The shopping season has officially returned to the Indian subcontinent. While the first phase of festivities (typically) kicks off with the onset of Navratri (sep 29) till Dussehra (oct 8), Indian retailers will have clocked above 40% of their annual sales within this ten day window alone. For consumers, ‘better deals’ take precedence over attributes like faster shipping during this season. In fact, retailers will have adjusted their pricing to strongly reflect these consumer preferences — a pair of women’s running shoes, for instance, will have a discounted price of 19% pre-diwali and upto a flat 50% discounted price on the day of.
In a country with over 400M active online users, customer fealty during this season is even more fickle than usual. The growing number of online consumers are heralding new buying behaviors especially from tier 2 and 3 cities. According to Google Insights, 70% of Indian netizens go online during the festive season to browse products, compare prices, read reviews and look for deals. For brands & retailers, getting in front of these potential customers and clamoring for their attention is the pivotal moment of truth.
Amazon and Walmart-owned Flipkart, India’s top two e-tailers, are using intelligent technologies to stave off each other’s aggressive discounting strategies. The two e-commerce giants have cumulatively created over 140,000 temporary jobs across supply chain, last-mile connectivity and customer support to handle the extra influx of trade. Daily shipments in India is expected to touch 4 million units during the ongoing festive season.
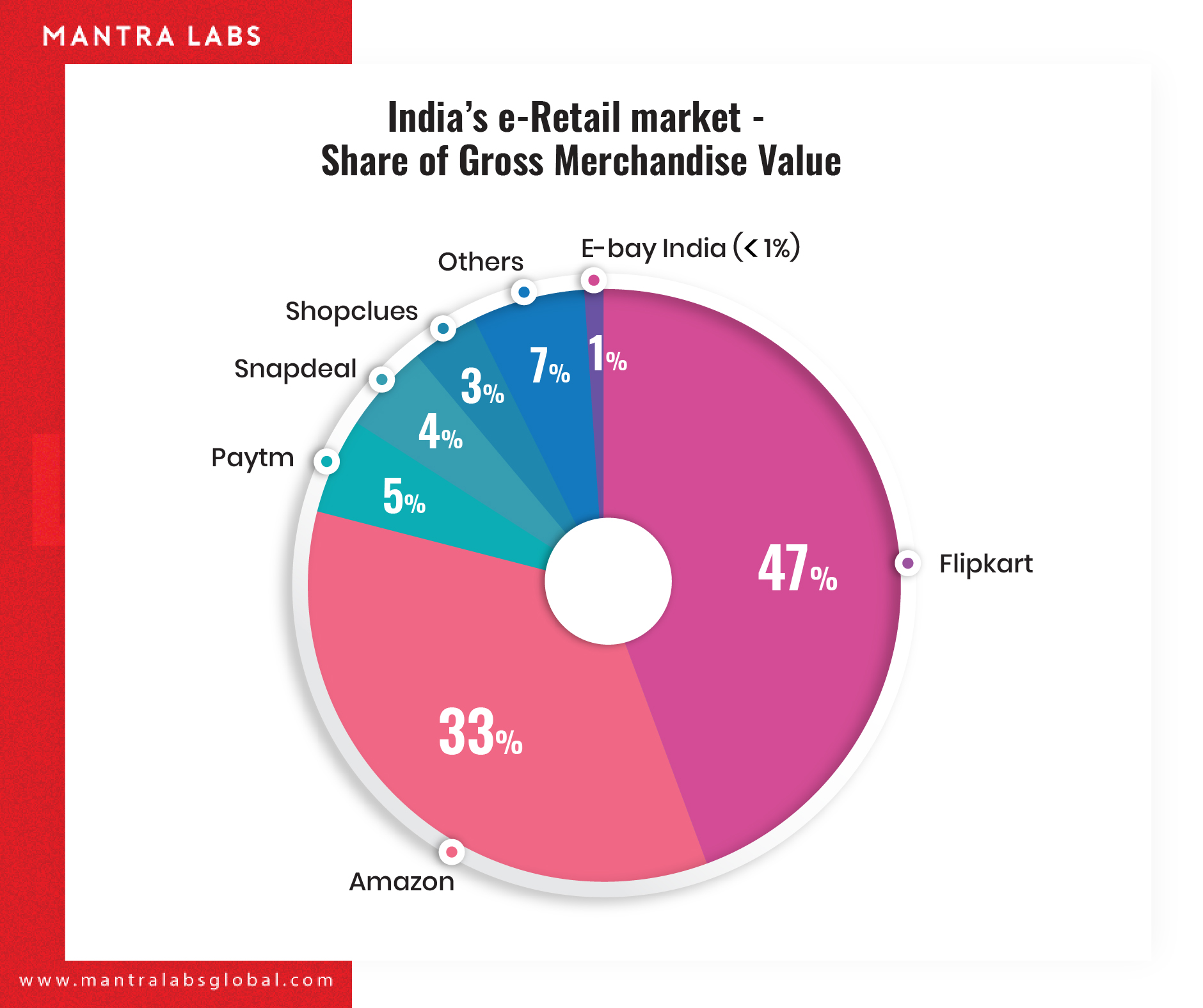
Which begs the question: How are they doing this? How are they using technology to stay-on-top?
It’s no secret, the retail spend on AI is forecast to grow from $2 billion in 2018 to $7.3 billion by 2022, according to Juniper Research.
In reality, they rely on Artificial Intelligence — it is where these companies have primarily invested a huge chunk of change to enhance their business. By leveraging the right set of AI-assisted tools in their operations, they are able to retain and convert more customers.
Artificial Intelligence and related technologies like machine learning and natural language processing has intensified over the digital buying landscape. This has forced brick & mortar stores including physical outlets with omni channel reach to a receding corner of the industry.
There’s more to the digital landscape than meets the eye. It is a space plagued with security concerns. E-commerce companies are using AI to detect and eliminate potential frauds on their platform. They’ve deployed AI models that constantly vets fraudulent accounts that have only signed up to make the most of promo codes, or bring cash out of stolen credit cards.
Yes, aggressive pricing does work as reflected by the higher EMI adoption this year. However, cash burn through discounts is not the overhaul the industry can sustain itself on. Big Data Analytics can prescribe a more proactive approach for suggestions based on statistical association evaluation, time spent on site, cookies behavior and method of accessing site which can tell a brand the how, what and when of the customer buying cycle — in turn, increasing sales.
AI has even infiltrated physical retail, and is now helping stores maximise marketing efforts, personalise the customer experience and optimise their store inventory.
Warehouses and stores, in India, are also making use of ‘Cobots’ (collaborative robots) to assist humans in performing tedious and repetitive shop-floor tasks. The cobots run on machine learning algorithms that have defined its capacity to perform specific tasks while also learning to get better with new data.
Ahead of this year’s festive sale, Flipkart has added 340 cobots or automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to its current fleet of 110. These bots can carry anything with them, from appliances to mobile phones.
After the first phase of the festive shopping marathon, Amazon and Flipkart have both made significant wins over the period. They will look to extend their market capture as we move into the second phase of the season (Diwali).
Interestingly, for Amazon, almost half the product sales came from lower-tier urban areas. Amazon India-owned Echo products even saw a record 70 fold increase in sales.
Flipkart receives over 90% of traffic from its android app, and has designed its app home screen personalized to each of its 120 million+ customers. They have deployed machine learning models and algorithms on various customer data points like customer location, language, gender, price, affinity to a store or brand, purchasing frequency, purchase volume, price group, etc. among others.
These data points help Flipkart make predictions even without the customer being on their platform. Using these machine learning models they are also able to predict if a customer is going to return a particular product.
This season, customers can continue to expect strides in personalization and tailored experiences. E-tailers can expect to see improvements to their order handling, and personalization efforts. Overtime, these improvements will pay dividends in the form of revenue enhancement, increased margins, and higher sales.
How can AI upscale e-commerce
AI has made smooth inroads into digital shopping aisles — with several intelligent use cases such as stock assortment, fraud reduction and self-checkout. Here is a brief compilation of adopted strategies used in retail with the potential to disrupt the future of online shopping.
Product Recommendations
Recommendation engines have become a staple of commercial AI usage. By looking at customers’ purchase histories, current activity (cart contents and page views), and other linked third-party data, e-tailers can make highly tailored suggestions. Amazon, for example, makes more than 40% of its sales via their recommendation engine which also suggests items based on what your friends have purchased recently.Demand Forecasting
E-tailers expect to know in advance how much of each product is projected to especially during peak season. AI can enhance demand predictions by minimizing overstock and out-of-stock situations. ML Algorithms can optimise what products should be made available in a particular geography. For example, Levi’s is using AI to improve size availability, and Nike is using geographical and behavioural data from its app to inform store offerings.
Personalization
AI systems can capture deep customer insights about their buying preferences and behavior using their social data, purchase history, and browsing habits. AI can fill in the gaps by looking at a user’s spending patterns and other data sources to come up with a very detailed view of the customer. This has proven to enhance the customer’s digital shopping experience with a more satisfying view of highly relevant and hyper-personalized offerings.
Shopping Assistant
An AI-powered shopping assistant is a natural extension of the chatbot, with layers of visual processing added in. For example, if a customer wants to choose an outfit for a special occasion. The AI shopping assistant could learn their tastes and help them select some garments. It could then walk them through the process of virtually trying on an outfit (virtual trial rooms). It could offer suggestions for complementary items or encourage them to buy the product, as a friend might. The shopping assistant can also suggest the complementary outfits, footwear and accessories just like a real fashion assistant/advisor would.
Swift Customer Service
Primarily dominated by chatbots over the last several years, bots can learn from the interactions between customers and human reps. Chatbots are trained using natural language processing techniques to understand jargon and ‘speech’ specific to retail. They can then use the data it harvests to create a more personable interaction. It can also quickly reduce the number of touchpoints for the customer and help address immediate queries related to pricing, product availability, returns and recommendations without the need for human intervention.
Also read – How Chatbots are changing the digital Indian?
Smarter Voice Searches
Voice-powered searches can act on a ton of customer insights and information fed into the recommendation engine from the customer’s profile. Voice-activated shopping, is a natural extension of human behavior — allowing consumers to take control of the omnichannel experience to learn more about the product, gather quick product information, compare prices etc. Orders placed via Alexa have increased three times more than the year-ago festive shopping season.
Product identification & visual search
esearch has shown customers who gravitate towards voice-powered searches, equally embrace visual searches. For example, an AI-powered matching algorithm could look at the images of a customer’s favorite products (shirts, sneakers etc.) and suggest similar ones based on attributes like pattern, fit, color, style etc. The AI program can also identify products kept in cart and website pages from browsing based on the customers’ past shopping data and other data from various sources, making the suggestions more accurate with time.
To know more about how Artificial Intelligence can help increase your persona capture and retention, reach out to us on hello@mantralabsglobal.com.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox






