Testing is a method to validate if the delivered product is developed as per the requirement and if the expected functionality is achieved. There are two types of testing methods namely Manual and Automation.
Manual testing is validating manually for defects in the developed product. This requires time and more resources and delays the testing process as well.
Automation Testing is a process where the product is tested using scripts, testing tools, or any framework to minimize manual intervention, human errors, and time. This is the best way to deliver the developed product in a short duration. But how is automation testing effective in Defect-Free Delivery?
In this article, we will talk about the pros and cons of automation testing and delivering the developed product defect-free.
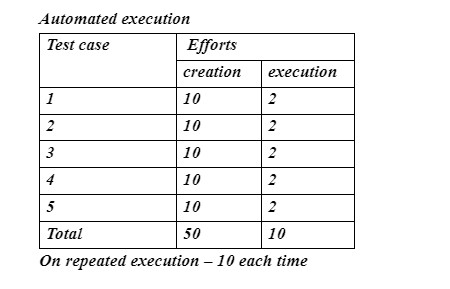
Automation Testing could be utilized to carry out Regression Testing, Load Testing, Performance Testing, and Repeated Execution for faster results.
It does not serve as a substitute for manual testing since some testing types, such as exploratory testing, usability testing, and ad-hoc testing, require manual verification to get the best results.
Why Automation Testing?
- It is less time-consuming.
- A list of consecutive sets of test cases called suites can be developed and executed any number of times.
- On Regression testing, human error is eliminated.
- Automation testing is best for Load and performance testing and repeated testing.
- It is best for optimized use of the test scripts for different versions of the application.
- Can be done even when a small modification is done to code on test suite execution.
Automation Testing Vs. Manual Testing
Automation testing is not required in all places, the decision has to be taken when to use manual or automation. When there is repeated testing of the scenarios to reduce repeated manual effort on execution, automation testing is required and when there is less repetition and the scripting takes a huge effort, then manual testing is the best.
Pros of Automation
- Can be done to run repeated testing
- Execution can be performed for the same scenario but with different inputs
- Execution can be performed in various triggering points at the same time
- To increase the accuracy and for quick test results.
Cons of Automation
- Automation takes more effort in the beginning
- There are some factors like visual appearances that cannot be automated
- Maintenance of scripts is required when any updation takes place
Pros of Manual
- Team interaction improvises between developers and testers.
- Best suited for Ad-hoc testing
Cons of Manual
- Requires more human resources
- Delayed results in case of repeated testing
- More occurrences of human errors
- Depends on the resources’ presence while executing.
Types of Automation Testing
- Keyword-driven testing.
- Integration testing.
- Unit testing.
- Smoke testing.
- Regression testing.
- Performance testing.
- Security testing.
- Data-driven testing.
Test automation life cycle
There are many phases/steps involved in the automation test life cycle:
- Test planning
- Analyse application under test
- Setup test environment
- Develop test scripts
- Enhance test scripts
- Debug the tests
- Execute the tests
- Analyze the test results
- Defects/Reports
Implementing A Test Automation Strategy
- Define the Scope Of Automation
- Decide On Testing Approach
- Select A Test Automation Framework
- Choose The Automation Tool To Use
- Test Execution
- Test Automation Maintenance
Conclusion
Automation testing reduces time, and resources and also provides accurate results.
While it may help organizations deliver a great product defect-free and stay competitive, it has its own challenges. It can be difficult at first, but with the appropriate procedures and actions, it could be implemented successfully.
About The Author:
Saranya N S is currently working in Mantra Labs as a QA manager. She has experience in multiple domains like telecom, IVR, and BFSI and is passionate about creating automation testing frameworks.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox