From uploading the first video on YouTube in 2005 by the founder (Jawed Karim) to the new age of YouTubers, the dynamics of the traditional economy have changed a lot. People feel that earning a living by creating content for their followers is worth more than their 9 to 5 desk job.
The rising number of social media influencers in domains like travel, culinary, art, design, etc. are inspiring many to choose off-beat careers. Moreover, celebrities endorsing these aspirations motivate people to pursue their passion. Millennials have been through many disruptions, which has made them anxious about their livelihoods in the future. Their priorities and aspirations have evolved through these disruptions. Uncertain of the future, this generation has turned towards creating careers driven by their core interests and beliefs. A generation with a ‘risk-taking’ attitude has taken the world head-on and dived into a new economy — Passion Economy. Millennials, in particular, have played an important role in taking this economy forward.
The Covid-19 Crisis
The 2008 economic recession took a huge toll on the job market. With massive lay-offs across various industries, people found themselves at difficult crossroads of their careers. Something similar and maybe on a larger scale might happen in the next couple of months. The COVID-19 crisis brought upon an unprecedented change in the way we think, eat, drink, behave, buy, and work. The disruption in supply-chains and trade has hurt many small and medium businesses. Lockdowns led to reduced demands in consumer products & services, which put many start-ups under pressure to stay functional. With depleting cash reserves, many companies have already laid-off or furloughed some part of their workforce.
According to the latest report by the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), the unemployment rate touched 27.11% in India for the week ended on 3rd May. We’re heading towards an economic slowdown. In a situation like this, many are under stress and not sure of how long they will have a paid job.
On a positive note, the home quarantine gave many people time and opportunity to learn new skill-sets or pursue their hobbies. The realization that it is now a survival issue, people are adding more effort into their work. The world will not be the same as it was before. We are heading towards a ‘New Normal’ where the rules of traditional 9 to 5 jobs and businesses will change drastically. This will make way for budding entrepreneurs to create new career paths for themselves.
The Key Elements of Passion Economy
Passion economy can be misunderstood with the Gig economy at times. The major difference is that a gig is limited to a particular number of times and people but in a passion economy, one can reach a much wider audience. This helps ensure stability over a period of time.
Here are the features which direct the functioning of Passion Economy-
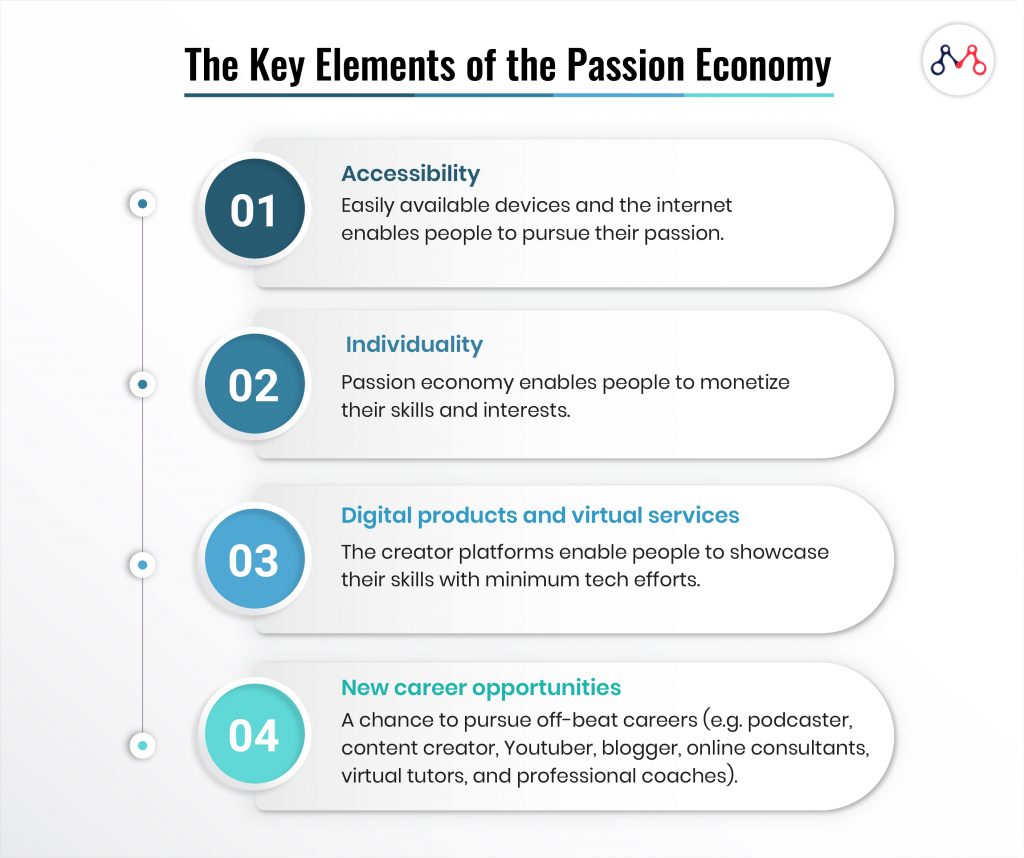
Accessibility
The beauty of this economy is that it is accessible to the population at large. With minimum to no investment, one can pursue their passions. Social Media platforms have made it easy for people to showcase their talents. Today, anyone with a smartphone and good content can become an influencer on Instagram or YouTube. Gone are the days when you had to work in agencies to be able to make a living out of creative skills. Now, you don’t necessarily have to be cast on a TV show or sign an album with a record company to kick-start your careers. Anyone with good content and the right strategy can build a follower base and create a place for oneself.
Individuality
Uniqueness is a quality that is always appreciated. As compared to earlier marketplaces built for standardized jobs, the new platforms in the passion economy give a chance for individuals to share their expertise. Individuality is no longer an outcast but rather an opportunity to monetize. Many people know a particular domain or product or service which they have learned through their personal experiences and deep study. The subject matter experts can procure capital by sharing their knowledge.
The edtech industry has evolved here where former teachers and professionals can create their courses that they teach to their students. Fashion is no longer just a space for slim models. Many plus-sized men and women are popular bloggers with a huge fan base who are making money by sharing their experiences and tips on fashion.
[Also read: A paradigm shift in Indian Edtech due to Covid]
Digital products and virtual services
The previous concept of entrepreneurship involved selling physical goods on online platforms. The passion economy changed this focus to creating digital products such as video courses and digital memberships for premium content. The service industry has transformed from an in-person exchange of services to virtual ones. Services such as teaching and consultations can be provided through digital platforms. The digital products are, in general, scalable which brings an advantage of maximizing earnings.
New career opportunities
The Passion economy is built on off-beat careers such as podcaster, content creator, Newsletter writer, Youtuber, blogger, online consultants, virtual tutors, and professional coaches. Previously, the education system focused on traditional career paths as there were not many opportunities in other fields. However, the advancement in technology, changes in environment and behaviors, rising competition have redefined the definition of earning a livelihood.
Today, one need not carry a degree or professional qualification to become a podcaster or a fashion blogger. The new career paths are defined by the quantum of influence one can create and the consistency of the follower base. This goes along the line of 1000 true fans concept by Kevin Kelly which says that all it takes for a business to be successful is 1000 true fans who support you financially.
[Podcast: Industry Insights on “The New Normal” in Insurance]
Role of Technology in Driving Passion Economy
Technology is the base on which the passion economy runs. Technology has provided new digital platforms to help increase the reach. The widespread internet connectivity has enabled many to learn and create new content. There was a time when a person with technical expertise was at the core to create even a website for your business. Today, no-code websites and app builders have reduced the dependency on software engineers. With free tools available in designing, video editing, etc. creating engaging content has become relatively easy. It doesn’t stop here. People monetize their expertise in operating various tools and software by creating online tutorials.
There are two mediums in passion economy, SAAS platforms and Marketplace. SAAS platforms are disrupting the way businesses run in a passion economy. Today, there are multiple SAAS platforms available in the market which enable entrepreneurs to conduct business smoothly. They offer many features and services such as customer support, websites, marketing, payment portals, etc. This proves to be a win-win situation for both entrepreneurs and SAAS platform owners where the former can grow its business without worrying about technicalities and latter earns a consistent revenue through monthly subscriptions. However, this model works well for people who have a strong client base.
On the other hand, a marketplace is a ready-to-go medium where providers can enter easily and earn revenue with minimum cost. The revenue generated in the model is proportional to the amount of engagement received. More the content consumed, the more the revenue. Though it takes time to create a follower base, this is a value-driven model for creators who are looking to establish themselves in the long term.
Benefits of Passion Economy in Post-COVID crisis
The after-effects of COVID-19 will be felt throughout the world for quite some time until a cure is in place. Practises such as social distancing, remote working, contact-free processes are not going away anytime soon. This will have long-term effects on many sectors such as retail, hospitality, QSR, travel etc. Currently, the economy is hit due to less demand in these industries. However, this will prove to be an opportunity for a rise in the passion economy.
Post this crisis, we will see a rise in the quality workforce. There’ll be a boost in creativity amongst creators. The quality of the content provided by creators will see a huge improvement. As more people put their heart and soul into their passions, small businesses will pick-up pace. This is indeed an unfortunate event, but it will possibly lead to more innovation in various fields. Newer ways of carrying out processes can bring about a reduction in costs and optimization of resources.
In a nutshell
In these unprecedented times, survival is the key. The current situation has closed one door taking the world economy into a recession, but it has opened another door making way for new career and business opportunities that will take the economy forward. Maybe, the passion economy might not give fixed income as compared to a traditional job but the sense of satisfaction pursuing their passion will be the driving force behind this economy. Government and private sector are taking initiatives to provide training to people, helping them enhance their skills. Furthermore, advancement in technology will accelerate the economy making way for off-beat careers and new business opportunities.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox






