Why do people opt for on-premise storage
Uploading an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) to Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) and downloading it to your on-premises machine can be useful for creating backups, sharing images with others, or moving images between regions. In this article, we will explain the process of uploading an AMI to S3 and downloading it to your data center, how to create an AMI from an on-premises backup, and how to launch an instance from that AMI.
Benefits of maintaining AMI on-premise data center
Compliance and security: Some organizations are required to keep specific data within their data centers for compliance or security reasons. Keeping AMIs in an on-premises data center allows them to maintain control over their data and ensure that it meets their compliance and security requirements.
Latency and bandwidth: Keeping AMIs in an on-premises data center can reduce the latency and bandwidth required to access the images since they are stored closer to the instances that will use them. This can be especially beneficial for firms with high traffic or large numbers of instances and also to avoid data transfer charges.
Cost savings: By keeping AMIs in an on-premises center, organizations can avoid the costs associated with storing them in the cloud. This can be especially beneficial for companies with large numbers of images or with high storage requirements.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: A copy of the AMI allows organizations to have an additional layer of backup and disaster recovery. In case of an unexpected event in the cloud, the firm can launch an instance from an on-premises copy of the AMI.
It’s important to note that keeping AMIs in an on-premises data center can also have some disadvantages, such as increased maintenance and management costs, and reduced flexibility. Organizations should weigh the benefits and drawbacks carefully before deciding to keep AMIs in an on-premises data center.
Uploading AMI to S3 bucket using AWS CLI
To upload an AMI to S3, you will need to have an AWS account and the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) installed on your local machine.
Step 1: Locate the AMI that you want to upload to S3 by going to the EC2 Dashboard in the AWS Management Console and selecting “AMIs” from the navigation menu.
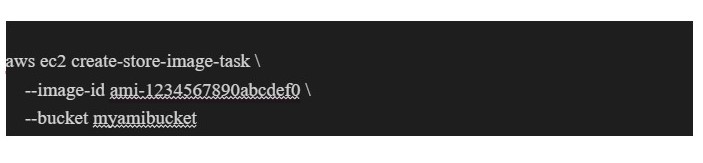
Step 2: Use the AWS ec2 create-store-image-task command to create a task that exports the image to S3. This command requires the image-id of the instance and the S3 bucket you want to store the image in.
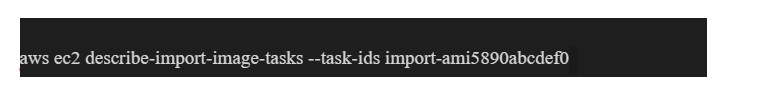
Step 3: Use the AWS ec2 describe-import-image-tasks command to check the status of the task you just created.
Once the task is complete, the AMI will be stored in the specified S3 bucket.
Downloading the AMI from the S3 bucket
Now that the AMI has been uploaded to S3, here’s how you can download it to your local machine.
Use the AWS s3 cp command to copy the AMI from the S3 bucket to your local machine. This requires the S3 bucket and key where the AMI is stored and the local file path where you want to save the AMI.

Or else you can use the AWS S3 console to download the AMI file from the S3 bucket.
By following these steps, you should be able to successfully upload an AMI to S3 and download it to your local machine. This process can be useful for creating backups, sharing images with others, or moving images between regions.
It’s important to note that uploading and downloading large images may take some time, and may incur some costs associated with using S3 and EC2 instances. It’s recommended to check the costs associated before proceeding with this process.
Creating AMI from the local backup in another AWS account
To create AMI from the local backup in another AWS account, you will need to have an AWS account and the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) installed on your local machine. Then, upload your local AMI backup on S3 on another AWS account
Step 1: Locate the backup that you want to create an AMI from. This backup should be stored in an S3 bucket in the format of an Amazon Machine Image (AMI).
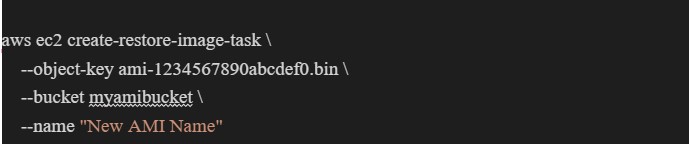
Step 2: Use the AWS ec2 create-restore-image-task command to create a task that imports the image to EC2. This requires the object key of the image in S3, the S3 bucket where the image is stored, and the name of the new image.
Step 3: Use the AWS ec2 describe-import-image-tasks command to check the task status you just created.

Once the task is complete, the AMI will be available in your EC2 Dashboard.
Now the AMI has been created, let’s discuss the process of launching an instance from that AMI.
Step 1: Go to the EC2 Dashboard in the AWS Management Console and select “Instances” from the navigation menu.
Step 2: Click the “Launch Instance” button to start the process of launching a new instance.
Step 3: Select the newly created AMI from the list of available AMIs.
Step 4: Configure the instance settings as desired and click the “Launch” button.
Step 5: Once the instance is launched, you can connect to it using SSH or Remote Desktop.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about the process of uploading and downloading an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) to Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) and downloading it to an on-premises machine. We dived into the benefits of maintaining AMIs in an on-premises data center, including compliance and security, reduced latency and bandwidth, cost savings, and backup and disaster recovery. The steps for uploading an AMI to S3 using the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) and downloading it from S3 were explained in detail. Finally, the process of creating an AMI from a local backup in another AWS account was discussed and demonstrated.
Hope you found this article helpful and interesting.
Want to read more such content?
Check out our blog: Implementing a Clean Architecture with Nest.JS
About the Author:
Suraj works as a Software Engineer at Mantra Labs. He’s responsible for designing, building, and maintaining the infrastructure and tools needed for software development and deployment. Suraj works closely with both development and operations teams to ensure that the software is delivered quickly and efficiently. During his spare time, he loves to play cricket and explore new places.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox