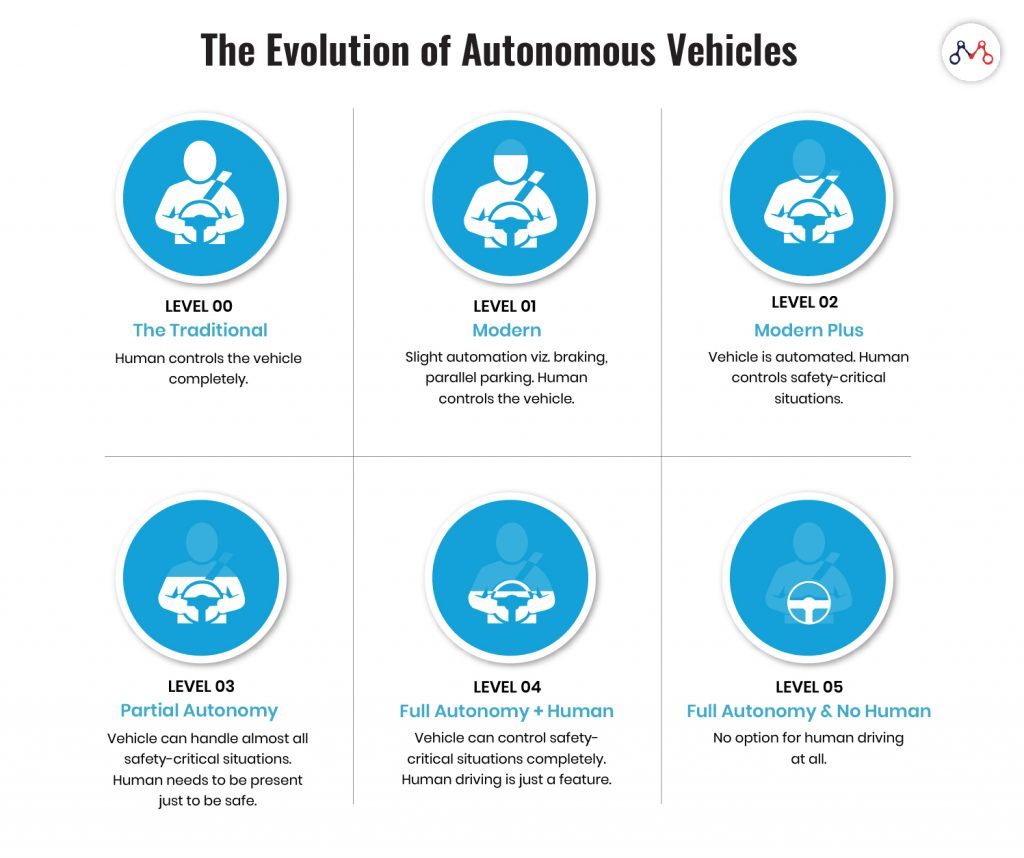
Potential Impact of ‘Autonomous Vehicles’ Revolution
The shift to autonomous vehicles tends to bring dramatic changes in auto insurance premiums.
Instead of individual policies, researchers foresee insurance policies turning towards original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and service providers such as ride-sharing companies. The new auto insurance products would be an outcome of the following transportation changes.
New Road Regulations
With autonomous vehicles on the roads, safety regulations are prone to change. For instance, the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration intends to reconsider its current safety standards to accommodate AVs in existing transportation. But, this reformation will take the presence of human drivers into account.
Increased Safety and Reduced Claims
With increased safety and reduced accident claims, the revenues from traditional premium policies might decline.
Insurers often follow a “no-fault” system to lower auto insurance costs by taking small claims out of the courts. For minor injuries, insurers compensate their policyholders regardless of who was at fault in the accident.
However, fender-benders would be more than it is with autonomous vehicles. Also, blockchain in insurance would become integral to investigate the root cause of the accident. And, of course, there won’t be much scope for lenient “no-fault” policies.
Change in Insurance Liability
Traditional liability insurance pays for the policyholder’s legal responsibility to others for bodily injury or property damage. With autonomous vehicles, the liability is going to shift towards OEMs, suppliers, or car-rental service providers.
Underwriting?
Currently, automakers must adhere to around 75 safety standards. This underwriting considers that a licensed driver will control the vehicle. The safety standards are going to change with more AVs on roads.
The present-day premium is high for a handful of autonomous vehicles because of insufficient data with underwriters and actuaries. However, chances are, major OEMs will cover the insurance premiums in the vehicle cost.
For instance, Tesla, one of the pioneers of autonomous vehicles, provides auto insurance at 30% lower rates than other insurance providers. Tesla having a better understanding of its vehicles’ technology and repair costs, believes can provide low-cost insurance. This is also a threat to insurance carrier fees.
Scope for New Autonomous Vehicle Insurance Products
Accenture estimates that autonomous vehicles will generate at least $81 billion in new insurance revenues in the US between 2020 and 2025. It also foresees opportunities for insurers in cybersecurity, product, and infrastructure landscapes. Let’s take a look at new auto insurance avenues.
Cyber Security
While AVs ensure safety, there are unidentified cybersecurity threats. Vehicles fueled by IoT technology deal with comprehensive telematics data. Capturing every moment of the user proposes risks like identity theft, privacy invasion, misuse of personal information, and attacks from ransomware. According to the Center for Strategic and International Studies and McAfee, globally cybercrimes cost around $600 billion annually. The shared data from autonomous vehicles bring the financial sector at risk.
On the other hand, monitoring the performance of vehicles and the driver’s behavior behind the wheel can reduce claim investigation turn around time.
Therefore, future insurance products will also focus on moral and financial threats to passengers.
Product Liability
The product liability insurance might shift from automotive to sensors and algorithms behind the autonomous vehicle. The OEMs will be also liable for communication or Internet connection failure along with machinery and software failures.
Insurance Against Existing Infrastructure
It will take more than 30 years for autonomous vehicles to completely dominate transportation. The upcoming insurance products will take existing infrastructure into account. For example, AVs need insurance if it damages due to puddles or potholes on the road.
Also, car ownership tends to decline with rental and pay-as-you-use models. This opens a fleet-level opportunity for insurers for driverless cars.
Source: Accenture X Stevens Institute of Technology “Insuring Autonomous Vehicles” report
Insurers need to adapt to the rapid technological advancements. Cloud-based insurance workflow platforms or IaaS (Insurance as a Service) models help in achieving operational gains in the entire insurance value chain.
Concluding Remarks
AVs are going to dominate the world’s highway because of improved safety and convenience. Companies can leverage this opportunity to introduce innovative autonomous vehicle insurance products.
Growing IoT is blurring the fine-line between different verticals of insurance. To stay competitive, insurers should also indulge in creating new distribution channels and partnerships with OEMs and technology service providers.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox






