The insurance market dynamics are changing rapidly. While a connected ecosystem is the need of the time, agility and new business models are a way through. The current edition of the World InsurTech Report (WITR) emphasizes on developing synergies between Insurers and InsurTechs for the success of the future insurance marketplace. Here are 10 key takeaways from WITR 2019.
Insurance Business Process Improvements
Tech giants like Alibaba, Amazon, Apple, Facebook, and Google are entering the Insurance space with enormous customer data. Moreover, customers (nearly 30%) are responding positively to buying insurance products from BigTech firms, according to the World Insurance Report 2018. WITR proposes the following business process improvement for Insurers to remain market-fit.
#1 Partnerships with Insurtechs, Financial Institutions and Industry Players
90% of InsurTechs and 70% of Incumbents believe partnerships are crucial. And these partnerships are not confined only to the insurance sector. These can include collaboration with financial, technology, healthcare, travel, transportation, hospitality, retail, and more.
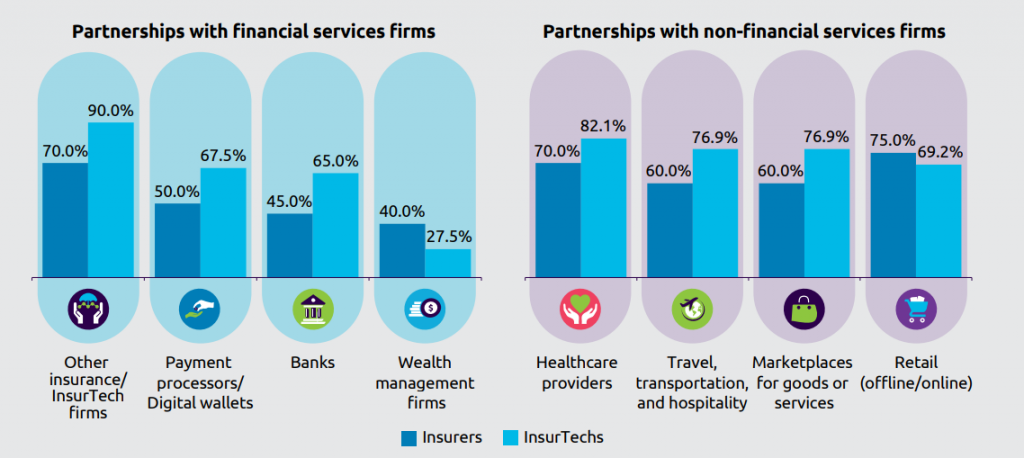
Baloise Insurance partnered with Swiss bank BLKB, and Swiss online insurance broker Anivo to develop a flexible and scalable digital insurance platform with B2C integration. The product released as Bancassurance 2.0 achieved a hit ratio of 50% for video-chat advisory sessions; more than 90% of customers rated the experience as good or very good.
Partnerships can also bring compound insurance products, which otherwise seems impossible. For example, Swiss Re and French cybersecurity InsurTech firm OZON together, launched CyberSolution 360°. It is a risk management solution combining insurance and cyber-attack protection services for small and medium-sized enterprises.
#2 Adopting New Business Models
Not only Insurers, but also customers approve of new insurance models. For instance, 41% of customers are ready to consider usage-based insurance and 37% are willing to explore on-demand coverage. To meet the coverage gaps, offer convenience and personalization, Insurers are adopting the following new business models.
- Usage-based model for as-you-go coverage/premiums for a customer’s potential risky behaviour.
- On-demand model for cost-effective requirement-based coverage.
- Parametric insurance for covering uninsured risks, based on an objective-triggering event.
- Microinsurance services with low-premium packages.
#3 Aligning Strategies with the Future Insurance Marketplace
An insurance marketplace is a viable solution to support a broad spectrum of customer demands. It can also offer coverage for emerging risks and can deliver easy-access compound offerings from individual players of the insurance, manufacturing, and technology ecosystem.
For example, Friday, a Berlin-based startup, launched in 2017, offers digital automotive insurance with kilometre-based billing, flexible tenure, and paperless administration. With telematics support from BMW CarData, Automotive services from ATU, car-rental marketplace Drivy, and distribution channel from Friendsurance, Friday offers customer-centric insurance products.
“The insurance marketplace of the future will provide data and insights about customers that the industry never had before. This will allow firms to design a product closer to customers’ needs and, more importantly, offer them the product when they need it!”
Stephen Barnham, Asia CIO, MetLife
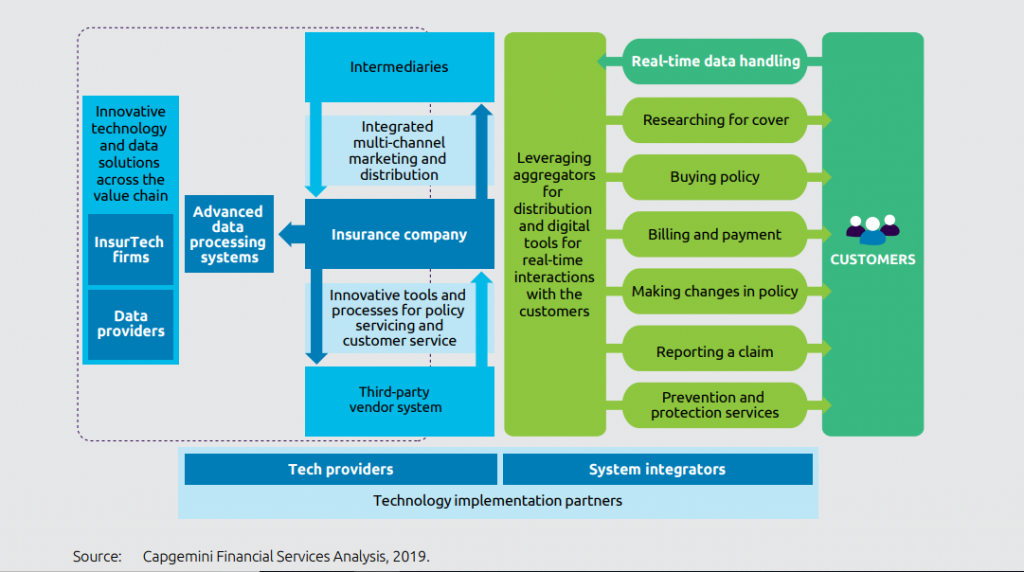
#4 Building an Integrated Ecosystem
As aggregators, OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers), policy management apps, and third parties enter the insurance value chain, an integrated insurance ecosystem can smoothen the overall functioning.
For instance, digital integration with aggregators and third parties can broaden the Insurers’ distribution channel. Partnering with OEMs can help them with real-time customer data. Further, APIs, cloud-based storage, and blockchain can foster the insurance ecosystem with data security and transparency.
#5 Being an Inventive Insurer
Inventive Insurers are the ones who have strategically updated their product portfolios, operating models, and distribution methods. They are realistic about their competencies. By identifying their distinct capabilities and partnering with other players to bridge their competency gap, Inventive Insurers can deliver an end-to-end product to the customers.
The World InsurTech Report 2019 defines the competencies of Inventive Insurers as follows –
- Capable of making business processes more intelligent, efficient, and effective using AI, automation, and analytics.
- Creating new scalable products with shorter development cycles.
- Enabling seamless integration with new data sources and distribution models.
- Offering value-added services to the customers.
Product Innovations
The tech-savvy customers are seeking easy-to-understand products with the facility of direct online purchases. Even leading Insurer like Berkshire Hathaway’s Insurance Group – BiBerk launched ‘THREE’ – only three pages long product covering workers’ compensation, liability, property, and auto to catch the pace. The drift is towards the following new insurance products.
#6 Bundling Financial and Non-financial offerings
An insurance package comprising both financial and non-financial products can expand an Insurer’s products portfolio, giving a competitive edge. It can also help in pitching new prospects. Bundling products and services will increase customer touchpoints and can help insurers identify their needs more effectively.
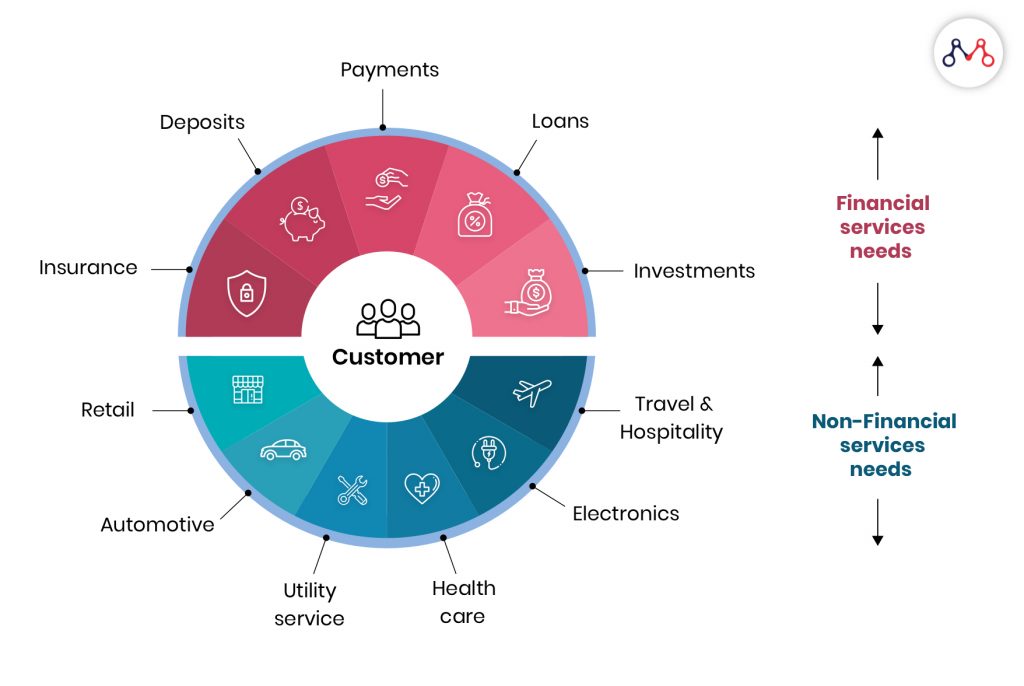
For example, Homeflix insurance provides renters and homeowners insurance to its core. In addition to insurance coverage, it also offers concierge maintenance services like plumbing and electricity. The company also plans home delivery, babysitting, and cleaning services next.
#7 Tailored Products
Traditional insurance policies don’t fit today’s desire for add-on services, personalization, and flexible offerings. The World Insurance Report 2019 survey found that more than 75% of B2B customers and 85% of retail policyholders believe they’re not covered against the emerging risks.
Being aware of the need for customized products, 84% of Insurers and 80% of InsurTechs say they are focusing on “developing new offerings.”
#8 Products that Engage and Educate Customers
Gamification, video-chat sessions, and social media are promising channels for engaging with customers and educating them about risks and their need for coverage. Healthy interactions with customers through their preferred channels can boost sales.
“Insurers should focus on providing user friendly, transparent information via digital channels, allowing customers to make an informed decision. This will be critical not only for upselling, but also for attracting more new-generation customers, who are tech savvy and want to make faster product decisions.”
Jas Maggu, CEO, Galaxy.AI
Operational Improvements
For operational success- understanding customer preferences, conceptualizing new products portfolio, partnerships, and an effective go-to-market strategy is crucial. Fundamental shifts in the current operational models towards experience-driven solutions, strategic use of data, partnerships, and shared ownership of assets portray emerging trends.
#9 Embracing Digital Agility
70% of insurers and 85% of InsurTechs believe a lack of technological readiness is a critical concern.
The more quickly Insurers implement initiatives, the closer they will be to achieve the digital maturity and hence actively participate in the connected ecosystem. The agile digital infrastructure demands real-time data gathering and analytics and automation of complex processes.
It will also lead to product agility. Insurers can offer new products at a faster pace and with reduced GTM (go-to-market) time, they can gain a competitive advantage.
#10 Automating Processes
Not only claims processing and underwriting, but much more insurance back and front-office operations can also be automated. Automation brings two-fold benefit to the insurers. One- mundane tasks are carried by machines, speeding the processes and freeing humans for sophisticated work. The other benefit lies in enhanced accuracy.
For example, AIA Hongkong has improved claims processing time by 40% through AI-driven ICR techniques and intelligent process automation.
Read claims automation case study: How AIA Hong Kong saves 60% through claims automation.
Deutsche Familienversicherung (DFV) provides a digital automated platform for property and supplementary health insurance. It can process the transactions in real-time enabling customers to file claims and receive feedback immediately. Moreover, policyholders can engage with the firm via several digital channels, including Amazon Alexa.
Source: World InsurTech Report 2019
InsurTech Report 2019: Summing-up
- Scope of business process improvements through partnerships, devising new business models, embracing insurance marketplace, building an integrated ecosystem, and being an inventive insurer.
- Introducing innovative products that are tailor-made and educate customers about potential risks; bundling financial and non-financial offerings.
- Operational improvement through automation and digital agility.
We’re AI-first products and solutions firm for the new-age digital insurer recognized among the InsurTech100 for pioneering the transformation of the global insurance industry. Drop us a line at hello@mantralabsglobal.com to know more about our offerings.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox







