Biometric authentication has emerged as a game-changer as conventional authentication techniques grow more susceptible to security breaches and user fatigue. Developers may improve both security and user experience while constructing a seamless and safe digital environment by integrating biometric technologies into User Experience. This blog post will examine biometric authentication’s advantages for individuals and organizations.
The Power of Biometric Authentication in User Experience
Traditional authentication methods are significantly outperformed by biometric authentication, which is based on distinctive physical or behavioral traits. Let’s explore how biometrics are transforming User Experience.
1. Streamlined User Experience
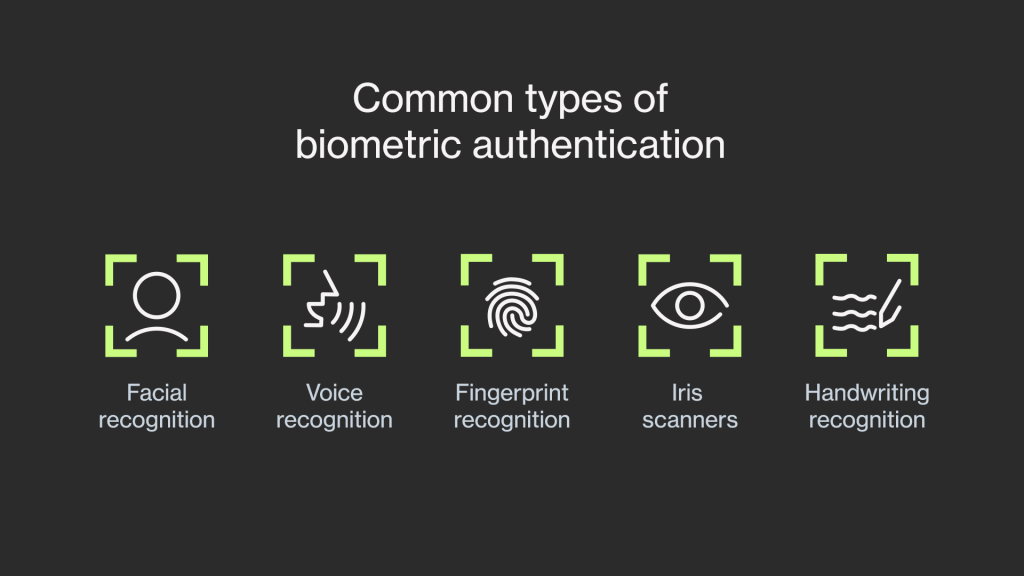
By eliminating the need to memorize complicated passwords or type long credentials, biometric authentication streamlines the user experience. Users can easily and rapidly confirm their identity by using biometric features like fingerprints, voice recognition, handwriting recognition, facial recognition, or iris scans in place of passwords or PINs. This frictionless authentication procedure lessens entry barriers and user irritation, creating a more positive and interesting user experience.
2. Enhanced Security
In User Experience, security is of the utmost importance, and biometric authentication offers a strong barrier against unauthorized access. Biometric features are exclusive to each person and far harder to duplicate than passwords, which can be stolen, guessed, or forgotten. As a result, there is a far lower chance of identity theft and unauthorized account access. Biometric data adds an extra layer of security against hacking efforts because it is challenging to intercept or fake. Businesses may protect user data and increase audience trust by incorporating biometrics into User Experience.
3. Personalization and Contextual Interaction
Within User Experience, biometric authentication enables highly personalized and contextually appropriate interactions. With the use of biometrics, the system may identify specific users and modify the user interface in accordance with their preferences, resulting in a unique and simple interaction. A banking app might, for instance, present pertinent account information or customized offers depending on the user’s biometrically validated profile. This degree of personalization improves user pleasure and engagement.
4. Speed and Efficiency
User onboarding may be completed quickly and effectively with biometric authentication. Users can validate their identity without typing anything in by using a quick scan or gesture. By doing this, you can avoid the frustration of frequently entering credentials and save a lot of time. User Experience may optimize the entire user journey by expediting the login process, which will increase productivity and boost user happiness.
5. Cross-Platform Consistency
A seamless experience is offered by biometric authentication on many platforms and gadgets. Users may continuously integrate biometric authentication into applications whether they access them on a PC, tablet, or smartphone, creating a seamless user experience. By maintaining a standardized and secure authentication method, this cross-platform consistency not only improves usability but also strengthens security measures.
Some Real-Life Examples
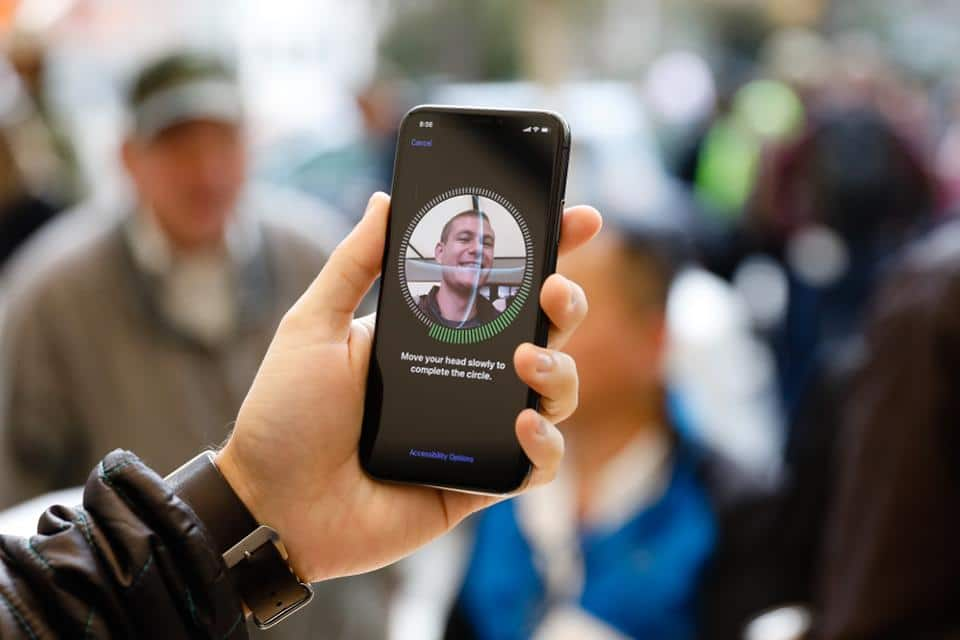
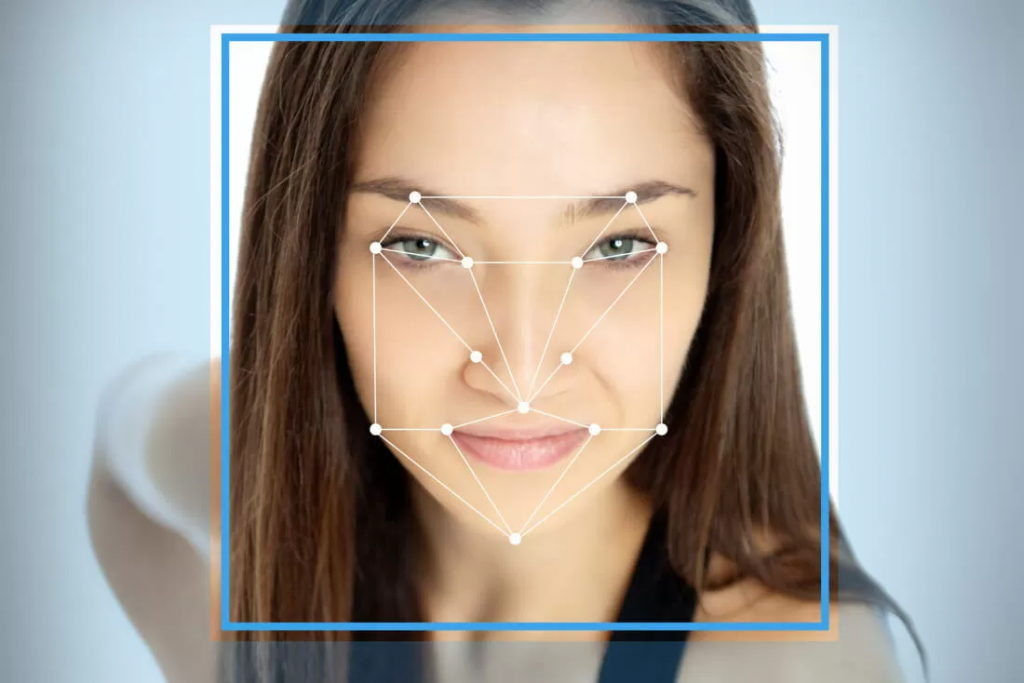
1. Apple’s Touch ID and Face ID:
Apple’s Touch ID and Face ID have completely changed mobile device biometric authentication. These features offer customers a safe and practical way to unlock their devices, authenticate purchases, and access sensitive data since they have been seamlessly incorporated into the User Experience of iPhones and iPads. On their official website, Apple provides further information about biometric authentication in User Experience
2. Login without a password using passkeys:
Users may access apps and websites using biometrics, PINs, or patterns with Passkeys, a safe and practical password substitute. They improve user experience by removing the need to manage and remember passwords. Passkeys satisfy the requirements for multi-factor authentication, taking the place of passwords and one-time passwords (such as SMS codes) to provide increased security from phishing attempts. Since they are standardized, they work with all devices, browsers, and operating systems without requiring a password.
The ease of signing in without having to type usernames, device authentication through the screen lock, and seamless device switching without having to re-enroll are all benefits of passkeys. Since just a public key, rather than passwords, is kept on servers, they are safer for developers and have less value to hackers. Passkeys save expenses by doing away with the requirement for SMS-based two-factor authentication, as well as protecting customers from phishing attacks by limiting authentication to registered websites and apps.
3. Microsoft’s Windows Hello:
Windows Hello is a biometric authentication feature from Microsoft that enables users to log into their Windows computers using fingerprint or facial recognition. An authentication process that is secure and tailored to the user is provided by Windows Hello’s incorporation into the User Experience of Windows operating systems. On the Microsoft website, you may learn more about Windows Hello:
The Future
Enhancing the security and usability of biometric authentication systems requires careful User Experience. Designers may produce interfaces that offer a seamless and safe authentication experience by concentrating on the intersection of usability, aesthetics, and security.
Multi-factor authentication is used by UX designers to increase security by including various biometric modalities to validate the user’s identification. To stop the fraudulent exploitation of biometric data, they also contain cutting-edge anti-spoofing technologies like liveness detection. Designers enable real-time identification of shady actions or unauthorized access by continuously analyzing biometric data in the background.
Accessibility issues are addressed using inclusive design principles. For those with disabilities, alternate authentication methods are available. User education is also a priority in UX designs, with feedback on the progress of the authentication process and clear explanations of how it works. On-device processing, encryption, and privacy-centric design strategies are used to safeguard biometric data and maintain user privacy.
UX design for biometric authentication produces user interfaces that foster user confidence and happiness by taking the trade-off between security and convenience into account. These designs place a high priority on a simple and safe authentication process, while also guaranteeing data security and encouraging user comprehension of the system’s capabilities.
Conclusion
By providing improved security, an improved user experience, personalization, and speed, biometric authentication has completely changed UX design. Biometric authentication replaces conventional passwords and PINs by utilizing distinctive physical or behavioral traits, lowering user friction and enhancing security safeguards. By incorporating biometrics into User Experience, a more secure and engaging digital ecosystem is created, encouraging user happiness and trust. Biometric authentication will undoubtedly play a bigger and bigger role in the future of UX design as the technology develops.

Further Reading: Essential UX Practices for Ed Tech
About the Author: Mohit Ravindran is currently working as a Senior UI/UX Designer at Mantra Labs. With a keen interest in design and art, he loves to create captivating experiences. When not immersed in design, he loves to explore the world through travel, strum his guitar, and embrace the thrill of being a car enthusiast.
Knowledge thats worth delivered in your inbox